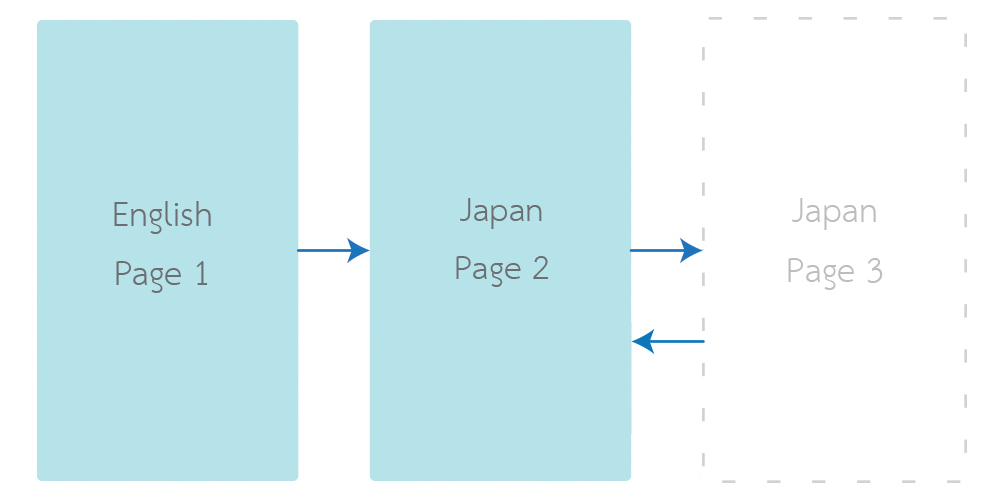
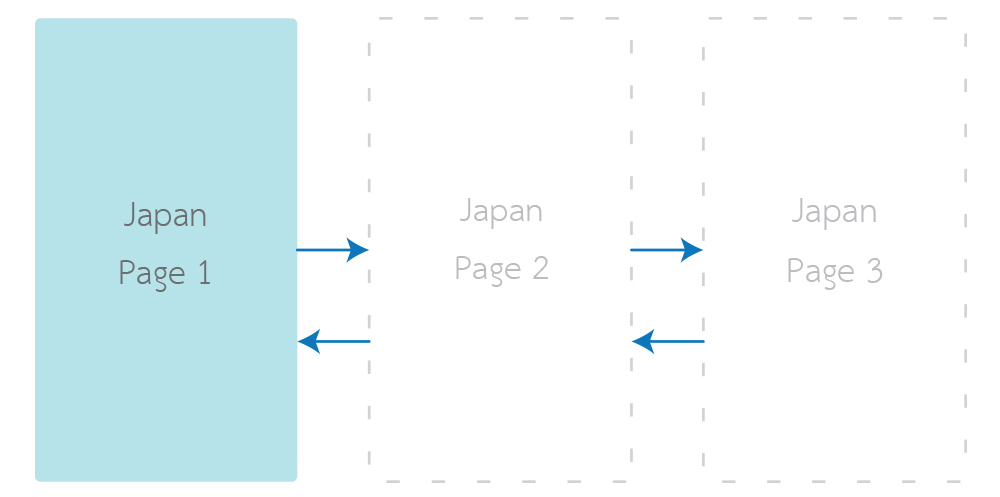
You can now chill out on supporting multiple languages on your android application.
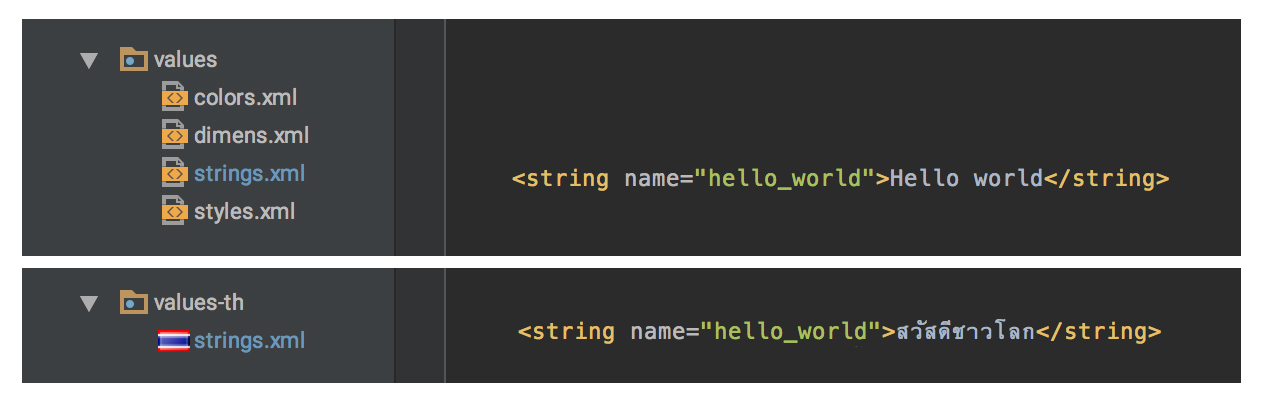
It is normal for your Android application to support multiple languages. And it is very easy because you can do them by putting each language in different String Resource folders. That is the only thing that developers has to do. The rest will be handled by Android system.
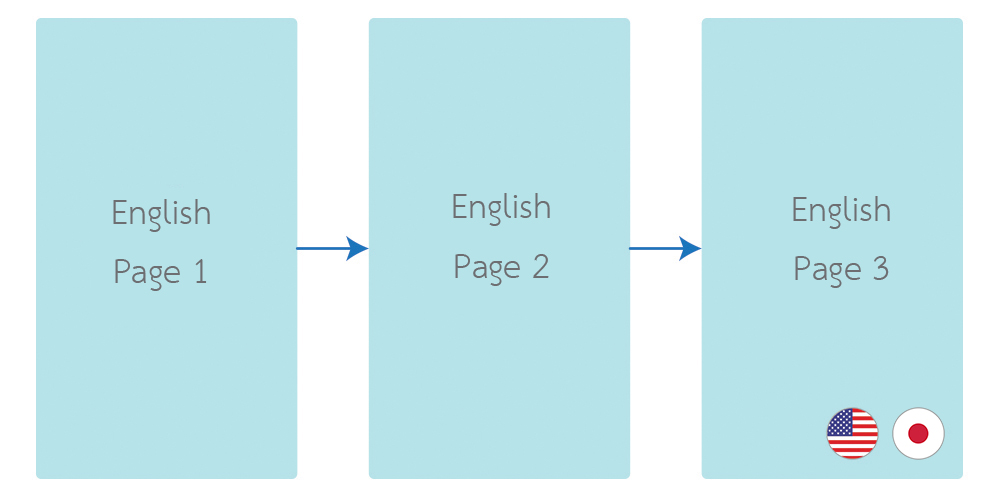
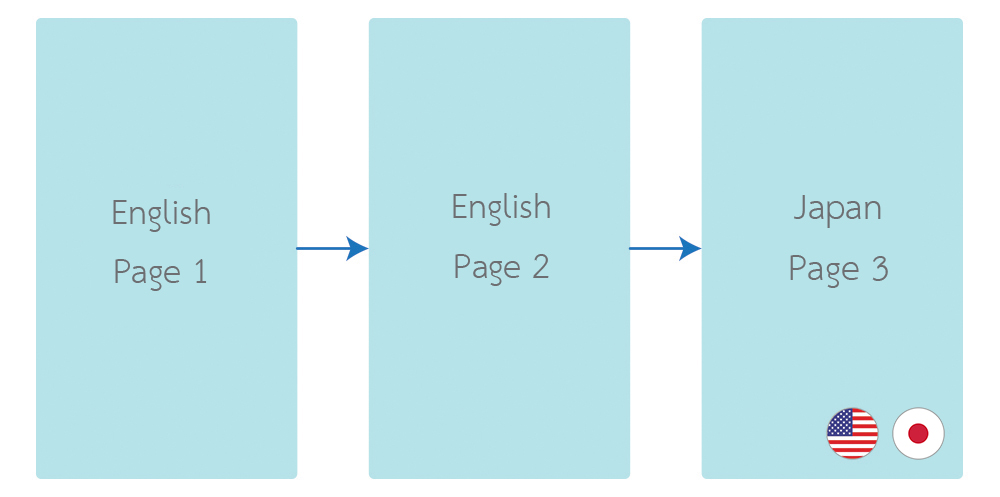
Its easiness comes with a limitation. The language of your application follows your Android System language. Life is hard when you change your application language on-the-fly. E.g., you have a language switcher button in your application. If you have this problem, you come to the right place. I have created a library to handle language changing at application level. It is called "Localization Activity".
- On-time language changing supported.
- Auto setup when activity was created.
- Current language config will save to
SharedPreferenceautomagically. - Very easy to use it.
Watch a short demo video from YouTube or try it at Google Play
Maven
<dependency>
<groupId>com.akexorcist</groupId>
<artifactId>localization</artifactId>
<version>1.2.4</version>
</dependency>
Gradle
implementation 'com.akexorcist:localization:1.2.4'
(Optional) You can exclude androidx.appcompat:appcompat, if your project doens't use AppCompat v7 and declare this library with delegate way.
- [bug] Bug fixed : Incorrect behavior in API level 24-27 (Android 7.0 - 8.1) #30 #37
- [bug] Bug fixed : setDefaultLanguage does not work properly #28
- Migrate to AndroidX and latest Gradle
- Migrate to Kotlin
- Add UI automated test in example code
- Move set default language to Application class (Please see the migrate instruction)
- Add pre-implemented application class for LocalizationApplicationDelegate
- [bug] Bug fixed #18
- Remove java 1.8 and lambda from the library
- Update gradle to 3.0 stable
- Support string resource from getApplicationContext()
- Add LocalizationApplicationDelegate. So you need to custom application class in your app
- LocalizationDelegate was deprecated, replace by LocalizationActivityDelegate
- [bug] Bug fixed : Android 7.0 language #14
- [bug] Language and country support #5
- [bug] RTL on orientation changes #15 #9
setDefaultLanguage has removed from the Activity class. You have to assign the default language in Application with LocalizationApplicationDelegate instead.
class MainActivity: LocalizationActivity() {
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
setDefaultLanguage("en")
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
// ...
}
}class MainApplication : Application() {
private var localizationDelegate = LocalizationApplicationDelegate()
override fun attachBaseContext(base: Context) {
localizationDelegate.setDefaultLanguage(base, Locale.ENGLISH)
super.attachBaseContext(localizationDelegate.attachBaseContext(base))
}
// ...
}If you don't have any additional code in application class, you can extend your application class from LocalizationApplication for more convenient.
class MainApplication: LocalizationApplication() {
override fun getDefaultLanguage(): Locale {
return Locale.ENGLISH
}
}LocalizationActivity is extended from AppCompatActivity class. So you still can use all methods from AppCompatActivity class.
(By @AleksanderMielczarek)
abstract class CustomActivity: Activity(), OnLocaleChangedListener {
private val localizationDelegate = LocalizationActivityDelegate(this)
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
localizationDelegate.addOnLocaleChangedListener(this)
localizationDelegate.onCreate()
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
}
override fun onResume() {
super.onResume()
localizationDelegate.onResume(this)
}
override fun attachBaseContext(newBase: Context) {
super.attachBaseContext(localizationDelegate.attachBaseContext(newBase))
}
override fun getApplicationContext(): Context {
return localizationDelegate.getApplicationContext(super.getApplicationContext())
}
override fun getResources(): Resources {
return localizationDelegate.getResources(super.getResources())
}
override fun onBeforeLocaleChanged() { }
override fun onAfterLocaleChanged() { }
fun setLanguage(language: String) {
localizationDelegate.setLanguage(this, language)
}
fun setLanguage(language: String, country: String) {
localizationDelegate.setLanguage(this, language, country)
}
fun setLanguage(locale: Locale) {
localizationDelegate.setLanguage(this, locale)
}
fun getCurrentLanguage(): Locale {
return localizationDelegate.getLanguage(this)
}
}You need to use custom application class in your project to extend the LocalizationApplication class or implement the LocalizationApplicationDelegate class if you want to do something more in the class.
// Extend the LocalizationApplication
class MainApplication: LocalizationApplication() {
fun getDefaultLanguage() = Locale.ENGLISH
}
// Implement the LocalizationApplicationDelegate
class MainApplication: Application(), LocalizationApplicationDelegate {
private val localizationDelegate = LocalizationApplicationDelegate(this)
override fun attachBaseContext(base: Context) {
localizationDelegate.setDefaultLanguage(Locale.ENGLISH)
super.attachBaseContext(localizationDelegate.attachBaseContext(base))
}
override fun onConfigurationChanged(newConfig: Configuration) {
super.onConfigurationChanged(newConfig)
localizationDelegate.onConfigurationChanged(this)
}
override fun getApplicationContext() {
return localizationDelegate.getApplicationContext(super.getApplicationContext())
}
}In your activities, just extends from LocalizationActivity class.
class MainActivity: LocalizationActivity() {
// ...
fun changeEnglishLanguage() {
setLanguage(Locale.ENGLISH)
}
fun changeThaiLanguage() {
setLanguage("th")
}
}It's very easy, right? You barely do anything.
Then just build up some String Resource for English and Thai language.
Complete! Your application now supports multiple languages now.
It have only 4 public methods.
fun setLanguage(language: String)
fun setLanguage(language: String, country: Strinng)
fun setLanguage(locale: Locale)
fun getCurrentLanguage(): StringsetLanguage Set the language that you need to change. The string value given will be use for setup Locale class later.
For example
setLanguage("th") // Language : Thailand
setLanguage("th_TH") // Language : Thailand, Country : Thai
setLanguage("en") // Language : English
setLanguage("en_GB") // Language : English, Country : Great Britain
setLanguage("en_US") // Language : English, Country : United States
setLanguage(Locale.KOREA) // Language : Korean, Country : Korea
setLanguage(Locale.KOREAN) // Language : Korean
setLanguage(Locale.CANADA_FRENCH) // Language : French, Country : CanadaSo you must determine the correct language for Locale class.
getLanguage Get current language. (Return to string locale)
and 2 optional override methods.
fun onBeforeLocaleChanged()
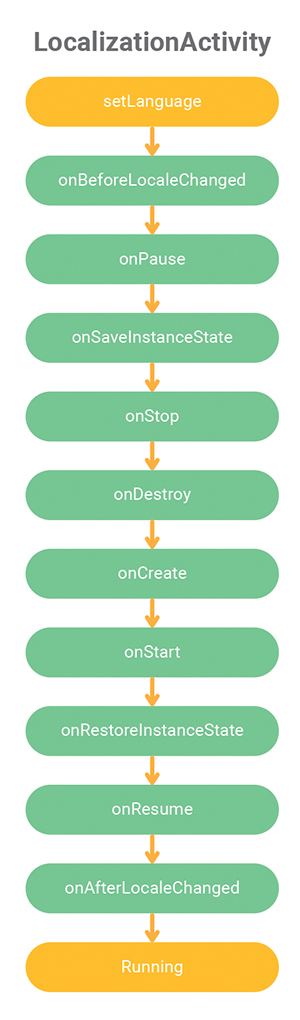
fun onAfterLocaleChanged()This override method will be called then activity language was changed. If you need to know when language has change, just override these methods.
Usually change the language code has a problem with activity that already created.
If latest activity can change the language. It does not apply to previous activity.
But no problem for this library when application getback to previous activity. If you extend that activity to LocalizationActivity. It will changed immediately.
You have to call setTitle(resId) or getActionBar().setTitle(resId) in onCreate(onSavedInstanceState: Bundle) every time.
For example
class MainActivity: LocalizationActivity() {
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
// ...
setTitle(R.string.main_acitivty_title)
}
}When language was changed. An activity wil recreated. So if you have any data object. It should be handle by save/restore instance state for complelely works. (It simple way to supported portrait/landscape orientation)
Therefore you have to override onSaveInstance and onRestoreInstance in to your code, and handle it.
class MainActivity: LocalizationActivity() {
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
// TODO Initial view and widget here
if (savedInstanceState == null) {
// TODO Activity first created
} else {
// TODO Activity recreated from screen orientation or change language
}
}
override fun onSaveInstanceState(outState: Bundle) {
super.onSaveInstanceState(outState)
// TODO Save instance here
}
override fun onRestoreInstanceState(savedInstanceState: Bundle) {
// TODO Restore instance here
super.onRestoreInstanceState(savedInstanceState)
}
}It's change the language on fragment as well.
Fragment language configuration is depending with activity. If activity language was changed and recreated. It will apply to fragment as well. So you have to handle to Instance State on fragment like an activity.
About Save/Restore Instance State. Read more on The Real Best Practices to Save/Restore Activity's and Fragment's state.
English Version : http://www.akexorcist.com/2015/07/localization-activity-best-way-to-handle-language-en.html
Thai Version : http://www.akexorcist.com/2015/07/localization-activity-best-way-to-handle-language.html
@first087 @AleksanderMielczarek @vhiribarren @yunusemrecetin @tiborviktorpasztor
Copyright 2019 Akexorcist
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this work except in compliance with the License. You may obtain a copy of the License in the LICENSE file, or at:
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.