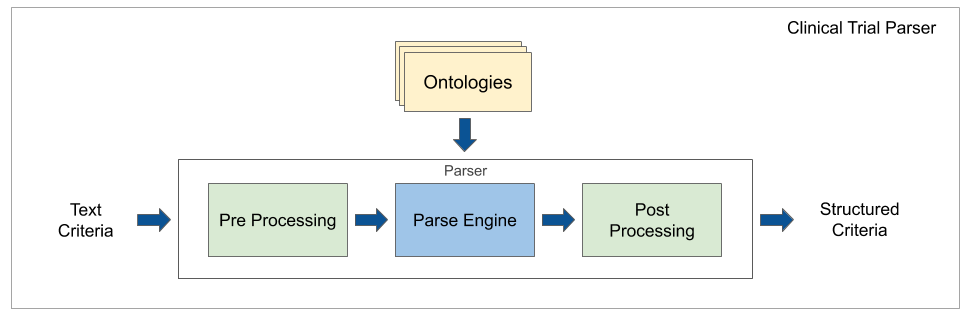
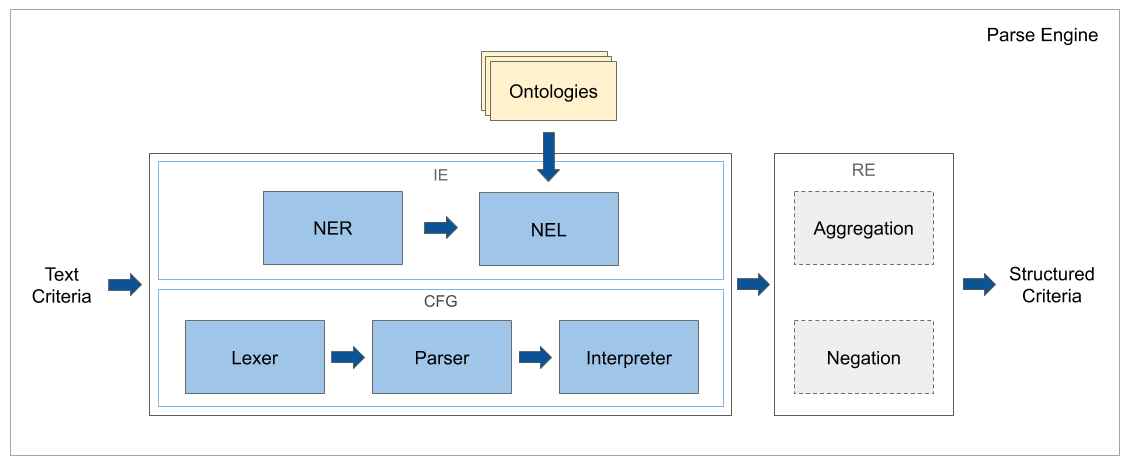
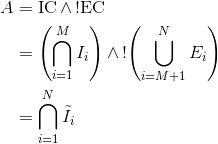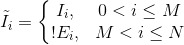This is a library for parsing clinical trial eligibility criteria. It contains context-free grammar (CFG) and information extraction (IE) parser models, annotated word labeling data, medical word embeddings and vocabulary tools.
Clinical trials face multiple problems:
- Trials cannot recruit enough participants
- Diverse populations are not well represented
- It is hard to find relevant trials and few eligible patients enlist
Due to these challenges, research is often slower and more biased than it should be.
Clinical trials use eligibility criteria to specify the participant population and to guarantee patient safety. The difficulty is to convert criteria to a machine-readable format. This library aims to reduce the amount of manual work needed to understand clinical trial eligibility, by extracting information algorithmically and using domain intelligence from the text itself (embeddings) and external expert data (vocabularies/ontologies).
Clinical Trial Parser relies on a combination of CFG and classic IE techniques to convert structured nominal, ordinal, and numerical requirements from eligibility criteria text. For details, see the architecture description.
The purpose of this library is to interpret and convert eligibility criteria to machine-readable relations. This way trials can easily be searched and discovered by their eligibility requirements.
To do this, inclusion (IC) and exclusion (EC) criteria sections are first extracted using regular expressions that identify the section headers. Next, the eligibility sections are split into individual criteria. Because the eligibility criteria must compute to one of the two values for each person – ‘eligible’ (yes) or ‘not eligible’ (no) – Boolean algebra can be used to express the eligibility logic. If an inclusion criterion is denoted by Ii and an exclusion criterion by Ei, the eligibility is computed as
where the effective inclusion criterion is defined as
A complete solution needs to consider a corner case where an exclusion criterion is actually an inclusion criterion. In this case, the negation cannot be applied. Fortunately, there are few such cases and they tend to affect only certain types of requirements.
The parser uses IE classifiers and CFG to convert individual eligibility criteria to machine-readable relations. Typically, both IE classifiers and CFG parsers are applied. Interpretations with confidence scores that are above a preset threshold are kept because a criterion may be a composite criterion built by joining multiple criteria together.
Variable is a convenient abstraction for interpreting eligibility criteria and defining machine-readable relations. It corresponds to a basic unit of clinical or demographic information that is extracted from a criterion and which determines a person’s eligibility.
Extracted relations on variables are formatted with the following JSON fields:
- id of the parsed variable (either its MeSH ID or curated ID)
- name of the parsed variable
- variableType (can be
nominal,ordinalornumerical) - value of the nominal or ordinal variable that makes a person eligible for a trial
- lower is the lower limit of the numerical variable, which contains the limit value and Boolean to indicate whether the limit is inclusive or not
- upper is the upper limit of the numerical variable, which contains the value and Boolean to indicate whether the limit is inclusive or not
- unit of the numerical variable
- score is the confidence score between 0 and 1 of the parsed result being correct
The parser splits extraction by variable type. It handles 3 types of variables:
-
Nominal requirements: Requirements comprising a nominal variable (e.g. pregnant, leukemia, allergy) and a condition on the variable (i.e. does the study require or forbid the participant to have said variable). These are the most common types of requirements. Examples:
-
The inclusion criterion for the clinical trial NCT03442400,
All patients who have coronary stenoses between 40-70% severity and who have severe aortic stenosis undergoing TAVR work-up.
would be parsed to
{"id":["C14.280.484.150","C14.280.955.249"],"name":"Aortic Valve Stenosis","value":["yes"],"variableType":"nominal","score":1} -
The inclusion criterion for the clinical trial NCT04344015,
Prior diagnosis of COVID-19 documented by a laboratory test approved by the FDA
would be parsed to
{"id":["C01.925"],"name":"COVID-19","value":["yes"],"variableType":"nominal","score":1}
-
-
Ordinal requirements: Requirements comprising an ordinal variable (e.g. ECOG score, NYHA class) and a set of eligible values. Examples:
- The exclusion criterion for the clinical trial NCT03367871,
Patients with an ECOG performance status of 2, 3 or 4.
is parsed to
{"id":"100","name":"ecog","value":["0","1"],"variableType":"ordinal","score":1}
- The exclusion criterion for the clinical trial NCT03367871,
-
Numerical requirements: Requirements comprising a numerical variable (e.g. age, BMI, platelet count) and an eligible range for the variable. Examples:
-
The inclusion criterion for the clinical trial NCT04272255,
Male or female, aged 18 to 59 (inclusive).
is parsed to
{"id":"203","name":"age","lower":{"incl":true,"value":"18"},"upper":{"incl":true,"value":"59"},"variableType":"numerical","score":1} -
The inclusion criterion for the clinical trial NCT04267796,
Self-reported height and weight indicating a BMI of at least 18.5 and < 25 kg/m^2
is parsed to
{"id":"203","name":"bmi","unit":"kg/m2","lower":{"incl":true,"value":"18.5"},"upper":{"incl":false,"value":"25"},"variableType":"numerical","score":1} -
The exclusion criterion for the clinical trial NCT04257136,
Absolute neutrophil count of < 1000 mm3
is parsed to
{"id":"408","name":"anc","unit":"cells/ul","lower":{"incl":true,"value":"1000"},"variableType":"numerical","score":1}
-
The quality of the parser is measured by randomly sampling eligibility criteria from recruiting trials. The CFG model is estimated to parse ordinal and numerical requirements with the precision of ≥ 90% and recall ≥ 85% per implemented variable. The IE model is estimated to parse nominal requirements with the precision of approximately 44% for heart-condition related criteria. Although the precision of NER is estimated to be ~ 88%, the grounding of extracted entity mentions to medical concepts lowers the IE quality, because the differences between the eligibility criteria and the Medical Subject Headings (MeSH) vocabulary lead to imperfect NEL and because criteria are sometimes written ambiguously. The extracted concepts are grounded to about 6K medical variables.
This library works with Mac OS X or Linux. The developer guide describes how to set up the project and prepare the resources.
-
The CFG parser module requires Go 1.11 or higher
-
The IE parser module requires Python 3.7 or higher, PyText, Natural Language Toolkit, and Go 1.11 or higher
-
The word embedding module requires Python 3.7 or higher, the fasttext python module, and Natural Language Toolkit
-
To download clinical trials from the AACT database using
aact.sh, a postgreSQL database needs to be installed (version 11 or higher)
To build and test the CFG parser, run:
go build ./...
go test ./...
To train a new NER model, run:
pytext train < src/resources/config/ner.json
To test the NER model, run:
pytext test < src/resources/config/ner.json
The CFG parser can be run by executing:
./script/cfg_parse.sh
The sample input and output of the script are clinical_trials.csv
and cfg_parsed_clinical_trials.tsv.
The IE parser can be run by executing:
./script/ie_parse.sh
The sample input and output of the script are clinical_trials.csv
and ie_parsed_clinical_trials.tsv.
Thanks to the Clinical Trials Transformation Initiative (CTTI) for providing the Aggregate Analysis of ClinicalTrials.gov (AACT) Database for the registered clinical studies at ClinicalTrials.gov.
Clinical Trial Parser is Apache 2.0 licensed, as found in the LICENSE file. Facebook assumes no responsibility for the resulting use of this library.