Learning purposes only. =D
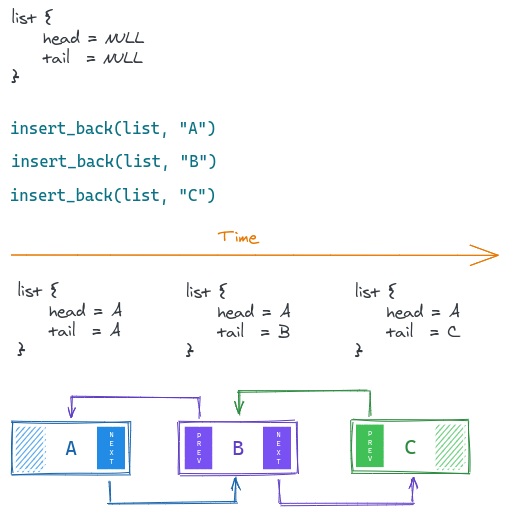
In a doubly-linked list, each node has two links. The first link points to the previous node in the list, and the second link points to the next node in the list.
This implementation covers a set of operations, such as:
Insertion
node_t *insert_front()time complexity:O(1)- Inserts a new node as the first node.node_t *insert_back()time complexity:O(1)– Inserts a new node at the end as the last node (it's a push operation).node_t *insert_before()time complexity:O(1)– Given a node, inserts a new node before it.node_t *insert_after()time complexity:O(1)– Given a node, inserts a new node after it.
Deletion
void delete_node()time complexity:O(1)– Deletes the given node.void delete_first_node()time complexity:O(1)- Delete the first node – Deletes the first node in the list.void delete_last_node()time complexity:O(1)– Deletes the last node in the list.
Search
node_t *list_search()time complexity:O(n)- Used to search for a particular node in the list.
Reverse
void list_reverse()time complexity:O(n)- Reverses the nodes, so the last one becomes the first one and so on.
This project uses Meson.
After cloning:
$ meson builddirIt will generate the buildir, then you can run the tests:
$ meson test -C builddir/ -v Testing using Valgrind (a tool to find memory leaks):
$ meson test -C builddir/ -v --wrap=valgrind