This is the official repository for distributing ECG-QA dataset.
For more detailed information about the dataset, please refer to ECG-QA: A Comprehensive Question Answering Dataset Combined With Electrocardiogram.
Note
As of 2024-04-11 (yyyy-mm-dd), we republished v1.0.2 after confirming that all sampling processes regarding MIMIC-IV-ECG-based ECG-QA have no error at all. Please re-download the dataset if your dataset is out-dated.
- May 2024
- Errors occurred in PTB-XL ECG-QA samples have been corrected, where we replaced
"late stage of myocardial infarction"with"old stage of myocardial infarction"in theanswers for the corresponding samples. Other samples remain the same with the last release. This change has been merged to v1.0.2
- Errors occurred in PTB-XL ECG-QA samples have been corrected, where we replaced
- April 2024
- (2024-04-11) Released a new version of v1.0.2 after ensuering all sampling processes regarding MIMIc-IV-ECG-based ECG-QA have no error at all. Please re-download the dataset if your dataset is out-dated.
- March 2024
Released v1.0.2(We've released a new version after correcting several errors in this version).- Released v1.0.1.
- Specified release information.
- Added citation info.
Question answering (QA) in the field of healthcare has received much attention due to significant advancements in natural language processing. However, existing healthcare QA datasets primarily focus on medical images, clinical notes, or structured electronic health record tables. This leaves the vast potential of combining electrocardiogram (ECG) data with these systems largely untapped. To address this gap, we present ECG-QA, the first QA dataset specifically designed for ECG analysis. The dataset comprises a total of 70 question templates that cover a wide range of clinically relevant ECG topics, each validated by an ECG expert to ensure their clinical utility. As a result, our dataset includes diverse ECG interpretation questions, including those that require a comparative analysis of two different ECGs. In addition, we have conducted numerous experiments to provide valuable insights for future research directions. We believe that ECG-QA will serve as a valuable resource for the development of intelligent QA systems capable of assisting clinicians in ECG interpretations.
- 1.0.2
- Errors occurred in PTB-XL ECG-QA samples have been corrected, where we replaced
"late stage of myocardial infarction"with"old stage of myocardial infarction"in theanswers for the corresponding samples. Other samples remain the same with the last release. - Released the expanded version of ECG-QA, where we sampled ECGs from MIMIC-IV-ECG v1.0 on the same template to acquire a significantly larger set of ECGs.
- Some modifications have been made to reflect the expanded version. For example,
- The file structure of the dataset
- (Added at 2024-04-11) Resampled QA samples for the MIMIC-IV-ECG version to ensure all sampling processes are error-free. Please re-download the dataset if your dataset is out-dated. This changes include the followings:
- Exclude ECG samples that contain
nanvalues from the sampling processes. - Typo error (
"paroxysmal idioventricualr rhythm") in some attributes has been corrected. lead V3has been involved to the sampling processes.ecg_ids for thecomparison-consecutive-verifyquestions of MIMIC-IV-ECG-based ECG-QA have been corrected.
- Exclude ECG samples that contain
- Errors occurred in PTB-XL ECG-QA samples have been corrected, where we replaced
- 1.0.1
- Renamed
late stage of myocardial infarctiontoold stage of myocardial infarctionin the corresponding questions. The rest of the contents remains the same with the original release.
- Renamed
- 1.0.0
- Initial release of the dataset.
We provide Google Colab Notebook to facilitate the users to skim over the dataset.
Note that this demonstration includes only the original ECG-QA dataset, which is based on the PTB-XL dataset.
As of v1.0.2, we are pleased to introduce the expanded version of ECG-QA, which is based on the MIMIC-IV-ECG v1.0 dataset.
Because the available data in MIMIC-IV-ECG comprises machine-generated statements with 12-lead ECG signals, we have manually labeled them according to the corresponding machine-generated statements with reference to SCP-ECG v3.0 standard. As a result, we could contain the following attributes in the expanded ECG-QA dataset:
- SCP Code
- By parsing the machine-generated statements, we retained a total of 155 SCP codes, which can be categorized into diagnostic, form-related, and rhythm-related symptoms, similar to those in PTB-XL.
- Noise
- Because the machine-generated statements in MIMIC-IV-ECG contained only information about "Baseline Wander" regarding noise, unlike PTB-XL which included attributes such as "Static Noise" or "Burst Noise", "Baseline Wander" alone was included as the sole attribute for Noise.
- Stage of infarction
- Similar to PTB-XL, we inferred the stage of infarction by parsing the keywords (e.g., early, recent, old) in the machine-generated statements for myocardial infarction.
- Heart Axis / Numeric Feature
- As same with the original ECG-QA, we calculated heart axis and numeric features by extracting P, Q, R, S, and T waves for each beat present in lead II.
We used almost the same set of templates for this expanded dataset; however, several templates were excluded from the question sets.
- Because we have the only one attribute (i.e., "Baseline Wander") for Noise attributes, the following templates were excluded:
- 28 - "Does this ECG show any kind of noises in ${lead}?"
- 29 - "Does this ECG show any kind of noises?"
- 30 - "Which noise does this ECG show, ${noise1} or ${noise2}?"
- 31 - "Which noise does this ECG show in ${lead}, ${noise1} or ${noise2}?"
- 32 - "What kind of noises does this ECG show?"
- 33 - "What kind of noises does this ECG show in ${lead}?"
- Because there is no information about "Extra systoles" in machine-generated statements of MIMIC-IV-ECG, the following templates were excluded:
- 35 - "Does this ECG show any kind of extra systoles?"
- 36 - "Does this ECG show ${extra_systole}?"
- 37 - "Which kind of extra systoles does this ECG show, ${extra_systole1} or ${extra_systole2}?"
- 38 - "What kind of extra systole does this ECG show?"
- While the machine statements in the PTB-XL dataset used for the original version of ECG-QA have been validated by cardiologists, those in MIMIC-IV-ECG have not undergone similar validation regarding their quality. Therefore, please note that there could be some mismatches between the assigned attributes based on the machine-generated statements and the true labels.
The dataset is organized as follows:
ecgqa
├── ptbxl
│ ├── answers_for_each_template.csv
│ ├── answers.csv
│ ├── test_ecgs.tsv
│ ├── train_ecgs.tsv
│ ├── valid_ecgs.tsv
│ ├── paraphrased
│ │ ├─ test
│ │ │ ├─ 00000.json
│ │ │ │ ...
│ │ │ └─ 80000.json
│ │ ├─ train
│ │ │ ├─ 00000.json
│ │ │ │ ...
│ │ │ └─ 260000.json
│ │ └─ valid
│ │ ├─ 00000.json
│ │ │ ...
│ │ └─ 60000.json
│ └── template
│ ├─ test
│ │ ├─ 00000.json
│ │ │ ...
│ │ └─ 80000.json
│ ├─ train
│ │ ├─ 00000.json
│ │ │ ...
│ │ └─ 260000.json
│ └─ valid
│ ├─ 00000.json
│ │ ...
│ └─ 60000.json
└── mimic-iv-ecg
├── ...
└── (similar with the above)
- All the QA samples are stored in each .json file, where paraphrased directory indicates its questions are paraphrased and template directory indicates its questions are not paraphrased.
- Each json file contains a list of python dictionary where each key indicates:
- template_id: a number indicating its template ID.
- question_id: a number indicating its question ID. Different paraphrases from the same template question share the same question ID.
- sample_id: a number indicating each QA sample for each split.
- question_type: a string indicating its question type, which can be one of this list:
single-verifysingle-choosesingle-querycomparison_consecutive-verifycomparison_consecutive-querycomparison_irrelevant-verifycomparison_irrelevant-query
- attribute_type: a string indicating its attribute type, which can be one of this list:
scp_codenoisestage_of_infarctionextra_systoleheart_axisnumeric_feature
- question: a question string
- answer: a list of answer strings
- ecg_id: a list of ecg IDs of the source ECG dataset. For the original version, it indicates
ecg_idin the PTB-XL dataset, whereasstudy_idin the MIMIC-IV-ECG dataset for the expanded version. For comparison questions, it contains two corresponding ecg IDs. Otherwise, it has only one element. - attribute: a list of strings indicating the relevant attributes with the question. For comparison questions, it is set to
Nonebecause the primary purpose of this information is aimed to the upperbound experiments where we need to convert each Single QA sample into appropriate ECG classification format.
answers_for_each_template.csvprovides the possible answer options for each template ID.answers.csvprovides the whole answer options over all the QA samples.*_ecgs.tsvindicates which ecg IDs of the source ECG dataset (ecg_idfor PTB-XL orstudy_idfor MIMIC-IV-ECG) are included in each split. (index, ecg_id) pair is written in each row, split by\t.
You can easily open and read data by the following codelines.
>>> import glob
>>> import json
>>> data = []
>>> for fname in sorted(glob.glob("ecgqa/ptbxl/paraphrased/train/*.json")):
... with open(fname, "r") as f:
... data.extend(json.load(f))
>>> len(data)
267539
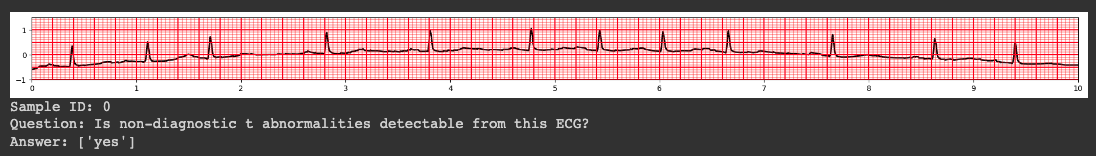
>>> data[0]
{
"template_id": 1,
"question_id": 0,
"sample_id": 0,
"question_type": "single-verify",
"attribute_type": "scp_code",
"question": "Is there evidence of non-diagnostic t abnormalities on this ECG?",
"answer": ["yes"],
"ecg_id": [12662],
"attribute": ["non-diagnostic t abnormalities"]
}For efficient data processing, we don't provide the raw ECG values paired with each question. Instead, we paired the ECG IDs corresponded with the source ECG dataset (PTB-XL or MIMIC-IV-ECG). So, you may need to manually map each QA sample to its corresponding ECG sample using the paired ECG IDs, by mapping either of the actual ECG values or the ECG file path to the QA samples. Because there are much more QA samples than unique ECGs, we recommend you to choose the latter approach which is mapping only the file path for each QA sample to save your disk space. We prepared a useful example python code to perform this, so please refer to the following commands when you try to process the ECG-QA dataset.
$ python mapping_ptbxl_samples.py ecgqa/ptbxl \
--ptbxl-data-dir $ptbxl_dir \
--dest $dest_dir*As of v1.0.2, you don't need to specify template or paraphrased in the root directory for the script. The script now automatically processes both template and paraphrased version of the dataset.
$ptbxl_dir should be set to the root directory of the PTB-XL dataset which contains records500/ directory. If you do not specify this argument, the script will automatically download the required PTB-XL data to the cache directory ($HOME/.cache/ecgqa/ptbxl).
Note that $dest_dir is set to ./output/ptbxl by default.
>>> import glob
>>> import json
>>>
>>> data = []
>>> for fname in sorted(glob.glob("output/ptbxl/train/*.json")):
... with open(fname, "r") as f:
... data.extend(json.load(f))
>>> data[0]
{
...,
"ecg_id": [12662],
"ecg_path": [
"$ptbxl_dir/records500/12000/12662_hr"
]
}$ python mapping_mimic_iv_ecg_samples.py ecgqa/mimic-iv-ecg/paraphrased \
--mimic-iv-ecg-data-dir $mimic_iv_ecg_dir \
--dest $dest_dirAs same with the above, you can also process the template version of ECG-QA by passing ecgqa/mimic-iv-ecg/template.
$mimic_iv_ecg_dir should be set to the root directory of the MIMIC-IV-ECG dataset which contains files/ directory and record_list.csv file. If you do not specify this argument, the script will automatically download the required MIMIC-IV-ECG data to the cache directory ($HOME/.cache/ecgqa/mimic-iv-ecg).
Note that $dest_dir is set to ./output/mimic-iv-ecg by default.
We implemented all the experiment codes specified in the paper on the fairseq-signals repostiory.
For detailed implementations, please refer to here (See ECG-QA section).
-
Install fairseq-signals following the guidelines.
$ git clone https://github.com/Jwoo5/fairseq-signals $ cd fairseq-signals $ pip install --editable ./ $ python setup.py build_ext --inplace $ pip install scipy wfdb pyarrow transformers -
Map
ecg_ids to the corresponding ECG file path (See the above section for the details).- For PTB-XL version:
$ python mapping_ptbxl_samples.py ecgqa/ptbxl \ --ptbxl-data-dir $ptbxl_dir \ --dest $dest_dir - For MIMIC-IV-ECG version:
$ python mapping_mimic_iv_ecg_samples.py ecgqa/mimic-iv-ecg \ --mimic-iv-ecg-data-dir $mimic_iv_ecg_dir \ --dest $dest_dir
- For PTB-XL version:
-
Pre-process ECG-QA dataset.
$ python fairseq_signals/data/ecg_text/preprocess/preprocess_ecgqa.py /path/to/ecgqa \ --dest /path/to/output \ --apply_paraphrase*
/path/to/ecgqashould be consistent with$dest_dirin the mapping script (i.e.,mapping_ptbxl_samples.pyormapping_mimic_iv_ecg_samples.py).
Note that if you run with--apply_paraphrase, the scripts will process the paraphrased version of ECG-QA dataset. Otherwise, it will process the template version. -
Run experiments.
$ fairseq-hydra-train task.data=/path/to/output/paraphrased \ model.num_labels=$num_labels \ --config-dir /fairseq-signals/examples/scratch/ecg_question_answering/$model_name \ --config-name $model_config_name$num_labels: the number of answers specified in
answers.csv. In other words,103for ptb-xl version, and187for mimic-iv-ecg version (Note that the answernoneis not counted because it is regardeed as an "empty label").
$model_name: the name of the ECG-QA model (e.g.,ecg_transformer)
$model_config_name the name of the configuration file (e.g.,base)
-
Install fairseq-signals as the same with the above.
-
Pre-process ECG-QA dataset to be compatible with upperbound experiments.
$ python fairseq_signals/data/ecg_text/preprocess/preprocess_ecgqa_for_classification.py /path/to/ecgqa \ --dest /path/to/output*Note that before running this script, you should have mapped ecg_id to the corresponding ECG file path by
mapping_ptbxl_samples.pyormapping_mimic_iv_ecg_samples.py. -
For W2V+CMSC+RLM:
$ fairseq-hydra-train task.data=/path/to/output \ model.num_labels=$num_labels \ model.model_path=/path/to/checkpoint.pt \ --config-dir /fairseq-signals/examples/w2v_cmsc/config/finetuning/ecg_transformer/grounding_classification \ --config-name base_total$num_labels: the number of attributes for the upperbound experiments.
83for ptb-xl version, and164for mimic-iv-ecg version. (seegrounding_class.csv)
Note that you need to pass the path to the pretrained model checkpoint throughmodel.model_path.
To pre-train the model, refer to here. -
For Resnet + Attention model:
$ fairseq-hydra-train task.data=/path/to/output \ model.num_labels=$num_labels \ --config-dir /fairseq-signals/examples/scratch/ecg_classification/resnet \ --config-name nejedly2021_total$num_labels: the number of attributes for the upperbound experiments.
83for ptb-xl version, and164for mimic-iv-ecg version. (seegrounding_class.csv) -
For SE-WRN model:
$ fairseq-hydra-train task.data=/path/to/output \ model.num_labels=$num_labels \ --config-dir /fairseq-signals/examples/scratch/ecg_classification/resnet \ --config-name se_wrn_total$num_labels: the number of attributes for the upperbound experiments.
83for ptb-xl version, and164for mimic-iv-ecg version. (seegrounding_class.csv)
-
Install fairseq-signals.
-
Map
ecg_ids to the corresponding ECG file path (See the above section for the details).- For PTB-XL version:
$ python mapping_ptbxl_samples.py ecgqa/ptbxl \ --ptbxl-data-dir $ptbxl_dir \ --dest $dest_dir - For MIMIC-IV-ECG version:
$ python mapping_mimic_iv_ecg_samples.py ecgqa/mimic-iv-ecg \ --mimic-iv-ecg-data-dir $mimic_iv_ecg_dir \ --dest $dest_dir
- For PTB-XL version:
-
Pre-process ECG-QA dataset.
$ python fairseq_signals/data/ecg_text/preprocess/preprocess_ecgqa.py /path/to/ecgqa \ --dest /path/to/output \ --apply_paraphrase -
Sample 10% from the test set.
$ python llm_modeling/random_sample.py /path/to/output \ --subset test \It will sample 10% from
test.tsvin the/path/to/output/directory and output the sampled manifest filetest_sampled.tsvin the same directory. -
Run the experiments:
$ python llm_modeling/llm_modeling.py \ +openai_model=$model_name \ +openai_api_key=$api_key \ +ptbxl_or_mimic_iv=ptbxl \ common_eval.path=/path/to/checkpoint.pt \ task.data=/path/to/output \ dataset.valid_subset=test_sampled \ --config-dir llm_modeling/config \ --config-name infer_llm*
ptbxl_or_mimic_ivshould be set to one of"ptbxl"(for PTB-XL ECG-QA) or"mimic-iv-ecg"(for MIMIC-IV ECG-QA) according to your desired dataset to be processed.
Note that you need to pass the path to the upper bound model checkpoint throughcommon_eval.path.- Make sure that the class indices specified in
llm_modeling/metadata/$ptbxl_or_mimic_iv/grounding_class.csvare consistent with the upperbound model. You can check the filegrounding_class.csvgenereated when you run preprocessing scripts for the upperbound experiments.
You also need to pass OpenAI's API key ($api_key) to load the OpenAI's GPT model.
$model_name should be consistent with OpenAI API Models (e.g.,gpt-4-turbo,gpt-3.5-turbo). - Make sure that the class indices specified in
If you have any questions or suggestions, feel free to contact me!
Please cite as:
@inproceedings{NEURIPS2023_d0b67349,
author = {Oh, Jungwoo and Lee, Gyubok and Bae, Seongsu and Kwon, Joon-myoung and Choi, Edward},
booktitle = {Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems},
editor = {A. Oh and T. Neumann and A. Globerson and K. Saenko and M. Hardt and S. Levine},
pages = {66277--66288},
publisher = {Curran Associates, Inc.},
title = {ECG-QA: A Comprehensive Question Answering Dataset Combined With Electrocardiogram},
url = {https://proceedings.neurips.cc/paper_files/paper/2023/file/d0b67349dd16b83b2cf6167fb4e2be50-Paper-Datasets_and_Benchmarks.pdf},
volume = {36},
year = {2023}
}