The Remote File Orchestrator allows for the remote management of file-based certificate stores. Discovery, Inventory, and Management functions are supported. The orchestrator performs operations by first converting the certificate store into a BouncyCastle PKCS12Store.
This repository contains a Universal Orchestrator Extension which is a plugin to the Keyfactor Universal Orchestrator. Within the Keyfactor Platform, Orchestrators are used to manage “certificate stores” — collections of certificates and roots of trust that are found within and used by various applications.
The Universal Orchestrator is part of the Keyfactor software distribution and is available via the Keyfactor customer portal. For general instructions on installing Extensions, see the “Keyfactor Command Orchestrator Installation and Configuration Guide” section of the Keyfactor documentation. For configuration details of this specific Extension see below in this readme.
The Universal Orchestrator is the successor to the Windows Orchestrator. This Orchestrator Extension plugin only works with the Universal Orchestrator and does not work with the Windows Orchestrator.
Remote File is supported by Keyfactor for Keyfactor customers. If you have a support issue, please open a support ticket via the Keyfactor Support Portal at https://support.keyfactor.com
To report a problem or suggest a new feature, use the Issues tab. If you want to contribute actual bug fixes or proposed enhancements, use the Pull requests tab.
This extension is compiled against Microsoft's .NET6 Framework and must be installed with the Keyfactor v11.5.1 Universal Orchestrator Framework or earlier. This is not compatible with v11.6+ or v12.x of the Keyfactor Universal Orchestrator Framework.
The Keyfactor Universal Orchestrator may be installed on either Windows or Linux based platforms. The certificate operations supported by a capability may vary based what platform the capability is installed on. The table below indicates what capabilities are supported based on which platform the encompassing Universal Orchestrator is running.
| Operation | Win | Linux |
|---|---|---|
| Supports Management Add | ✓ | ✓ |
| Supports Management Remove | ✓ | ✓ |
| Supports Create Store | ✓ | ✓ |
| Supports Discovery | ✓ | ✓ |
| Supports Reenrollment | ||
| Supports Inventory | ✓ | ✓ |
This orchestrator extension has the ability to connect to a variety of supported PAM providers to allow for the retrieval of various client hosted secrets right from the orchestrator server itself. This eliminates the need to set up the PAM integration on Keyfactor Command which may be in an environment that the client does not want to have access to their PAM provider.
The secrets that this orchestrator extension supports for use with a PAM Provider are:
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| ServerUsername | The user id that will be used to authenticate into the server hosting the store |
| ServerPassword | The password that will be used to authenticate into the server hosting the store |
| StorePassword | The optional password used to secure the certificate store being managed |
It is not necessary to use a PAM Provider for all of the secrets available above. If a PAM Provider should not be used, simply enter in the actual value to be used, as normal.
If a PAM Provider will be used for one of the fields above, start by referencing the Keyfactor Integration Catalog. The GitHub repo for the PAM Provider to be used contains important information such as the format of the json needed. What follows is an example but does not reflect the json values for all PAM Providers as they have different "instance" and "initialization" parameter names and values.
General PAM Provider Configuration
To use a PAM Provider to resolve a field, in this example the Server Password will be resolved by the Hashicorp-Vault provider, first install the PAM Provider extension from the Keyfactor Integration Catalog on the Universal Orchestrator.
Next, complete configuration of the PAM Provider on the UO by editing the manifest.json of the PAM Provider (e.g. located at extensions/Hashicorp-Vault/manifest.json). The "initialization" parameters need to be entered here:
"Keyfactor:PAMProviders:Hashicorp-Vault:InitializationInfo": {
"Host": "http://127.0.0.1:8200",
"Path": "v1/secret/data",
"Token": "xxxxxx"
}After these values are entered, the Orchestrator needs to be restarted to pick up the configuration. Now the PAM Provider can be used on other Orchestrator Extensions.
With the PAM Provider configured as an extenion on the UO, a json object can be passed instead of an actual value to resolve the field with a PAM Provider. Consult the Keyfactor Integration Catalog for the specific format of the json object.
To have the Server Password field resolved by the Hashicorp-Vault provider, the corresponding json object from the Hashicorp-Vault extension needs to be copied and filed in with the correct information:
{"Secret":"my-kv-secret","Key":"myServerPassword"}This text would be entered in as the value for the Server Password, instead of entering in the actual password. The Orchestrator will attempt to use the PAM Provider to retrieve the Server Password. If PAM should not be used, just directly enter in the value for the field.
The Remote File Orchestrator Extension is a multi-purpose integration that can remotely manage a variety of file-based certificate stores and can easily be extended to manage others. The certificate store types that can be managed in the current version are:
RFPkcs12
The RFPkcs12 store type can be used to manage any PKCS#12 compliant file format INCLUDING java keystores of type PKCS12.
Use cases supported:
- One-to-many trust entries - A trust entry is considered single certificate without a private key in a certificate store. Each trust entry is identified with a custom alias.
- One-to-many key entries - One-to-many certificates with private keys and optionally the full certificate chain. Each certificate identified with a custom alias.
- A mix of trust and key entries.
RFJKS
The RFJKS store type can be used to manage java keystores of types JKS or PKCS12. If creating a new java keystore and adding a certificate all via Keyfactor Command, the created java keystore will be of type PKCS12, as java keystores of type JKS have been deprecated as of JDK 9.
Use cases supported:
- One-to-many trust entries - A trust entry is considered single certificate without a private key in a certificate store. Each trust entry is identified with a custom alias.
- One-to-many key entries - One-to-many certificates with private keys and optionally the full certificate chain. Each certificate identified with a custom alias.
- A mix of trust and key entries.
RFPEM
The RFPEM store type can be used to manage PEM encoded files.
Use cases supported:
- Trust stores - A file with one-to-many certificates (no private keys, no certificate chains).
- Single certificate stores with private key in the file.
- Single certificate stores with certificate chain and private key in the file.
- Single certificate stores with private key in an external file.
- Single certificate stores with certificate chain in the file and private key in an external file
NOTE: PEM stores may only have one private key (internal or external) associated with the store, as only one certificate/chain/private key combination can be stored in a PEM store supported by RFPEM.
RFDER
The RFDER store type can be used to manage DER encoded files.
Use cases supported:
- Single certificate stores with private key in an external file.
- Single certificate stores with no private key.
RFKDB
The RFKDB store type can be used to manage IBM Key Database Files (KDB) files. The IBM utility, GSKCAPICMD, is used to read and write certificates from and to the target store and is therefore required to be installed on the server where each KDB certificate store being managed resides, and its location MUST be in the system $Path.
Use cases supported:
- One-to-many trust entries - A trust entry is considered single certificate without a private key in a certificate store. Each trust entry is identified with a custom alias.
- One-to-many key entries - One-to-many certificates with private keys and optionally the full certificate chain. Each certificate identified with a custom alias.
- A mix of trust and key entries.
RFORA
The RFORA store type can be used to manage Pkcs12 Oracle Wallets. Please note that while this should work for Pkcs12 Oracle Wallets installed on both Windows and Linux servers, this has only been tested on wallets installed on Windows. Please note, when entering the Store Path for an Oracle Wallet in Keyfactor Command, make sure to INCLUDE the eWallet.p12 file name that by convention is the name of the Pkcs12 wallet file that gets created.
Use cases supported:
- One-to-many trust entries - A trust entry is considered single certificate without a private key in a certificate store. Each trust entry is identified with a custom alias.
- One-to-many key entries - One-to-many certificates with private keys and optionally the full certificate chain. Each certificate identified with a custom alias.
- A mix of trust and key entries.
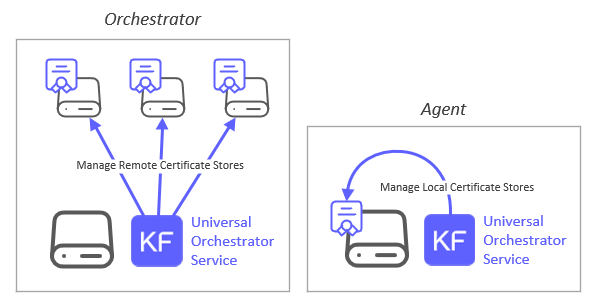
The Keyfactor Univeral Orchestrator (UO) and RemoteFile Extension can be installed on either Windows or Linux operating systems as well as manage certificates residing on servers of both operating systems. A UO service managing certificates on remote servers is considered to be acting as an Orchestrator, while a UO service managing local certificates on the same server running the service is considered an Agent. When acting as an Orchestrator, connectivity from the orchestrator server hosting the RemoteFile extension to the orchestrated server hosting the certificate store(s) being managed is achieved via either an SSH (for Linux and possibly Windows orchestrated servers) or WinRM (for Windows orchestrated servers) connection. When acting as an agent, SSH/WinRM may still be used, OR the certificate store can be configured to bypass these and instead directly access the orchestrator server's file system.
Please review the Prerequisites and Security Considerations and Certificate Stores and Discovery Jobs sections for more information on proper configuration and setup for these different architectures. The supported configurations of Universal Orchestrator hosts and managed orchestrated servers are detailed below:
| UO Installed on Windows | UO Installed on Linux | |
|---|---|---|
| Orchestrated Server hosting certificate store(s) on remote Windows server | WinRM connection | SSH connection |
| Orchestrated Server hosting certificate store(s) on remote Linux server | SSH connection | SSH connection |
| Certificate store(s) on same server as orchestrator service (Agent) | WinRM connection or local file system | SSH connection or local file system |
The version number of a the Remote File Orchestrator Extension can be verified by right clicking on the RemoteFile.dll file in the Extensions/RemoteFile installation folder, selecting Properties, and then clicking on the Details tab.
Certificate stores hosted on Linux servers:
- The Remote File Orchestrator Extension makes use of a few common Linux commands when managing stores on Linux servers. If the credentials you will be connecting with need elevated access to run these commands or to access the certificate store files these commands operate against, you must set up the user id as a sudoer with no password necessary and set the config.json "UseSudo" value to "Y". When RemoteFile is using orchestration, managing local or external certificate stores using SSH or WinRM, the security context is determined by the user id entered in the Keyfactor Command certificate store or discovery job screens. When RemoteFile is running as an agent, managing local stores only, the security context is the user id running the Keyfactor Command Universal Orchestrator service account. The full list of these commands below:
| Shell Command | Used For |
|---|---|
| echo | Used to append a newline and terminate all commands sent. |
| find | Used by Discovery jobs to locate potential certificate stores on the file system. |
| cp | Used by Inventory and Management Add/Remove jobs to copy the certificate store file to a temporary file (only when an alternate download folder has been configured). |
| chown | Used by the Inventory and Management Add/Remove jobs to set the permissions on the temporary file (only when an alternate download folder has been configured). |
| tee | Used by Management Add/Remove jobs to copy the temporary uploaded certificate file to the certificate store file (only when an alternate upload folder has been configured). |
| rm | Used by Inventory and Management Add/Remove jobs to remove temporary files (only when an alternate upload/download folder has been configured). |
| install | Used by the Management Create Store job when initializing a certificate store file. |
| orapki | Oracle Wallet CLI utility used by Inventory and Management Add/Remove jobs to manipulate an Oracle Wallet certificate store. Used for the RFORA store type only. |
| gskcapicmd | IBM Key Database CLI utility used by Inventory and Management Add/Remove jobs to manipulate an IBM Key Database certificate store. Used for the RFKDB store type only. |
-
When orchestrating management of local or external certificate stores, the Remote File Orchestrator Extension makes use of SFTP and/or SCP to transfer files to and from the orchestrated server. SFTP/SCP cannot make use of sudo, so all folders containing certificate stores will need to allow SFTP/SCP file transfer for the user assigned to the certificate store/discovery job. If this is not possible, set the values in the config.json apprpriately to use an alternative upload/download folder that does allow SFTP/SCP file transfer. If the certificate store/discovery job is configured for local (agent) access, the account running the Keyfactor Universal Orchestrator service must have access to read/write to the certificate store location, OR the config.json file must be set up to use the alternative upload/download file.
-
SSH Authentication: When creating a Keyfactor certificate store for the remote file orchestrator extension, you may supply either a user id and password for the certificate store credentials (directly or through one of Keyfactor Command's PAM integrations), or supply a user id and SSH private key. When using a password, the connection is attempted using SSH Password Authentication. If that fails, Keyboard Interactive Authentication is automatically attempted. One or both of these must be enabled on the Linux box being managed. If private key authentication is desired, copy and paste the full SSH private key into the Password textbox (or pointer to the private key if using a PAM provider). Please note that SSH Private Key Authentication is not available when running locally as an agent. The following private key formats are supported:
- PKCS#1 (BEGIN RSA PRIVATE KEY)
- PKCS#8 (BEGIN PRIVATE KEY)
- ECDSA OPENSSH (BEGIN OPENSSH PRIVATE KEY)
Please reference Configuration File Setup for more information on setting up the config.json file and Certificate Stores and Discovery Jobs for more information on the items above.
Certificate stores hosted on Windows servers:
1. When orchestrating management of external (and potentially local) certificate stores, the RemoteFile Orchestrator Extension makes use of WinRM to connect to external certificate store servers. The security context used is the user id entered in the Keyfactor Command certificate store or discovery job screen. Make sure that WinRM is set up on the orchestrated server and that the WinRM port (by convention, 5585 for HTTP and 5586 for HTTPS) is part of the certificate store path when setting up your certificate stores/discovery jobs. If running as an agent, managing local certificate stores, local commands are run under the security context of the user account running the Keyfactor Universal Orchestrator Service. Please reference [Certificate Stores and Discovery Jobs](#certificate-stores-and-discovery-jobs) for more information on creating certificate stores for the RemoteFile Orchestrator Extension.Please consult with your company's system administrator for more information on configuring SSH/SFTP/SCP or WinRM in your environment.
- Review the Prerequisites and Security Considerations section and make sure your environment is set up as required.
- Refer to the Creating Certificate Store Types section to create the certificate store types you wish to manage.
- Stop the Keyfactor Universal Orchestrator Service on the server you plan to install this extension to run on.
- In the Keyfactor Orchestrator installation folder (by convention usually C:\Program Files\Keyfactor\Keyfactor Orchestrator for a Windows install or /opt/keyfactor/orchestrator/ for a Linux install), find the "Extensions" folder. Underneath that, create a new folder named "RemoteFile". You may choose to use a different name if you wish.
- Download the latest version of the RemoteFile orchestrator extension from GitHub. Click on the "Latest" release link on the right hand side of the main page and download the first zip file.
- Copy the contents of the download installation zip file to the folder created in step 4.
- (Optional) If you decide to create one or more certificate store types with short names different than the suggested values, edit the manifest.json file in the folder you created in step 4, and modify each "ShortName" in each "Certstores.{ShortName}.{Operation}" line with the ShortName you used to create the respective certificate store type.
- Modify the config.json file to use the settings you desire. Please go to Configuration File Setup to learn more.
- Start the Keyfactor Universal Orchestrator Service.
The Remote File Orchestrator Extension uses a JSON configuration file. It is located in the {Keyfactor Orchestrator Installation Folder}\Extensions\RemoteFile. None of the values are required, and a description of each follows below:
{
"UseSudo": "N",
"DefaultSudoImpersonatedUser": "",
"CreateStoreIfMissing": "N",
"UseNegotiate": "N",
"SeparateUploadFilePath": "",
"FileTransferProtocol": "SCP",
"DefaultLinuxPermissionsOnStoreCreation": "600",
"DefaultOwnerOnStoreCreation": ""
}
UseSudo (Applicable for Linux hosted certificate stores only)
- Determines whether to prefix Linux command with "sudo". This can be very helpful in ensuring that the user id running commands over an ssh connection uses "least permissions necessary" to process each task. Setting this value to "Y" will prefix all Linux commands with "sudo" with the expectation that the command being executed on the orchestrated Linux server will look in the sudoers file to determine whether the logged in ID has elevated permissions for that specific command. Setting this value to "N" will result in "sudo" not being added to Linux commands.
- Allowed values - Y/N
- Default value - N
DefaultSudoImpersonatedUser (Applicable for Linux hosted certificate stores only)
- Used in conjunction with UseSudo="Y", this optional setting can be used to set an alternate user id you wish to impersonate with sudo. If this option does not exist or is set to an empty string, the default user of "root" will be used. Any user id used here must have permissions to SCP/SFTP files to/from each certificate store location OR the SeparateUploadFilePath (see later in this section) as well as permissions to execute the commands listed in the "Prerequisites and Security Considerations" section above. This value will be used for all certificate stores managed by this orchestrator extension implementation UNLESS overriden by the SudoImpersonatedUser certificate store type custom field setting described later in the Creating Certificate Store Types section.
- Allowed values - Any valid user id that the destination Linux server will recognize
- Default value - blank (root will be used)
CreateStoreOnAddIfMissing
- Determines, during a Management-Add job, if a certificate store should be created if it does not already exist. If set to "N", and the store referenced in the Management-Add job is not found, the job will return an error with a message stating that the store does not exist. If set to "Y", the store will be created and the certificate added to the certificate store.
- Allowed values - Y/N
- Default value - N
UseNegotiateAuth (Applicable for Windows hosted certificate stores only)
- Determines if WinRM should use Negotiate (Y) when connecting to the remote server.
- Allowed values - Y/N
- Default value - N
SeparateUploadFilePath (Applicable for Linux hosted certificate stores only)
- Set this to the path you wish to use as the location on the orchestrated server to upload/download and later remove temporary work files when processing jobs. If set to "" or not provided, the location of the certificate store itself will be used. File transfer is performed using the SCP or SFTP protocols (see the File TransferProtocol setting).
- Allowed values - Any valid, existing Linux path configured to allow SCP/SFTP file upload/download tranfers.
- Default value - blank (actual store path will be used)
FileTransferProtocol (Applicable for Linux hosted certificate stores only)
- Determines the protocol to use when uploading/downloading files while processing a job.
- Allowed values - SCP, SFTP or Both. If "Both" is entered, SCP will be attempted first, and if that does not work, SFTP will be tried.
- Default value - SCP.
DefaultLinuxPermissionsOnStoreCreation (Applicable for Linux hosted certificate stores only)
- The Linux file permissions that will be set on a new certificate store created via a Management Create job or a Management Add job where CreateStoreOnAddIsMissing is set to "Y". This value will be used for all certificate stores managed by this orchestrator instance unless overridden by the optional "Linux File Permissions on Store Creation" custom parameter setting on a specific certificate store. See the Creating Certificate Store Types section for more information on creating RemoteFile certificate store types.
- Allowed values - Any 3 digit value from 000-777.
- Default Value - 600.
DefaultOwnerOnStoreCreation (Applicable for Linux hosted certificate stores only)
- When a Management job is run to remotely create the physical certificate store on a remote server, by default the file owner and group will be set to the user name associated with the Keyfactor certificate store. Setting DefaultOwnerOnStoreCreation to an alternate valid Linux user name will set that as the owner instead. The owner AND group may be supplied by adding a ":" as a delimitter between the owner and group values, such as ownerId:groupId. Supplying only the ownerId will set that value as the file owner. The group name will default to how the Linux "install" command handles assigning the group. The optional "Linux File Owner on Store Creation" custom parameter setting for a specific certificate store can override this value for a specific store. See the Creating Certificate Store Types section for more information on creating RemoteFile certificate store types.
- Allowed values - Any valid user id that the destination Linux server will recognize
- Default Value - blank (the ID associated with the Keyfactor certificate store will be used).
Below are the various certificate store types that the RemoteFile Orchestator Extension manages. To create a new Certificate Store Type in Keyfactor Command, first click on settings (the gear icon on the top right) => Certificate Store Types => Add. Next, follow the incstructions under each store type you wish to set up.
RFPkcs12 - Pkcs12 formatted certificate file (including java keystores of type PKCS12)
-
Basic Tab:
- Name – Required. The display name you wish to use for the new Certificate Store Type.
- Short Name – Required. Suggested value - RFPkcs12. If you choose to use a different value you must make the corresponding modification to the manifest.json file. See Remote File Orchestrator Extension Installation, step 7 above.
- Custom Capability - Unchecked
- Supported Job Types - Inventory, Add, Remove, Create, and Discovery should all be checked.
- Needs Server - Checked
- Blueprint Allowed - Checked if you wish to make use of blueprinting. Please refer to the Keyfactor Command Reference Guide for more details on this feature.
- Uses PowerShell - Unchecked
- Requires Store Password - Checked. NOTE: This does not require that a certificate store have a password, but merely ensures that a user who creates a Keyfactor Command Certificate Store MUST click the Store Password button and either enter a password or check No Password. Certificate stores with no passwords are still possible for certain certificate store types when checking this option.
- Supports Entry Password - Unchecked.
-
Advanced Tab:
- Store Path Type - Freeform
- Supports Custom Alias - Required.
- Private Key Handling - Optional.
- PFX Password Style - Default
-
Custom Fields Tab:
- Name: LinuxFilePermissionsOnStoreCreation, Display Name: Linux File Permissions on Store Creation, Type: String, Default Value: none. This custom field is not required. If not present, value reverts back to the DefaultLinuxPermissionsOnStoreCreation setting in config.json (see Configuration File Setup section above). This value, applicable to certificate stores hosted on Linux orchestrated servers only, must be 3 digits all between 0-7. This represents the Linux file permissions that will be set for this certificate store if created via a Management Create job or a Management Add job where the config.json option CreateStoreOnAddIsMissing is set to "Y".
- Name: LinuxFileOwnerOnStoreCreation, Display Name: Linux File Owner on Store Creation, Type: String, Default Value: none. This custom field is not required. If not present, value reverts back to the DefaultOwnerOnStoreCreation setting in config.json (see Configuration File Setup section above). This value, applicable to certificate stores hosted on Linux orchestrated servers only, represents the alternate Linux file owner:group that will be set for this certificate store if created via a Management Create job or a Management Add job where the config.json option CreateStoreOnAddIsMissing is set to "Y". If the group needs to be set as well, use a ":" as a delimitter between the owner and group values, such as ownerId:groupId. If the group is NOT supplied, the group value will be set per normal behavior of the Linux "Install" command.
- Name: SudoImpersonatedUser, Display Name: Sudo Impersonated User Id, Type: String, Default Value: none. This custom field is not required. If not present, value reverts back to the DefaultSudoImpersonatedUser setting in config.json (see Configuration File Setup section above). Used in conjunction with UseSudo="Y", this optional setting can be used to set an alternate user id you wish to impersonate with sudo. If this option does not exist or is empty, and nothing is set for DefaultSudoImpersonatedUser in your config.json, the default user of "root" will be used. Any user id used here must have permissions to SCP/SFTP files to/from each certificate store location OR the SeparateUploadFilePath (see Configuration File Setup section above) as well as permissions to execute the commands listed in the "Security Considerations" section above.
- Name: RemoveRootCertificate, Display Name: Remove Root Certificate from Chain, Type: Bool, Default Value: False. This custom field is not required. If not present, value is set to the Default Value. This value determines whether root CA certificates should be included in the certificate chain when adding/renewing certificates in Management Add jobs. If set to False, the root CA certificate is included in the chain. If True, it is removed and only the non-root CA certificates are included in the chain when adding the entry to the certificate store.
-
Entry Parameters Tab:
- no additional entry parameters
RFJKS - Java keystore
-
Basic Tab:
- Name – Required. The display name you wish to use for the new Certificate Store Type.
- Short Name – Required. Suggested value - RFJKS. If you choose to use a different value you must make the corresponding modification to the manifest.json file. See Remote File Orchestrator Extension Installation, step 7 above.
- Custom Capability - Unchecked
- Supported Job Types - Inventory, Add, Remove, Create, and Discovery should all be checked.
- Needs Server - Checked
- Blueprint Allowed - Checked if you wish to make use of blueprinting. Please refer to the Keyfactor Command Reference Guide for more details on this feature.
- Uses PowerShell - Unchecked
- Requires Store Password - Checked. NOTE: This does not require that a certificate store have a password, but merely ensures that a user who creates a Keyfactor Command Certificate Store MUST click the Store Password button and either enter a password or check No Password. Certificate stores with no passwords are still possible for certain certificate store types when checking this option.
- Supports Entry Password - Unchecked.
-
Advanced Tab:
- Store Path Type - Freeform
- Supports Custom Alias - Required.
- Private Key Handling - Optional.
- PFX Password Style - Default
-
Custom Fields Tab:
- Name: LinuxFilePermissionsOnStoreCreation, Display Name: Linux File Permissions on Store Creation, Type: String, Default Value: none. This custom field is not required. If not present, value reverts back to the DefaultLinuxPermissionsOnStoreCreation setting in config.json (see Configuration File Setup section above). This value, applicable to certificate stores hosted on Linux orchestrated servers only, must be 3 digits all between 0-7. This represents the Linux file permissions that will be set for this certificate store if created via a Management Create job or a Management Add job where the config.json option CreateStoreOnAddIsMissing is set to "Y".
- Name: LinuxFileOwnerOnStoreCreation, Display Name: Linux File Owner on Store Creation, Type: String, Default Value: none. This custom field is not required. If not present, value reverts back to the DefaultOwnerOnStoreCreation setting in config.json (see Configuration File Setup section above). This value, applicable to certificate stores hosted on Linux orchestrated servers only, represents the alternate Linux file owner:group that will be set for this certificate store if created via a Management Create job or a Management Add job where the config.json option CreateStoreOnAddIsMissing is set to "Y". If the group needs to be set as well, use a ":" as a delimitter between the owner and group values, such as ownerId:groupId. If the group is NOT supplied, the group value will be set per normal behavior of the Linux "Install" command.
- Name: SudoImpersonatedUser, Display Name: Sudo Impersonated User Id, Type: String, Default Value: none. This custom field is not required. If not present, value reverts back to the DefaultSudoImpersonatedUser setting in config.json (see Configuration File Setup section above). Used in conjunction with UseSudo="Y", this optional setting can be used to set an alternate user id you wish to impersonate with sudo. If this option does not exist or is empty, and nothing is set for DefaultSudoImpersonatedUser in your config.json, the default user of "root" will be used. Any user id used here must have permissions to SCP/SFTP files to/from each certificate store location OR the SeparateUploadFilePath (see Configuration File Setup section above) as well as permissions to execute the commands listed in the "Security Considerations" section above.**.
- Name: RemoveRootCertificate, Display Name: Remove Root Certificate from Chain, Type: Bool, Default Value: False. This custom field is not required. If not present, value is set to the Default Value. This value determines whether root CA certificates should be included in the certificate chain when adding/renewing certificates in Management Add jobs. If set to False, the root CA certificate is included in the chain. If True, it is removed and only the non-root CA certificates are included in the chain when adding the entry to the certificate store.
-
Entry Parameters Tab:
- no additional entry parameters
RFPEM - PEM formatted certificate file
-
Basic Tab:
- Name – Required. The display name you wish to use for the new Certificate Store Type.
- Short Name – Required. Suggested value - RFPEM. If you choose to use a different value you must make the corresponding modification to the manifest.json file. See Remote File Orchestrator Extension Installation, step 7 above.
- Custom Capability - Unchecked
- Supported Job Types - Inventory, Add, Remove, Create, and Discovery should all be checked.
- Needs Server - Checked
- Blueprint Allowed - Checked if you wish to make use of blueprinting. Please refer to the Keyfactor Command Reference Guide for more details on this feature.
- Uses PowerShell - Unchecked
- Requires Store Password - Checked. NOTE: This does not require that a certificate store have a password, but merely ensures that a user who creates a Keyfactor Command Certificate Store MUST click the Store Password button and either enter a password or check No Password. Certificate stores with no passwords are still possible for certain certificate store types when checking this option.
- Supports Entry Password - Unchecked.
-
Advanced Tab:
- Store Path Type - Freeform
- Supports Custom Alias - Forbidden.
- Private Key Handling - Optional.
- PFX Password Style - Default
-
Custom Fields Tab:
- Name: LinuxFilePermissionsOnStoreCreation, Display Name: Linux File Permissions on Store Creation, Type: String, Default Value: none. This custom field is not required. If not present, value reverts back to the DefaultLinuxPermissionsOnStoreCreation setting in config.json (see Configuration File Setup section above). This value, applicable to certificate stores hosted on Linux orchestrated servers only, must be 3 digits all between 0-7. This represents the Linux file permissions that will be set for this certificate store if created via a Management Create job or a Management Add job where the config.json option CreateStoreOnAddIsMissing is set to "Y".
- Name: LinuxFileOwnerOnStoreCreation, Display Name: Linux File Owner on Store Creation, Type: String, Default Value: none. This custom field is not required. If not present, value reverts back to the DefaultOwnerOnStoreCreation setting in config.json (see Configuration File Setup section above). This value, applicable to certificate stores hosted on Linux orchestrated servers only, represents the alternate Linux file owner:group that will be set for this certificate store if created via a Management Create job or a Management Add job where the config.json option CreateStoreOnAddIsMissing is set to "Y". If the group needs to be set as well, use a ":" as a delimitter between the owner and group values, such as ownerId:groupId. If the group is NOT supplied, the group value will be set per normal behavior of the Linux "Install" command.
- Name: SudoImpersonatedUser, Display Name: Sudo Impersonated User Id, Type: String, Default Value: none. This custom field is not required. If not present, value reverts back to the DefaultSudoImpersonatedUser setting in config.json (see Configuration File Setup section above). Used in conjunction with UseSudo="Y", this optional setting can be used to set an alternate user id you wish to impersonate with sudo. If this option does not exist or is empty, and nothing is set for DefaultSudoImpersonatedUser in your config.json, the default user of "root" will be used. Any user id used here must have permissions to SCP/SFTP files to/from each certificate store location OR the SeparateUploadFilePath (see Configuration File Setup section above) as well as permissions to execute the commands listed in the "Security Considerations" section above.**.
- Name: RemoveRootCertificate, Display Name: Remove Root Certificate from Chain, Type: Bool, Default Value: False. This custom field is not required. If not present, value is set to the Default Value. This value determines whether root CA certificates should be included in the certificate chain when adding/renewing certificates in Management Add jobs. If set to False, the root CA certificate is included in the chain. If True, it is removed and only the non-root CA certificates are included in the chain when adding the entry to the certificate store.
- Name: IsTrustStore, Display Name: Trust Store, Type: Bool, Default Value: false. This custom field is not required. Default value if not present is 'false'. If 'true', this store will be identified as a trust store. Any certificates attempting to be added via a Management-Add job that contain a private key will raise an error with an accompanying message. Multiple certificates may be added to the store in this use case. If set to 'false', this store can only contain a single certificate with chain and private key. Management-Add jobs attempting to add a certificate without a private key to a store marked as IsTrustStore = 'false' will raise an error with an accompanying message.
- Name: IncludesChain, Display Name: Store Includes Chain, Type: Bool, Default Value: false. This custom field is not required. Default value if not present is 'false'. If 'true' the full certificate chain, if sent by Keyfactor Command, will be stored in the file. The order of appearance is always assumed to be 1) end entity certificate, 2) issuing CA certificate, and 3) root certificate. If additional CA tiers are applicable, the order will be end entity certificate up to the root CA certificate. if set to 'false', only the end entity certificate and private key will be stored in this store. This setting is only valid when IsTrustStore = false.
- Name: SeparatePrivateKeyFilePath, Display Name: Separate Private Key File Location, Type: String, Default Value: empty. This custom field is not required. If empty, or not provided, it will be assumed that the private key for the certificate stored in this file will be inside the same file as the certificate. If the full path AND file name is put here, that location will be used to store the private key as an external file. This setting is only valid when IsTrustStore = false.
- Name: IsRSAPrivateKey, Display Name: Is RSA Private Key, Type: Bool, Default Value: false. This custom field is not required. Default value if not present is 'false'. If 'true' it will be assumed that the private key for the certificate is a PKCS#1 RSA formatted private key (BEGIN RSA PRIVATE KEY). If 'false' (default), encrypted/non-encrypted PKCS#8 (BEGIN [ENCRYPTED] PRIVATE KEY) is assumed If set to 'true' the store password must be set to "no password", as PKCS#1 does not support encrypted keys. This setting is only valid when IsTrustStore = false.
- Name: IgnorePrivateKeyOnInventory, Display Name: Ignore Private Key On Inventory, Type: Bool, Default Value: false. This custom field is not required. Default value if not present is 'false'. If 'true', inventory for this certificate store will be performed without accessing the certificate's private key or the store password. This will functionally make the store INVENTORY ONLY, as all certificates will be returned with "Private Key Entry" = false. Also, no certificate chain relationships will be maintained, and all certificates will be considered separate entries (basically a trust store). This may be useful in situations where the client does not know the store password at inventory run time, but would still like the certificates to be imported into Keyfactor Command. Once the correct store password is entered for the store, the client may de-select this option (change the value to False), schedule an inventory job, and then the appropriate private key entry and chain information should be properly stored in the Keyfactor Command location, allowing for renewal/removal of the certificate at a later time.
-
Entry Parameters Tab:
- no additional entry parameters
RFDER - DER formatted certificate file
-
Basic Tab:
- Name – Required. The display name you wish to use for the new Certificate Store Type.
- Short Name – Required. Suggested value - RFDER. If you choose to use a different value you must make the corresponding modification to the manifest.json file. See Remote File Orchestrator Extension Installation, step 7 above.
- Custom Capability - Unchecked
- Supported Job Types - Inventory, Add, Remove, Create, and Discovery should all be checked.
- Needs Server - Checked
- Blueprint Allowed - Checked if you wish to make use of blueprinting. Please refer to the Keyfactor Command Reference Guide for more details on this feature.
- Uses PowerShell - Unchecked
- Requires Store Password - Checked. NOTE: This does not require that a certificate store have a password, but merely ensures that a user who creates a Keyfactor Command Certificate Store MUST click the Store Password button and either enter a password or check No Password. Certificate stores with no passwords are still possible for certain certificate store types when checking this option.
- Supports Entry Password - Unchecked.
-
Advanced Tab:
- Store Path Type - Freeform
- Supports Custom Alias - Forbidden.
- Private Key Handling - Optional.
- PFX Password Style - Default
-
Custom Fields Tab:
- Name: LinuxFilePermissionsOnStoreCreation, Display Name: Linux File Permissions on Store Creation, Type: String, Default Value: none. This custom field is not required. If not present, value reverts back to the DefaultLinuxPermissionsOnStoreCreation setting in config.json (see Configuration File Setup section above). This value, applicable to certificate stores hosted on Linux orchestrated servers only, must be 3 digits all between 0-7. This represents the Linux file permissions that will be set for this certificate store if created via a Management Create job or a Management Add job where the config.json option CreateStoreOnAddIsMissing is set to "Y".
- Name: LinuxFileOwnerOnStoreCreation, Display Name: Linux File Owner on Store Creation, Type: String, Default Value: none. This custom field is not required. If not present, value reverts back to the DefaultOwnerOnStoreCreation setting in config.json (see Configuration File Setup section above). This value, applicable to certificate stores hosted on Linux orchestrated servers only, represents the alternate Linux file owner:group that will be set for this certificate store if created via a Management Create job or a Management Add job where the config.json option CreateStoreOnAddIsMissing is set to "Y". If the group needs to be set as well, use a ":" as a delimitter between the owner and group values, such as ownerId:groupId. If the group is NOT supplied, the group value will be set per normal behavior of the Linux "Install" command.
- Name: SudoImpersonatedUser, Display Name: Sudo Impersonated User Id, Type: String, Default Value: none. This custom field is not required. If not present, value reverts back to the DefaultSudoImpersonatedUser setting in config.json (see Configuration File Setup section above). Used in conjunction with UseSudo="Y", this optional setting can be used to set an alternate user id you wish to impersonate with sudo. If this option does not exist or is empty, and nothing is set for DefaultSudoImpersonatedUser in your config.json, the default user of "root" will be used. Any user id used here must have permissions to SCP/SFTP files to/from each certificate store location OR the SeparateUploadFilePath (see Configuration File Setup section above) as well as permissions to execute the commands listed in the "Security Considerations" section above.
- Name: RemoveRootCertificate, Display Name: Remove Root Certificate from Chain, Type: Bool, Default Value: False. This custom field is not required. If not present, value is set to the Default Value. This value determines whether root CA certificates should be included in the certificate chain when adding/renewing certificates in Management Add jobs. If set to False, the root CA certificate is included in the chain. If True, it is removed and only the non-root CA certificates are included in the chain when adding the entry to the certificate store.
- Name: SeparatePrivateKeyFilePath, Display Name: Separate Private Key File Location, Type: String, Default Value: empty. This custom field is not required. If empty, or not provided, it will be assumed that there is no private key associated with this DER store. If the full path AND file name is entered here, that location will be used to store the private key as an external file in DER format.
-
Entry Parameters Tab:
- no additional entry parameters
RFKDB - IBM Key Database File
-
Basic Tab:
- Name – Required. The display name you wish to use for the new Certificate Store Type.
- Short Name – Required. Suggested value - RFKDB. If you choose to use a different value you must make the corresponding modification to the manifest.json file. See Remote File Orchestrator Extension Installation, step 7 above.
- Custom Capability - Unchecked
- Supported Job Types - Inventory, Add, Remove, Create, and Discovery should all be checked.
- Needs Server - Checked
- Blueprint Allowed - Checked if you wish to make use of blueprinting. Please refer to the Keyfactor Command Reference Guide for more details on this feature.
- Uses PowerShell - Unchecked
- Requires Store Password - Checked. NOTE: This does not require that a certificate store have a password, but merely ensures that a user who creates a Keyfactor Command Certificate Store MUST click the Store Password button and either enter a password or check No Password. Certificate stores with no passwords are still possible for certain certificate store types when checking this option.
- Supports Entry Password - Unchecked.
-
Advanced Tab:
- Store Path Type - Freeform
- Supports Custom Alias - Required.
- Private Key Handling - Optional.
- PFX Password Style - Default
-
Custom Fields Tab:
- Name: LinuxFilePermissionsOnStoreCreation, Display Name: Linux File Permissions on Store Creation, Type: String, Default Value: none. This custom field is not required. If not present, value reverts back to the DefaultLinuxPermissionsOnStoreCreation setting in config.json (see Configuration File Setup section above). This value, applicable to certificate stores hosted on Linux orchestrated servers only, must be 3 digits all between 0-7. This represents the Linux file permissions that will be set for this certificate store if created via a Management Create job or a Management Add job where the config.json option CreateStoreOnAddIsMissing is set to "Y".
- Name: LinuxFileOwnerOnStoreCreation, Display Name: Linux File Owner on Store Creation, Type: String, Default Value: none. This custom field is not required. If not present, value reverts back to the DefaultOwnerOnStoreCreation setting in config.json (see Configuration File Setup section above). This value, applicable to certificate stores hosted on Linux orchestrated servers only, represents the alternate Linux file owner:group that will be set for this certificate store if created via a Management Create job or a Management Add job where the config.json option CreateStoreOnAddIsMissing is set to "Y". If the group needs to be set as well, use a ":" as a delimitter between the owner and group values, such as ownerId:groupId. If the group is NOT supplied, the group value will be set per normal behavior of the Linux "Install" command.
- Name: SudoImpersonatedUser, Display Name: Sudo Impersonated User Id, Type: String, Default Value: none. This custom field is not required. If not present, value reverts back to the DefaultSudoImpersonatedUser setting in config.json (see Configuration File Setup section above). Used in conjunction with UseSudo="Y", this optional setting can be used to set an alternate user id you wish to impersonate with sudo. If this option does not exist or is empty, and nothing is set for DefaultSudoImpersonatedUser in your config.json, the default user of "root" will be used. Any user id used here must have permissions to SCP/SFTP files to/from each certificate store location OR the SeparateUploadFilePath (see Configuration File Setup section above) as well as permissions to execute the commands listed in the "Security Considerations" section above.
- Name: RemoveRootCertificate, Display Name: Remove Root Certificate from Chain, Type: Bool, Default Value: False. This custom field is not required. If not present, value is set to the Default Value. This value determines whether root CA certificates should be included in the certificate chain when adding/renewing certificates in Management Add jobs. If set to False, the root CA certificate is included in the chain. If True, it is removed and only the non-root CA certificates are included in the chain when adding the entry to the certificate store.
-
Entry Parameters Tab:
- no additional entry parameters
RFORA - Oracle Wallet
-
Basic Tab:
- Name – Required. The display name you wish to use for the new Certificate Store Type.
- Short Name – Required. Suggested value - RFORA. If you choose to use a different value you must make the corresponding modification to the manifest.json file. See Remote File Orchestrator Extension Installation, step 7 above.
- Custom Capability - Unchecked
- Supported Job Types - Inventory, Add, Remove, Create, and Discovery should all be checked.
- Needs Server - Checked
- Blueprint Allowed - Checked if you wish to make use of blueprinting. Please refer to the Keyfactor Command Reference Guide for more details on this feature.
- Uses PowerShell - Unchecked
- Requires Store Password - Checked. NOTE: This does not require that a certificate store have a password, but merely ensures that a user who creates a Keyfactor Command Certificate Store MUST click the Store Password button and either enter a password or check No Password. Certificate stores with no passwords are still possible for certain certificate store types when checking this option.
- Supports Entry Password - Unchecked.
-
Advanced Tab:
- Store Path Type - Freeform
- Supports Custom Alias - Required.
- Private Key Handling - Optional.
- PFX Password Style - Default
-
Custom Fields Tab:
- Name: LinuxFilePermissionsOnStoreCreation, Display Name: Linux File Permissions on Store Creation, Type: String, Default Value: none. This custom field is not required. If not present, value reverts back to the DefaultLinuxPermissionsOnStoreCreation setting in config.json (see Configuration File Setup section above). This value, applicable to certificate stores hosted on Linux orchestrated servers only, must be 3 digits all between 0-7. This represents the Linux file permissions that will be set for this certificate store if created via a Management Create job or a Management Add job where the config.json option CreateStoreOnAddIsMissing is set to "Y".
- Name: LinuxFileOwnerOnStoreCreation, Display Name: Linux File Owner on Store Creation, Type: String, Default Value: none. This custom field is not required. If not present, value reverts back to the DefaultOwnerOnStoreCreation setting in config.json (see Configuration File Setup section above). This value, applicable to certificate stores hosted on Linux orchestrated servers only, represents the alternate Linux file owner:group that will be set for this certificate store if created via a Management Create job or a Management Add job where the config.json option CreateStoreOnAddIsMissing is set to "Y". If the group needs to be set as well, use a ":" as a delimitter between the owner and group values, such as ownerId:groupId. If the group is NOT supplied, the group value will be set per normal behavior of the Linux "Install" command.
- Name: SudoImpersonatedUser, Display Name: Sudo Impersonated User Id, Type: String, Default Value: none. This custom field is not required. If not present, value reverts back to the DefaultSudoImpersonatedUser setting in config.json (see Configuration File Setup section above). Used in conjunction with UseSudo="Y", this optional setting can be used to set an alternate user id you wish to impersonate with sudo. If this option does not exist or is empty, and nothing is set for DefaultSudoImpersonatedUser in your config.json, the default user of "root" will be used. Any user id used here must have permissions to SCP/SFTP files to/from each certificate store location OR the SeparateUploadFilePath (see Configuration File Setup section above) as well as permissions to execute the commands listed in the "Security Considerations" section above.
- Name: RemoveRootCertificate, Display Name: Remove Root Certificate from Chain, Type: Bool, Default Value: False. This custom field is not required. If not present, value is set to the Default Value. This value determines whether root CA certificates should be included in the certificate chain when adding/renewing certificates in Management Add jobs. If set to False, the root CA certificate is included in the chain. If True, it is removed and only the non-root CA certificates are included in the chain when adding the entry to the certificate store.
- Name: WorkFolder, Display Name: Work Folder, Type: String, Default Value: empty. This custom field is required. This required field should contain the path on the managed server where temporary work files can be created during Inventory and Management jobs. These files will be removed at the end of each job Please make sure that user id you have assigned to this certificate store will have access to create, modify, and delete files from this folder.
-
Entry Parameters Tab:
- no additional entry parameters
When creating new certificate stores or scheduling discovery jobs in Keyfactor Command, there are a few fields that are important to highlight here:
Client Machine (certificate stores and discovery jobs)
For Linux orchestrated servers, "Client Machine" should be the DNS name or IP address of the remote orchestrated server, while for Windows orchestratred servers, it should be the following URL format: protocol://dns-or-ip:port, where
- protocol is http or https, whatever your WinRM configuration uses
- dns-or-ip is the DNS name or IP address of the server
- port is the port WinRM is running under, usually 5985 for http and 5986 for https.
Example: https://myserver.mydomain.com:5986
If running as an agent (accessing stores on the server where the Universal Orchestrator Services is installed ONLY), Client Machine can be entered as stated above, OR you can bypass SSH/WinRM and access the local file system directly by adding "|LocalMachine" to the end of your value for Client Machine, for example "1.1.1.1|LocalMachine". In this instance the value to the left of the pipe (|) is ignored. It is important to make sure the values for Client Machine and Store Path together are unique for each certificate store created, as Keyfactor Command requires the Store Type you select, along with Client Machine, and Store Path together must be unique. To ensure this, it is good practice to put the full DNS or IP Address to the left of the | character when setting up a cerificate store that will accessed without a WinRM/SSH connection.
Store Path (certificate stores only)
For Linux orchestrated servers, "StorePath" will begin with a forward slash (/) and contain the full path and file name, including file extension if one exists (i.e. /folder/path/storename.ext). For Windows orchestrated servers, it should be the full path and file name, including file extension if one exists, beginning with a drive letter (i.e. c:\folder\path\storename.ext).
Server Username/Password (certificate stores and discovery jobs)
A username and password (or valid PAM key if the username and/or password is stored in a KF Command configured PAM integration). The password can be an SSH private key if connecting via SSH to a server using SSH private key authentication. If acting as an agent using local file access, just check "No Value" for the username and password.
Directories to Search (discovery jobs only)
Enter one or more comma delimitted file paths to search (please reference the Keyfactor Command Reference Guide for more information), but there is also a special value that can be used on Windows orchestrated servers instead - "fullscan". Entering fullscan in this field will tell the RemoteFile discovery job to search all available drive letters at the root and recursively search all of them for files matching the other search criteria.
Extensions (discovery jobs only)
In addition to entering one or more comma delimitted extensions to search for (please reference the Keyfactor Command Reference Guide for more information), a reserved value of "noext" can be used that will cause the RemoteFile discovery job to search for files that do not have an extension. This value can be chained with other extensions using the comma delimiter. For example, entering pem,jks,noext will cause the RemoteFile discovery job to return file locations with extensions of "pem", "jks", and files that do not have extensions.
Please refer to the Keyfactor Command Reference Guide for complete information on creating certificate stores and scheduling discovery jobs in Keyfactor Command.
The Remote File Orchestrator Extension is meant to be extended to be used for other file based certificate store types than the ones referenced above. The advantage to extending this integration rather than creating a new one is that the configuration, remoting, and Inventory/Management/Discovery logic is already written. The developer needs to only implement a few classes and write code to convert the destired file based store to a common format. This section describes the steps necessary to add additional store/file types. Please note that familiarity with the .Net Core BouncyCastle cryptography library is a prerequisite for adding additional supported file/store types.
Steps to create a new supported file based certificate store type:
- Clone this repository from GitHub
- Open the .net core solution in the IDE of your choice
- Under the ImplementationStoreTypes folder, create a new folder named for the new certificate store type
- Create a new class (with namespace of Keyfactor.Extensions.Orchestrator.RemoteFile.{NewType}) in the new folder that will implement ICertificateStoreSerializer. By convention, {StoreTypeName}CertificateSerializer would be a good choice for the class name. This interface requires you to implement three methods:
- DesrializeRemoteCertificateStore - This method takes in a byte array containing the contents of file based store you are managing. The developer will need to convert that to an Org.BouncyCastle.Pkcs.Pkcs12Store class and return it.
- SerializeRemoteCertificateStore - This method takes in an Org.BouncyCastle.Pkcs.Pkcs12Store and converts it to a collection of custom file representations.
- GetPrivateKeyPath - This method returns the location of the external private key file for single certificate stores. Currently this is only used for RFPEM, and all other implementations return NULL for this method. If this is not applicable to your implementation just return a NULL value for this method.
- Create an Inventory.cs class (with namespace of Keyfactor.Extensions.Orchestrator.RemoteFile.{NewType}) under the new folder and have it inherit InventoryBase. Override the internal GetCertificateStoreSerializer() method with a one line implementation returning a new instantiation of the class created in step 4.
- Create a Management.cs class (with namespace of Keyfactor.Extensions.Orchestrator.RemoteFile.{NewType}) under the new folder and have it inherit ManagementBase. Override the internal GetCertificateStoreSerializer() method with a one line implementation returning a new instantiation of the class created in step 4.
- Modify the manifest.json file to add three new sections (for Inventory, Management, and Discovery). Make sure for each, the "NewType" in Certstores.{NewType}.{Operation}, matches what you will use for the certificate store type short name in Keyfactor Command. On the "TypeFullName" line for all three sections, make sure the namespace matches what you used for your new classes. Note that the namespace for Discovery uses a common class for all supported types. Discovery is a common implementation for all supported store types.
- After compiling, move all compiled files, including the config.json and manifest.json to {Keyfactor Orchestrator Installation Folder}\Extensions\RemoteFile.
- Create the certificate store type in Keyfactor Command
- Add a new CURL script to build the proper Keyfactor Command certificate store type and place it under "Certificate Store Type CURL Scripts". The name of the file should match the ShortName you are using for the new store type.
- Update the documenation in readme_source.md by adding a new section under Creating Certificate Store Types for this new supported file based store type. Include a pointer to the CURL script created in step 10.
When creating cert store type manually, that store property names and entry parameter names are case sensitive