Binarytree: Python Library for Studying Binary Trees
Are you studying binary trees for your next exam, assignment or technical interview?
Binarytree is a Python library which lets you generate, visualize, inspect and manipulate binary trees. Skip the tedious work of setting up test data, and dive straight into practising your algorithms. Heaps and BSTs (binary search trees) are also supported.
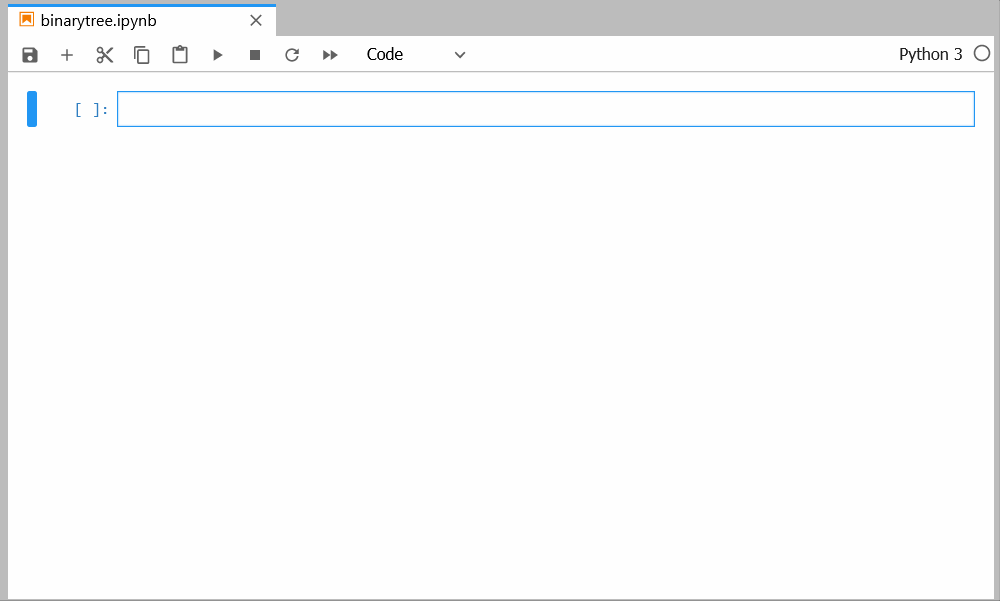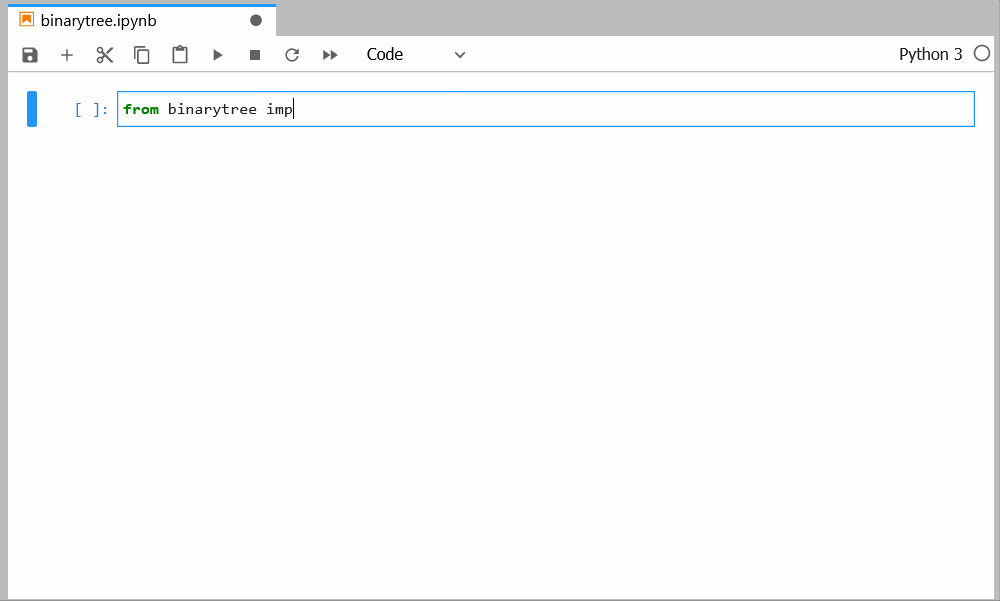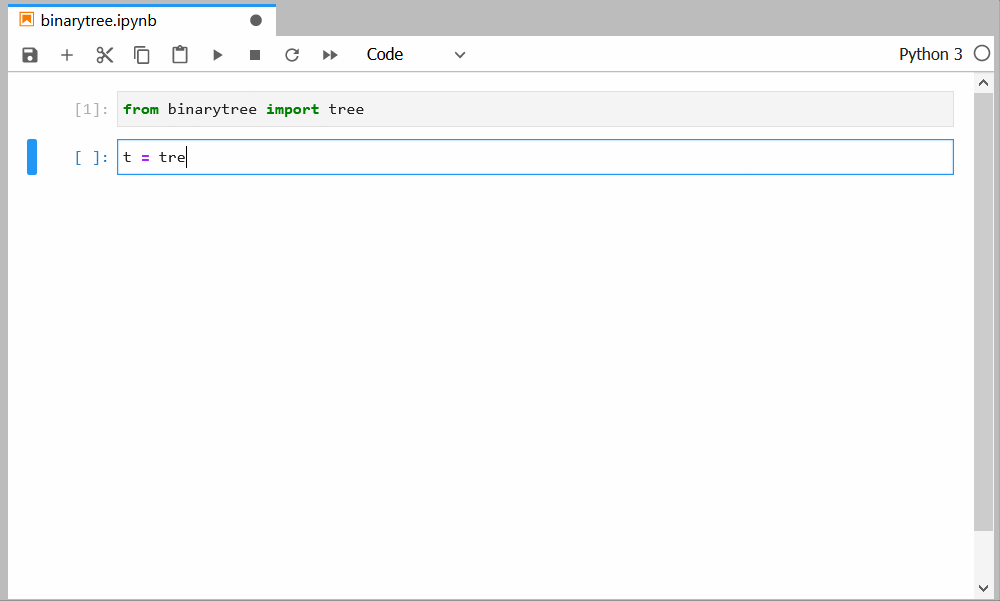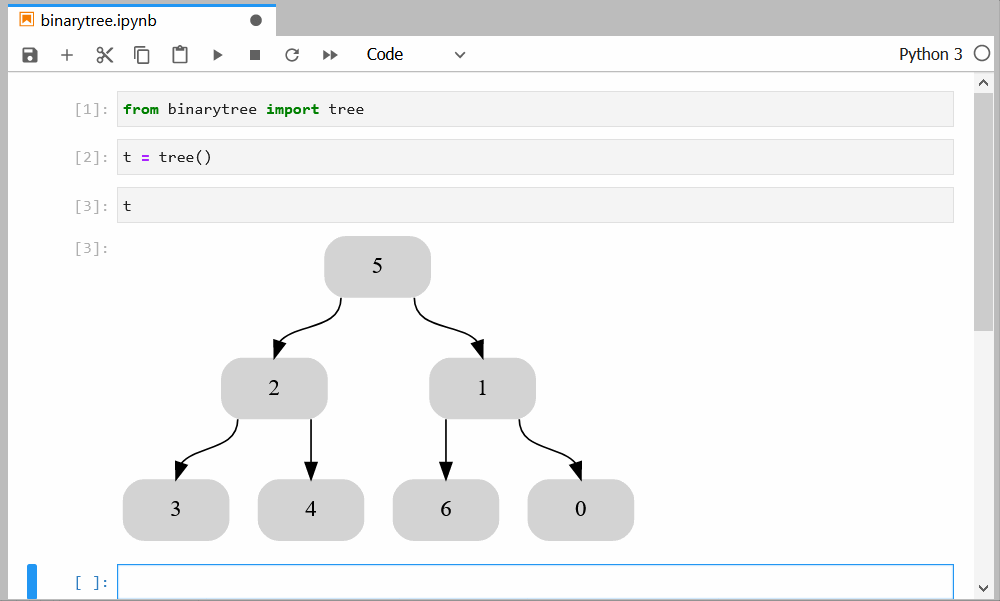
Binarytree can be used with Graphviz and Jupyter Notebooks as well:
Requirements
Python 3.6+
Installation
Install via pip:
pip install binarytreeFor conda users:
conda install binarytree -c conda-forgeGetting Started
Binarytree uses the following class to represent a node:
class Node:
def __init__(self, value, left=None, right=None):
self.value = value # The node value (integer)
self.left = left # Left child
self.right = right # Right childGenerate and pretty-print various types of binary trees:
from binarytree import tree, bst, heap
# Generate a random binary tree and return its root node.
my_tree = tree(height=3, is_perfect=False)
# Generate a random BST and return its root node.
my_bst = bst(height=3, is_perfect=True)
# Generate a random max heap and return its root node.
my_heap = heap(height=3, is_max=True, is_perfect=False)
# Pretty-print the trees in stdout.
print(my_tree)
#
# _______1_____
# / \
# 4__ ___3
# / \ / \
# 0 9 13 14
# / \ \
# 7 10 2
#
print(my_bst)
#
# ______7_______
# / \
# __3__ ___11___
# / \ / \
# 1 5 9 _13
# / \ / \ / \ / \
# 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14
#
print(my_heap)
#
# _____14__
# / \
# ____13__ 9
# / \ / \
# 12 7 3 8
# / \ /
# 0 10 6
#Build your own trees:
from binarytree import Node
root = Node(1)
root.left = Node(2)
root.right = Node(3)
root.left.right = Node(4)
print(root)
#
# __1
# / \
# 2 3
# \
# 4
#Inspect tree properties:
from binarytree import Node
root = Node(1)
root.left = Node(2)
root.right = Node(3)
root.left.left = Node(4)
root.left.right = Node(5)
print(root)
#
# __1
# / \
# 2 3
# / \
# 4 5
#
assert root.height == 2
assert root.is_balanced is True
assert root.is_bst is False
assert root.is_complete is True
assert root.is_max_heap is False
assert root.is_min_heap is True
assert root.is_perfect is False
assert root.is_strict is True
assert root.leaf_count == 3
assert root.max_leaf_depth == 2
assert root.max_node_value == 5
assert root.min_leaf_depth == 1
assert root.min_node_value == 1
assert root.size == 5
# See all properties at once.
assert root.properties == {
'height': 2,
'is_balanced': True,
'is_bst': False,
'is_complete': True,
'is_max_heap': False,
'is_min_heap': True,
'is_perfect': False,
'is_strict': True,
'leaf_count': 3,
'max_leaf_depth': 2,
'max_node_value': 5,
'min_leaf_depth': 1,
'min_node_value': 1,
'size': 5
}
print(root.leaves)
# [Node(3), Node(4), Node(5)]
print(root.levels)
# [[Node(1)], [Node(2), Node(3)], [Node(4), Node(5)]]Compare and clone trees:
from binarytree import tree
original = tree()
# Clone the binary tree.
clone = original.clone()
# Check if the trees are equal.
original.equals(clone)Use level-order (breadth-first) indexes to manipulate nodes:
from binarytree import Node
root = Node(1) # index: 0, value: 1
root.left = Node(2) # index: 1, value: 2
root.right = Node(3) # index: 2, value: 3
root.left.right = Node(4) # index: 4, value: 4
root.left.right.left = Node(5) # index: 9, value: 5
print(root)
#
# ____1
# / \
# 2__ 3
# \
# 4
# /
# 5
#
root.pprint(index=True)
#
# _________0-1_
# / \
# 1-2_____ 2-3
# \
# _4-4
# /
# 9-5
#
print(root[9])
# Node(5)
# Replace the node/subtree at index 4.
root[4] = Node(6, left=Node(7), right=Node(8))
root.pprint(index=True)
#
# ______________0-1_
# / \
# 1-2_____ 2-3
# \
# _4-6_
# / \
# 9-7 10-8
#
# Delete the node/subtree at index 1.
del root[1]
root.pprint(index=True)
#
# 0-1_
# \
# 2-3Traverse trees using different algorithms:
from binarytree import Node
root = Node(1)
root.left = Node(2)
root.right = Node(3)
root.left.left = Node(4)
root.left.right = Node(5)
print(root)
#
# __1
# / \
# 2 3
# / \
# 4 5
#
print(root.inorder)
# [Node(4), Node(2), Node(5), Node(1), Node(3)]
print(root.preorder)
# [Node(1), Node(2), Node(4), Node(5), Node(3)]
print(root.postorder)
# [Node(4), Node(5), Node(2), Node(3), Node(1)]
print(root.levelorder)
# [Node(1), Node(2), Node(3), Node(4), Node(5)]
print(list(root)) # Equivalent to root.levelorder
# [Node(1), Node(2), Node(3), Node(4), Node(5)]Convert to list representations:
from binarytree import build
# Build a tree from list representation
values = [7, 3, 2, 6, 9, None, 1, 5, 8]
root = build(values)
print(root)
#
# __7
# / \
# __3 2
# / \ \
# 6 9 1
# / \
# 5 8
#
# Go back to list representation
print(root.values)
# [7, 3, 2, 6, 9, None, 1, 5, 8]Binarytree supports another representation which is more compact but without the indexing properties:
from binarytree import build, build2, Node
# First let's create an example tree.
root = Node(1)
root.left = Node(2)
root.left.left = Node(3)
root.left.left.left = Node(4)
root.left.left.right = Node(5)
print(root)
#
# 1
# /
# __2
# /
# 3
# / \
# 4 5
# First representation is was already shown above.
# All "null" nodes in each level are present.
print(root.values)
# [1, 2, None, 3, None, None, None, 4, 5]
# Second representation is more compact but without the indexing properties.
print(root.values2)
# [1, 2, None, 3, None, 4, 5]
# Build trees from the list representations
tree1 = build(root.values)
tree2 = build2(root.values2)
assert tree1.equals(tree2) is TrueCheck out the documentation for more details.