This guide walks you through the process of creating a “Hello, World” RESTful web service with Spring that includes headers for Cross-Origin Resource Sharing (CORS) in the response. You can find more information about Spring CORS support in this blog post.
You will build a service that accepts HTTP GET requests at
http://localhost:8080/greeting and responds with a JSON representation of a greeting, as
the following listing shows:
{"id":1,"content":"Hello, World!"}You can customize the greeting with an optional name parameter in the query string, as
the following listing shows:
http://localhost:8080/greeting?name=UserThe name parameter value overrides the default value of World and is reflected in the
response, as the following listing shows:
{"id":1,"content":"Hello, User!"}This service differs slightly from the one described in Building a RESTful Web Service, in that it uses Spring Framework CORS support to add the relevant CORS response headers.
For all Spring applications, you should start with the Spring Initializr. The Initializr offers a fast way to pull in all the dependencies you need for an application and does a lot of the setup for you. This example needs only the Spring Web dependency.
The following listing shows the pom.xml file that is created when you choose Maven:
link:initial/pom.xml[role=include]The following listing shows the build.gradle file that is created when you choose Gradle:
link:initial/build.gradle[role=include]The tests (in
complete/src/test/java/com/example/restservicecors/GreetingIntegrationTests.java)
require the Apache httpclient library.
To add the Apache httpclient library to Maven, add the following dependency:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.httpcomponents</groupId>
<artifactId>httpclient</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>The following listing shows the finished pom.xml file:
link:complete/pom.xml[role=include]To add the Apache httpclient library to Gradle, add the following dependency:
testImplementation 'org.apache.httpcomponents:httpclient'The following listing shows the finished build.gradle file:
link:complete/build.gradle[role=include]Now that you have set up the project and build system, you can create your web service.
Begin the process by thinking about service interactions.
The service will handle GET requests to /greeting, optionally with a name parameter
in the query string. The GET request should return a 200 OK response with JSON in the
body to represent a greeting. It should resemble the following listing:
{
"id": 1,
"content": "Hello, World!"
}The id field is a unique identifier for the greeting, and content is the textual
representation of the greeting.
To model the greeting representation, create a resource representation class. Provide a
plain old Java object with fields, constructors, and accessors for the id and content
data, as the following listing (from
src/main/java/com/example/restservicecors/Greeting.java) shows:
link:complete/src/main/java/com/example/restservicecors/Greeting.java[role=include]|
Note
|
Spring uses the Jackson JSON library to automatically marshal instances
of type Greeting into JSON.
|
In Spring’s approach to building RESTful web services, HTTP requests are handled by a
controller. These components are easily identified by the @Controller
annotation, and the GreetingController shown in the following listing (from
src/main/java/com/example/restservicecors/GreetingController.java) handles GET
requests for /greeting by returning a new instance of the Greeting class:
link:complete/src/main/java/com/example/restservicecors/GreetingController.java[role=include]This controller is concise and simple, but there is plenty going on under the hood. We break it down step by step.
The @RequestMapping annotation ensures that HTTP requests to /greeting are mapped to the greeting() method.
|
Note
|
The preceding example uses the @GetMapping annotation, which acts as a shortcut
for @RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.GET).
|
@RequestParam binds the value of the name query string parameter into the name
parameter of the greeting() method. This query string parameter is not required. If it
is absent in the request, the defaultValue of World is used.
The implementation of the method body creates and returns a new Greeting object, with
the value of the id attribute based on the next value from the counter and the value
of the content based on the query parameter or the default value. It also formats the
given name by using the greeting template.
A key difference between a traditional MVC controller and the RESTful web service
controller shown earlier is the way that the HTTP response body is created. Rather than
relying on a view technology to perform server-side rendering of the greeting data to
HTML, this RESTful web service controller populates and returns a Greeting object. The
object data is written directly to the HTTP response as JSON.
To accomplish this, the @ResponseBody annotation on the greeting()
method tells Spring MVC that it does not need to render the greeting object through a
server-side view layer. Instead, the returned greeting object is the response body and
should be written out directly.
The Greeting object must be converted to JSON. Thanks to Spring’s HTTP message converter
support, you need not do this conversion manually. Because Jackson is on the
classpath, Spring’s
MappingJackson2HttpMessageConverter is
automatically chosen to convert the Greeting instance to JSON.
You can enable cross-origin resource sharing (CORS) from either in individual controllers or globally. The following topics describe how to do so:
So that the RESTful web service will include CORS access control headers in its response,
you have to add a @CrossOrigin annotation to the handler method, as the following
listing (from src/main/java/com/example/restservicecors/GreetingController.java) shows:
link:complete/src/main/java/com/example/restservicecors/GreetingController.java[role=include]This @CrossOrigin annotation enables cross-origin resource sharing only for this
specific method. By default, its allows all origins, all headers, and the HTTP methods
specified in the @RequestMapping annotation. Also, a maxAge of 30 minutes is used. You
can customize this behavior by specifying the value of one of the following annotation
attributes:
-
origins -
methods -
allowedHeaders -
exposedHeaders -
allowCredentials -
maxAge.
In this example, we allow only http://localhost:9000 to send cross-origin requests.
|
Note
|
You can also add the @CrossOrigin annotation at the controller class level as
well, to enable CORS on all handler methods of this class.
|
In addition (or as an alternative) to fine-grained annotation-based configuration, you can
define some global CORS configuration as well. This is similar to using a Filter but can
be declared within Spring MVC and combined with fine-grained @CrossOrigin configuration.
By default, all origins and GET, HEAD, and POST methods are allowed.
The following listing (from
src/main/java/com/example/restservicecors/GreetingController.java) shows the
greetingWithJavaconfig method in the GreetingController class:
link:complete/src/main/java/com/example/restservicecors/GreetingController.java[role=include]|
Note
|
The difference between the greetingWithJavaconfig method and the greeting method
(used in the controller-level CORS configuration)
is the route (/greeting-javaconfig rather than /greeting) and the presence of the
@CrossOrigin origin.
|
The following listing (from
src/main/java/com/example/restservicecors/RestServiceCorsApplication.java) shows how to
add CORS mapping in the application class:
link:complete/src/main/java/com/example/restservicecors/RestServiceCorsApplication.java[role=include]You can easily change any properties (such as allowedOrigins in the example), as well as
apply this CORS configuration to a specific path pattern.
|
Tip
|
You can combine global- and controller-level CORS configuration. |
The Spring Initializr creates a bare-bones application class for you. The following
listing (from
initial/src/main/java/com/example/restservicecors/RestServiceCorsApplication.java) shows
that initial class:
link:initial/src/main/java/com/example/restservicecors/RestServiceCorsApplication.java[role=include]You need to add a method to configure how to handle cross-origin resource sharing. The
following listing (from
complete/src/main/java/com/example/restservicecors/RestServiceCorsApplication.java)
shows how to do so:
link:complete/src/main/java/com/example/restservicecors/RestServiceCorsApplication.java[role=include]The following listing shows the completed application class:
link:complete/src/main/java/com/example/restservicecors/RestServiceCorsApplication.java[role=include]Logging output is displayed. The service should be up and running within a few seconds.
Now that the service is up, visit http://localhost:8080/greeting, where you should see:
{"id":1,"content":"Hello, World!"}Provide a name query string parameter by visiting
http://localhost:8080/greeting?name=User. The value of the content attribute changes
from Hello, World! to Hello User!, as the following listing shows:
{"id":2,"content":"Hello, User!"}This change demonstrates that the @RequestParam arrangement in GreetingController
works as expected. The name parameter has been given a default value of World but can
always be explicitly overridden through the query string.
Also, the id attribute has changed from 1 to 2. This proves that you are working
against the same GreetingController instance across multiple requests and that its
counter field is being incremented on each call, as expected.
Now you can test that the CORS headers are in place and allow a Javascript client from another origin to access the service. To do so, you need to create a Javascript client to consume the service. The following listing shows such a client:
First, create a simple Javascript file named hello.js (from complete/public/hello.js)
with the following content:
link:complete/public/hello.js[role=include]This script uses jQuery to consume the REST service at http://localhost:8080/greeting.
It is loaded by index.html, as the following listing (from complete/public/index.html)
shows:
link:complete/public/index.html[role=include]|
Note
|
This is essentially the REST client created in Consuming a RESTful Web Service with jQuery, modified slightly to consume the service when it runs on localhost at port 8080. See that guide for more details on how this client was developed. |
Because the REST service is already running on localhost at port 8080, you need to be sure to start the client from another server or port. Doing so not only avoids a collision between the two applications but also ensures that the client code is served from a different origin than the service. To start the client running on localhost at port 9000, run the following Maven command:
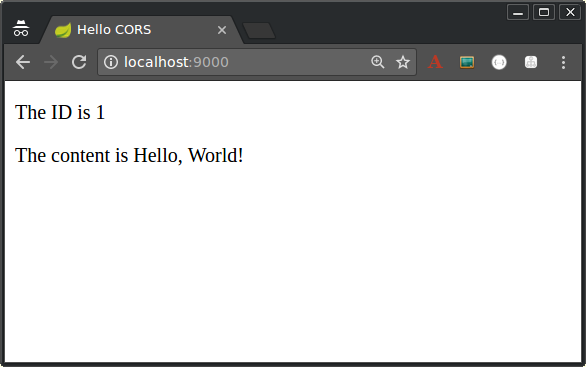
./mvnw spring-boot:run -Dserver.port=9000Once the client starts, open http://localhost:9000 in your browser, where you should see the following:
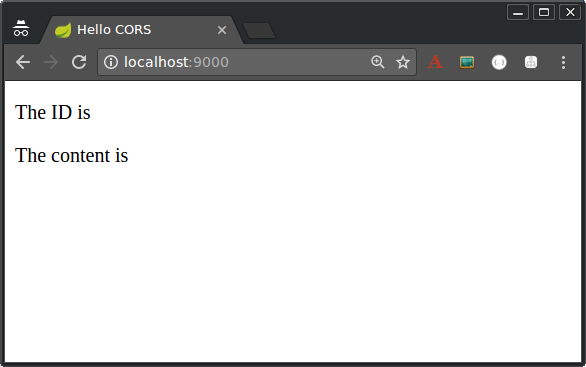
If the service response includes the CORS headers, then the ID and content are rendered into the page. But if the CORS headers are missing (or insufficiently defined for the client), the browser fails the request and the values are not rendered into the DOM. In that case, you should see the following:
Congratulations! You have just developed a RESTful web service that includes Cross-Origin Resource Sharing with Spring.
The following guides may also be helpful: