Monocle is designed for development teams to provide:
- analytics on project changes
- boards to display changes by criteria
It helps teams and individual to better organize daily duties and to detect anomalies in the way changes are produced and reviewed.
Monocle supports GitHub, GitLab and Gerrit.
How to get started with Monocle:
- Explore the website and blog: changemetrics.io
- Try on the demo instance: demo.changemetrics.io
- Chat with us in the project Matrix room: #monocle:matrix.org
- Run your own instance: Read the installation guide
- Hack on it: Read the contributing guide
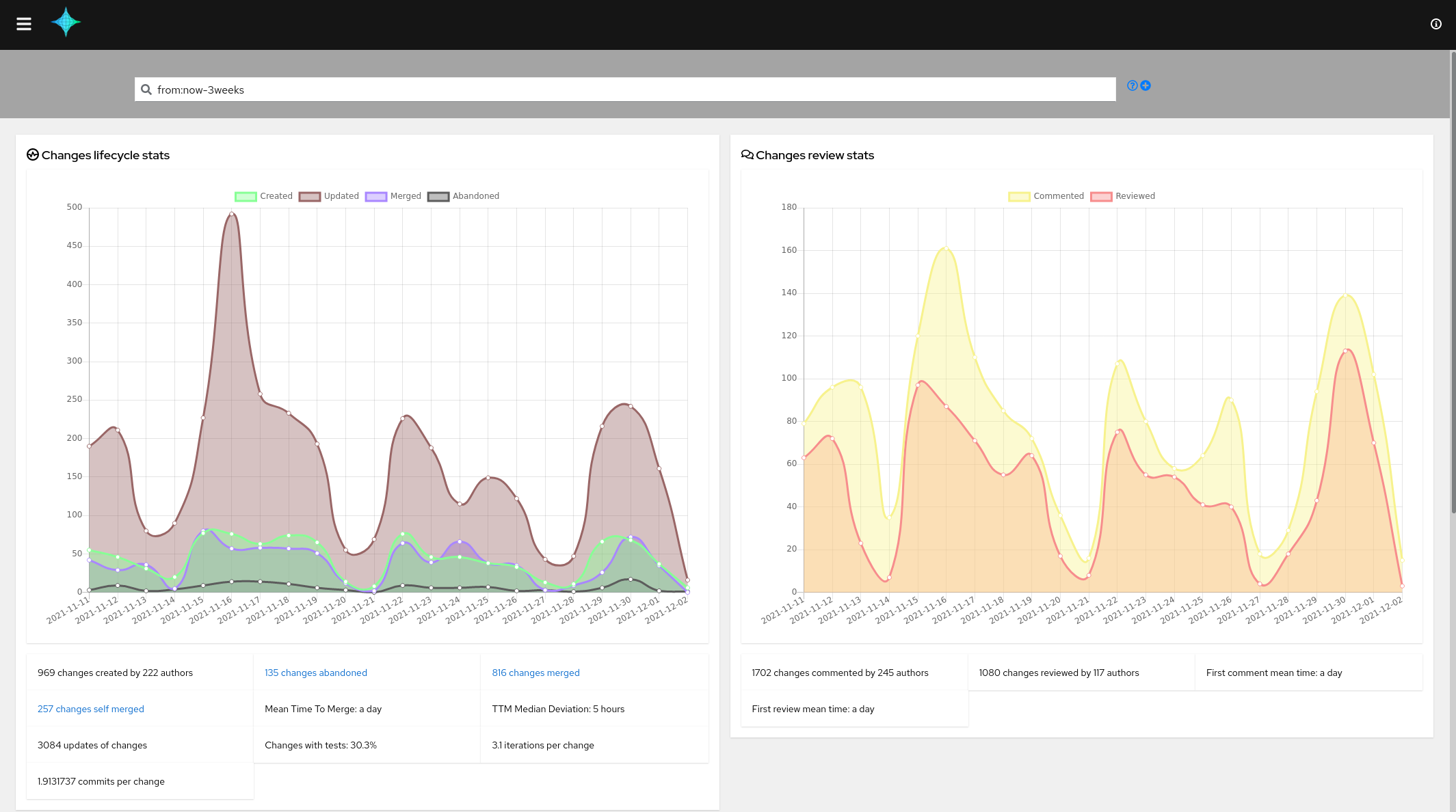
The activity view:
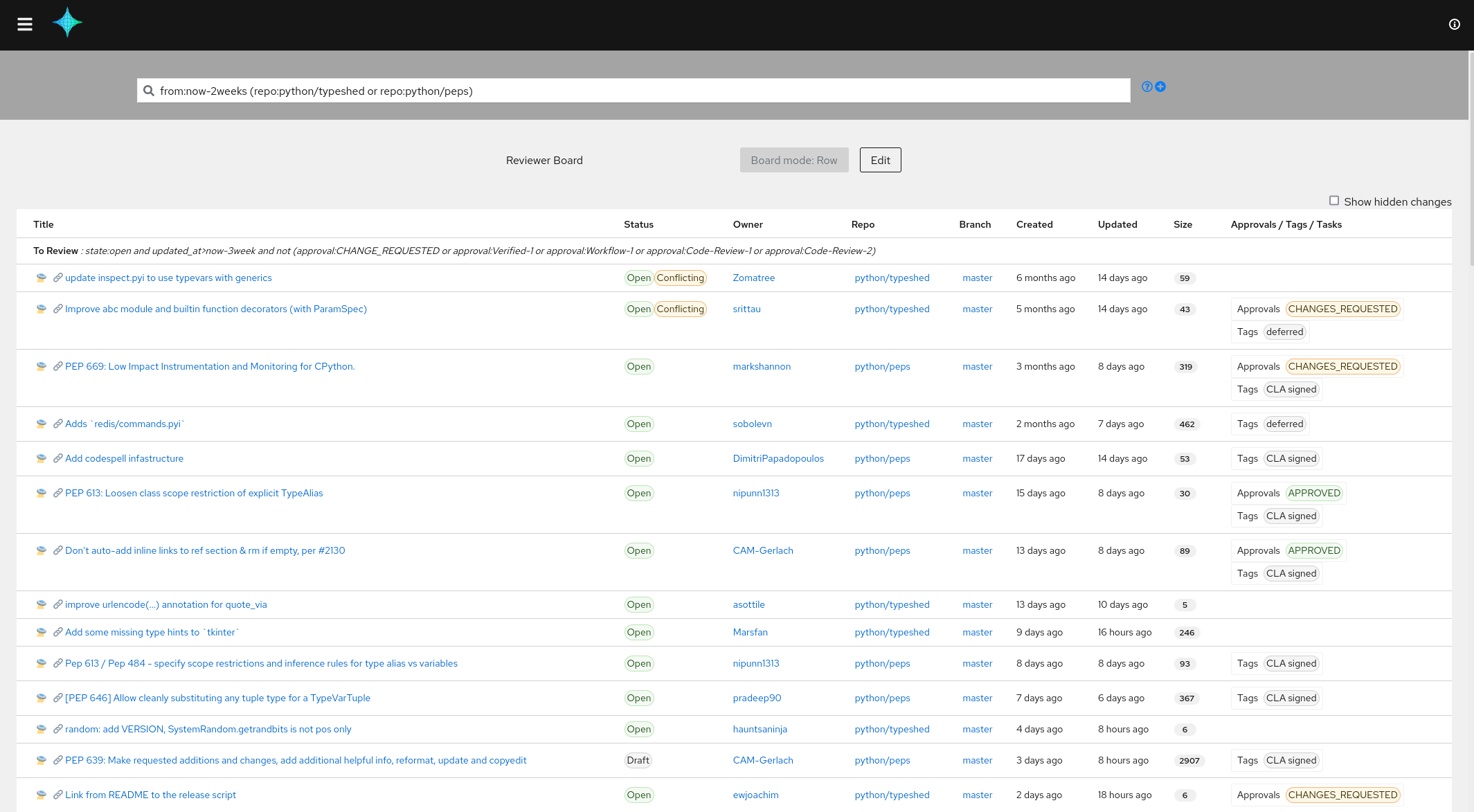
The developer board:
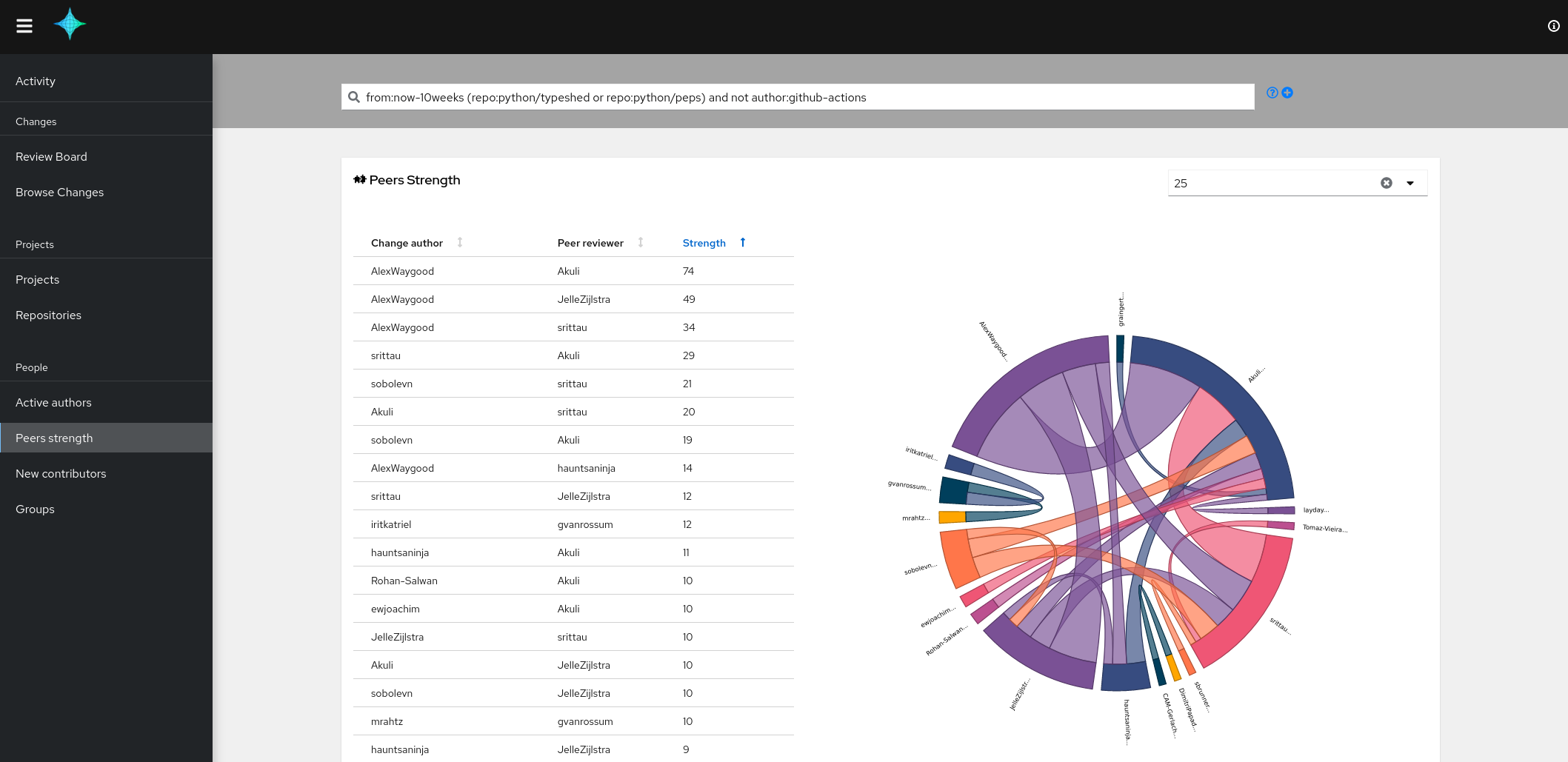
The peers strength view:
The process below describes how to index changes from GitHub repositories and then how to start the web UI to browse metrics.
The deployment is based on Docker via a docker-compose definition.
Note that you can also deploy from source code.
git clone https://github.com/change-metrics/monocle.git
cd monocle
git submodule update --init --recursive
# Init a .secret file with a default API key for the crawler process
echo CRAWLERS_API_KEY=$(uuidgen) > .secretsThe config.yaml file is used by the crawler and api services.
To crawl GitHub public repositories, you must generate a personal access token on GitHub (w/o any specific rights) at https://github.com/settings/tokens.
Then create the config file etc/config.yaml. Here is an example your could start with.
Make sure to write GITHUB_TOKEN=<github_token> in the .secrets file:
---
workspaces:
- name: monocle
crawlers:
- name: github-tektoncd
provider:
github_organization: tektoncd
github_repositories:
- operator
- pipeline
update_since: '2021-01-01'To crawl the full tektoncd GitHub organization then remove the github_repositories entry from the file.
Check the section Workspaces for a complete description of
the configuration.
By default docker-compose will fetch the latest published container images. Indeed, we produce container images for the master version of Monocle. If running master does not fit your needs, you could still use the last release by setting the MONOCLE_VERSION to 1.4.0 in the .env file. Please refer to System configuration section.
Start Monocle:
# Set to the Docker compose file to use the published container images
ln -s docker-compose.yml.img docker-compose.yml
# Then start services
docker-compose up -dEnsure services are running and healthy:
docker-compose psInspect services logs:
docker-compose logs -fYou should be able to access the web UI at http://localhost:8080.
See Troubleshooting section if needed.
For a local deployment, default settings are fine.
The following settings are available in the .env file:
MONOCLE_PUBLIC_URL=<url>to configure the public URL to access the UI and API. This is required for the github oauth redirection.MONOCLE_VERSION=<version>to use a specific version. By default it useslatest.MONOCLE_TITLE=<title>to change the title of the web application. By default it isMonocle.ES_XMS and ES_XMXto change the ElasticSearch JVM HEAP SIZE. By default 512m.MONOCLE_WEB_ADDRto change the IP address the web service will bind on. By default 0.0.0.0.MONOCLE_WEB_PORTto change the TCP port the web service will bind on. By default 8080.
The Monocle configuration file defines workspaces. The file is used by the API and crawlers processes. The format of the file is YAML. You might want to use Dhall to manage it or to better understand the schema (dhall-monocle).
A workspace uses a dedicated ElasticSearch index. A workspace defines:
Monocle provides two kinds of crawlers:
- Change: A crawler to fetch Changes proposed to a repository. Monocle supports Gerrit (Reviews), GitHub (Pull-Requests), GitLab (Merge-Requests).
- TaskData: A crawler to fetch task data related to a repository. Monocle supports GitHub (issues), and BugZilla (Bugs).
The .secrets file is used to store credentials and API keys used by crawlers to authenticate on providers.
The crawlers value is a list of crawler. Each crawler is composed of:
name: an abitrary name used to identify the crawler.update_since: the crawler will fetch changes that has been created/updated since that date.provider: provider settings
workspaces:
- name: demo
crawlers:
- name: spinnaker
update_since: "2020-01-01"
provider: {}A GitHub provider settings
provider:
github_organization: spinnaker
# Optional settings
github_repositories:
- pipeline
github_url: https://github.com
github_token: GITHUB_TOKENgithub_organization is the only mandatory key. If github_repositories is not specified then
the crawler will crawl the whole organization repositories. If specified then it will crawl only
the listed repositories. To crawl repositories from a personnal GitHub account, you need to set
github_organization to you account name and list repositories under the github_repositories key.
github_url might be specified in case of an alternate url. Default is "github.com".
github_token might be specified to use an alternate environment variable name to look for the
token value. Default is "GITHUB_TOKEN"
To crawl privates repositories, either you must use a GitHub Application or you must generate a Personal Access Token with the "repo" scope.
A Gerrit provider settings
provider:
gerrit_url: https://review.opendev.org
gerrit_repositories:
- openstack/nova
- openstack/neutron
# Optional settings
gerrit_login: monocle
gerrit_password: GERRIT_PASSWORD
gerrit_url_insecure: true
gerrit_prefix: opendev/gerrit_url is mandatory and must be the url of the Gerrit provider.
gerrit_repositories is mandatory and is the list of repositories from which the crawler will fetch Reviews from.
gerrit_login might be specified to authenticate on the provider API.
gerrit_passwordmight be specified to use an alternate environment variable name to look for the
password. Default is "GERRIT_PASSWORD"
gerrit_url_insecure could be set to true to prevent HTTP certificate check.
gerrit_prefix might be set to configure the crawler to prepend the repository name with a prefix.
A GitLab provider settings
provider:
gitlab_organization: redhat/centos-stream/ci-cd/zuul
# Optional settings
gitlab_repositories:
- jobs-config
gitlab_url: https://gitlab.com/api/graphql
gitlab_token: GITLAB_TOKENgitlab_organization is the only mandatory key. If gitlab_repositories is not specified then
the crawler will crawl the whole organization repositories. If specified then it will crawl only
the listed repositories.
gitlab_url might be specified in case of an alternate url. Default is "https://gitlab.com/api/graphql".
gitlab_token might be specified to use an alternate environment variable name to look for the
token value. Default is "GITLAB_TOKEN"
Monocle provides additional crawlers to attach tasks/issues/RFEs to changes based on a
match on change_url. Then, Changes can be enhanced with information about related
tasks such as a priority or a score.
The GitHub TaskData crawler run automatically whenever repositories are specified into a GitHub Changes crawler definition.
A BugZilla provider settings
provider:
bugzilla_url: https://redhat.bugzilla.com
bugzilla_products:
- Awesome product
# Optional settings
bugzilla_token: BUGZILLA_TOKENbugzilla_product must be specified. The crawler will crawl listed products for bugs that
contain an external bug references ext_bz_bug_id. The crawler assumes that the external
reference is used to link to a change (Pull-Request/Review).
bugzilla_token might be specified to use an alternate environment variable name to look for the
token value. Default is "BUGZILLA_TOKEN"
Note that this crawler is managed by the crawler container.
Projects could be defined within a workspace configuration. A project is identified by a name and allows to set the following filter attributes:
- repository_regex
- branch_regex
- file_regex
Here is an example of configuration.
workspaces:
- name: example
crawlers:
- name: openstack
provider:
gerrit_url: https://review.opendev.org
gerrit_repositories:
- ^openstack/.*
update_since: "2021-01-01"
projects:
- name: compute
repository_regex: ".*nova.*"
- name: compute-tests
file_regex: "test[s]/.*"
repository_regex: ".*nova.*"
- name: deployment
repository_regex: ".*tripleo.*|.*puppet.*|.*ansible.*"
branch_regex: "master"The monocle API endpoint api/1/get_projects can be queried to
retrieved the list defined projects for a given workspace. See the
Monocle OpenAPI.
The monocle query endpoint handles the query parameter: project.
Monocle is able to index changes from multiple code review systems. A contributor might get different identities across code review systems. Thus Monocle provides a configuration section to define aliases for contributors.
Let say a Monocle workspace is configured to fetch changes from github.com and
review.opendev.org (Gerrit) and we would like that John's metrics are merged under
the John Doe identity.
workspaces:
- name: example
idents:
- ident: John Doe
aliases:
- github.com/john-doe
- review.opendev.org/John Doe/12345
crawlers:
- name: github-containers
provider:
github_organization: containers
github_token: <github_token>
update_since: '2000-01-01'
- name: gerrit-opendev
provider:
gerrit_url: https://review.opendev.org
gerrit_repositories:
- ^openstack/.*
update_since: '2000-01-01'A contributor id on github.com or a GitHub enterprise instance is formated as <domain>/<login>.
A contributor id on a Gerrit instance is formated as <domain>/<Full Name>/<gerrit-user-id>.
A group in Monocle permits to group authors of Changes and filter them from the web interface.
Group memberships are defined through the idents section of the configuration.
Here is an example:
workspaces:
- name: example
idents:
- ident: John Doe
aliases:
- github.com/john-doe
- review.opendev.org/John Doe/12345
groups:
- devs
- ident: Jane Doe
aliases:
- github.com/jane-doe
groups:
- devs
- ptlDatabase objects must be updated to reflect the configuration. Once config.yaml is updated, run the following commands:
docker-compose restart crawler-legacy
docker-compose run --rm --no-deps api monocle janitor update-idents --elastic elastic:9200 --config /etc/monocle/config.yamlHere are the expected environment variables that need to be added to the .secrets file:
CRAWLERS_API_KEY: an arbitrary api key used by the crawler to index data.GITHUB_TOKEN: an API key for GitHub crawler.GITLAB_TOKEN: an API key for GitLab crawler.
Open the sample config.yaml.
ElasticSearch could need some capabilities to run in container mode. Take a look at the logs to see if it started correctly:
$ docker-compose logs elasticFor example, you could need to increase this system parameter:
$ sudo sysctl -w vm.max_map_count=262144or make the data directory writable for other:
$ chmod o+w dataTo delete a workspace (a workspace is an elasticsearch index):
# List indexes with:
docker-compose run --rm --no-deps api curl http://elastic:9200/_aliases?pretty=true
# Delete an index with
docker-compose run --rm --no-deps api curl -XDELETE http://elastic:9200/<index-name>ElasticSearch sets defaults settings on new indexes. The default setting for queries based on regex is set to a value that might not fit your usage especially when your project definitions uses regex above that limit. However the limit could be increased using the following command:
docker-compose run --rm --no-deps api curl \
-XPUT http://localhost:9200/monocle.changes.1.<index-name>/_settings \
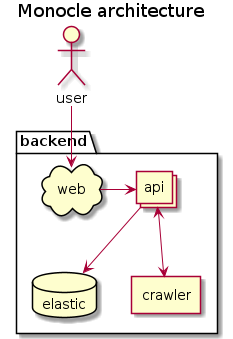
-H "Content-Type: application/json" -d '{"index": {"max_regex_length": 50000}}'Monocle is composed of the following services:
- an Elasticsearch data store.
- an API service to serve user and crawler requests.
- a crawler service to retrieve change from providers.
- a web proxy and web application as a frontend for users.
The APIs are defined using protobuf and served over HTTP through Monocle OpenAPI.
To setup the monitoring:
- Create the prometheus service by providing the API and CRAWLER location
export API_TARGET=localhost:9879
export CRAWLER_TARGET=localhost:9001
mkdir -p /srv/prometheus
podman create --network host -v /srv/prometheus:/var/lib/prometheus:Z -e API_TARGET=${API_TARGET} -e CRAWLER_TARGET=${CRAWLER_TARGET} --name monocle-prometheus quay.io/change-metrics/monocle-prometheus:latest- Create the grafana service (on the prometheus host)
mkdir -p /srv/grafana
podman create --network host -v /srv/grafana:/var/lib/grafana:Z -e GRAFANA_PASS=secret --name monocle-grafana quay.io/change-metrics/monocle-grafana:latest- Starts the services with systemd
mkdir -p ~/.config/systemd/user/
for service in prometheus grafana; do podman generate systemd -n monocle-$service > ~/.config/systemd/user/monocle-$service.service; done
systemctl --user daemon-reload
for service in prometheus grafana; do systemctl --user start monocle-$service; done- Check metrics with grafana dashboard at http://localhost:19030/ (login with 'admin:secret')