This is a small collection of tools to convert data from the new 6D6 datalogger to other formats.
The main supported format is the MiniSEED format. It is widely accepted in the seismological community and ensures maximum compatibility with different workflows.
For compatibility with SEND software, the s2x format can be used. This is especially useful when you are in the process of migrating to the new 6D6 Datalogger but still have a lot of old recorders and wish to use all the models side by side.
As a planned feature, the implementation of the SEG-Y format is in progress.
To install, copy this into your terminal and press enter:
curl -fsSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/KUM-Kiel/6d6-compat/master/install | bash
If that does not work, try this instead:
wget -qO- https://raw.githubusercontent.com/KUM-Kiel/6d6-compat/master/install | bash
Or download one of the binary realeases.
To compile the programs from source you need to have installed a C compiler, Ruby and the rake-c gem.
$ sudo apt-get install build-essential gcc-multilib git ruby
$ sudo gem install rake-c
$ git clone https://github.com/KUM-Kiel/6d6-compat.git
$ cd 6d6-compat
$ rake
$ rake install
Several commands need the device path of a StiK or SD card.
A device path normally looks like /dev/sdb.
On newer Linux distributions the following command can be tried:
$ sudo dmesg -w
If that does not work one can try
$ sudo tail -f /var/log/syslog
Now the StiK or SD card can be plugged in.
Once it is detected by the computer, a message with the device path should appear in the terminal.
The device path normally looks like /dev/sdb but it could also be like /dev/mmcblk0.
The message log can now be stopped with Ctrl+C.
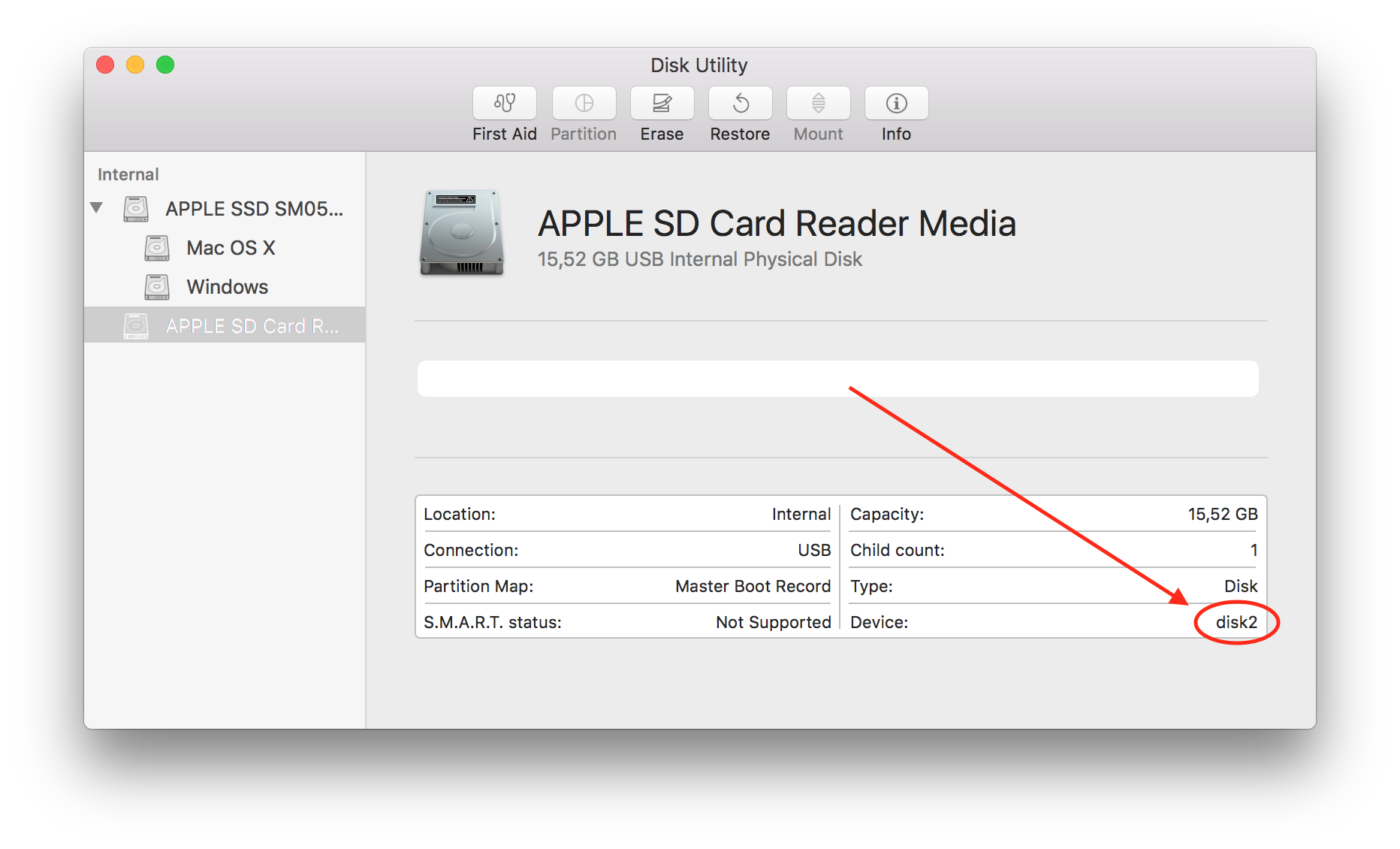
On macOS the device path looks like /dev/disk2.
The device path can be found by opening the Disk Utility.app (search for “Disk Utility” in Spotlight).
Now select the proper device in the list on the left.
The device name will now be displayed on the bottom right.
If the device name is disk2, the device path will be /dev/disk2.
See our FAQ file.
The program is published under the terms of the GNU GPL 3.0. See the LICENCE file.
Some parts of the program incorporate public domain or BSD licensed code.