Project for "Software Engineering" at Imperial College London Department of Electrical and Electronic Engineering.
The purpose of the assignment is to recreate the famous game 2048 in C++.
"The aim of the course is to introduce the basic principles of software engineering and basic practice in program design and implementation. Students will be able to design a relatively complex computer application, and implement it using development environments in the target language (C++). Students will acquire the necessary competence to undertake other coursework or laboratory exercises that requires computer programming. Students will become familiar with software design, programming concepts, and tool use: these are all transferable skills relevant to whatever programming language/environment students encounter." [EE1-07-Software Engineering 1: Introduction to Computing]
“2048” Assignment Overview/Basic Idea
For the assignment, I used one 4x4 array of integer elements (one 4 array with element pointers to 4 integer arrays). I am defining the size of my array making it applicable for other dimensions as well.
The basic idea behind my implementation for additions involves two steps:
- To swift all elements and eliminate zeros in between.
- To do possible additions starting from the start of the array.
Since these steps are common for every direction I wrote the functions based on one direction (left) and I rotated the array for the other directions to match this.
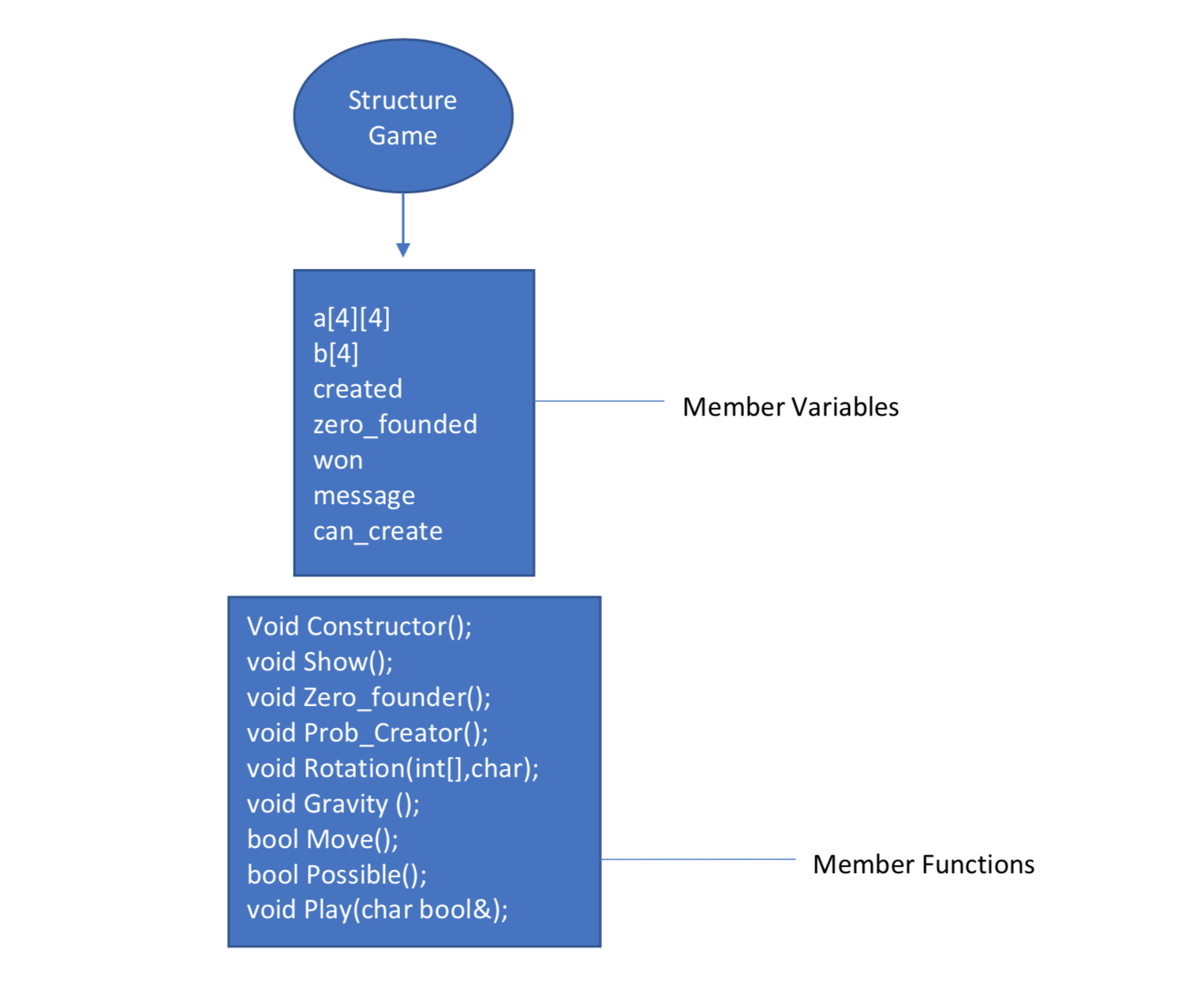
Variables and Structures Used I used a data z structure zero_points to create points where a zero has been found. I used a data structure with member variables:
a is our basic 4x4 array which is our game output, b is used as a buffer array to rotate elements and do possible changes. Zero_founded variable is used to determinate if we have zeros on our table, can_create in order to check if we can move on the table or the game is over, won in order to check if the user won and created if a new element was created. Finally, message is the final message to the user either “won” or “lost”. The check variable is used in order to avoid Move function do addition but just check for possible additions when no zeros are on the table.
Member Functions
-
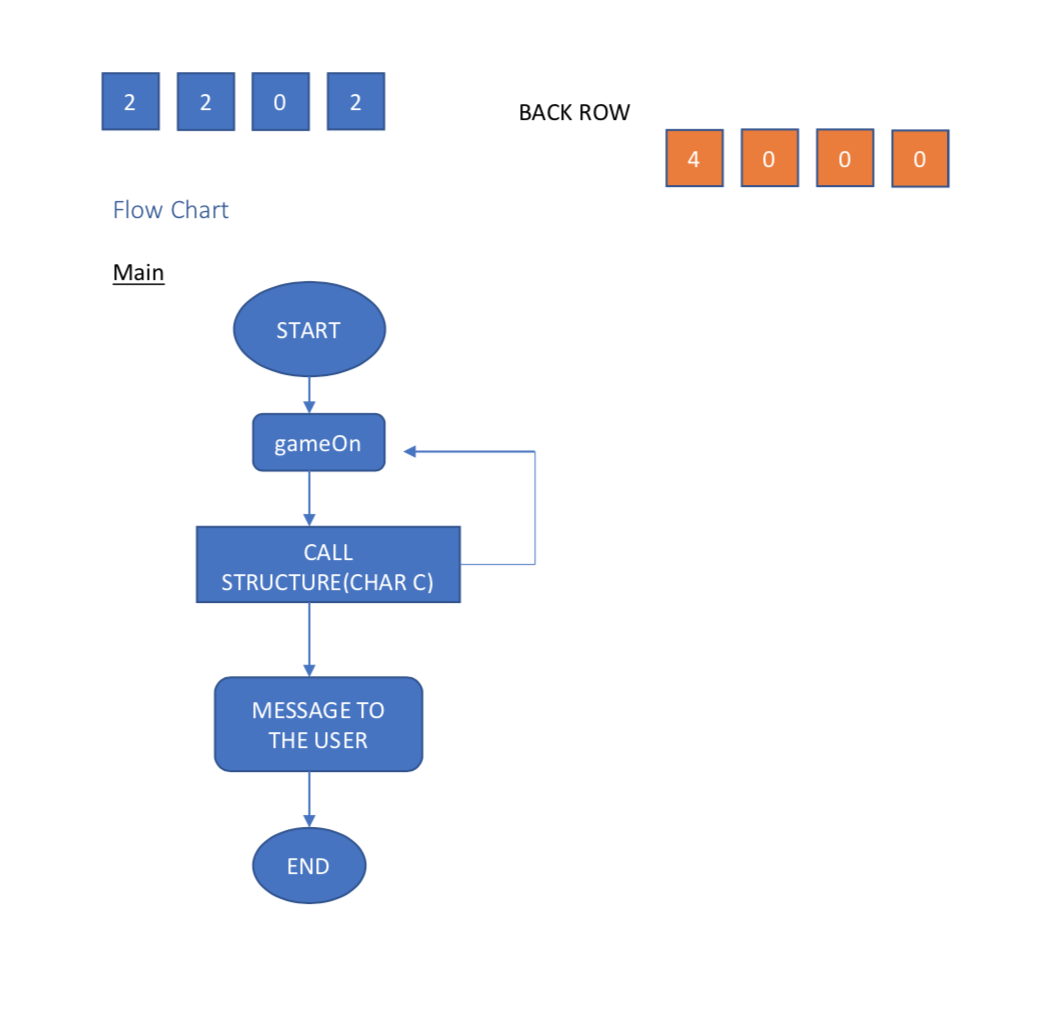
void Constructor() This is function creates my 4x4 table which is either from 2048.txt text file and if it can not find it creates the default (All elements zero except the a[3][3] which is 2).
-
void Show() This function displays the current state of my 4x4 table.
-
void Zero_founder() This function checks if there is a zero element on my table.
-
void Prob_Creator() This function creates a random 2 element on my table if a zero element has been found. It creates elements of zero_points structure and puts them into an array. After that randomly chooses one and makes it a zero.
-
bool Possible() This function checks if a move can be done on my 4x4 table given my current state.
-
void Rotation() This function makes the necessary rotation of the table as it is described in the next section.
-
void Gravity () This function swifts all elements and eliminates zeros in between.
-
bool Move() This function does possible additions starting from the start of the array. It also checks for winner of the game.
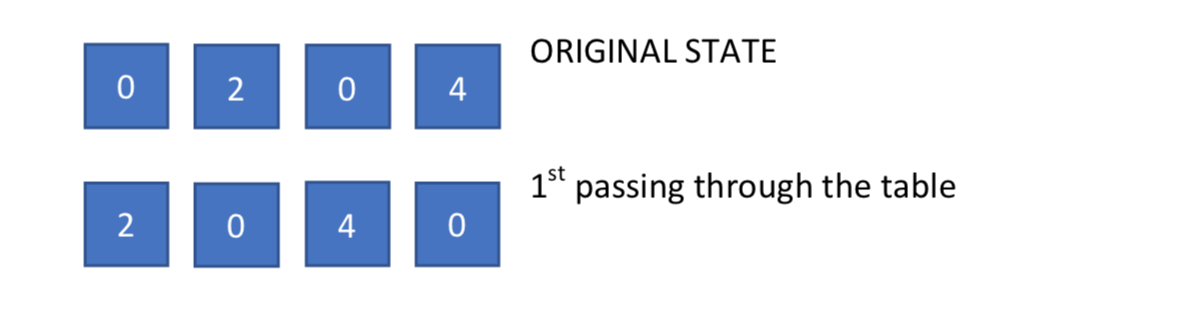
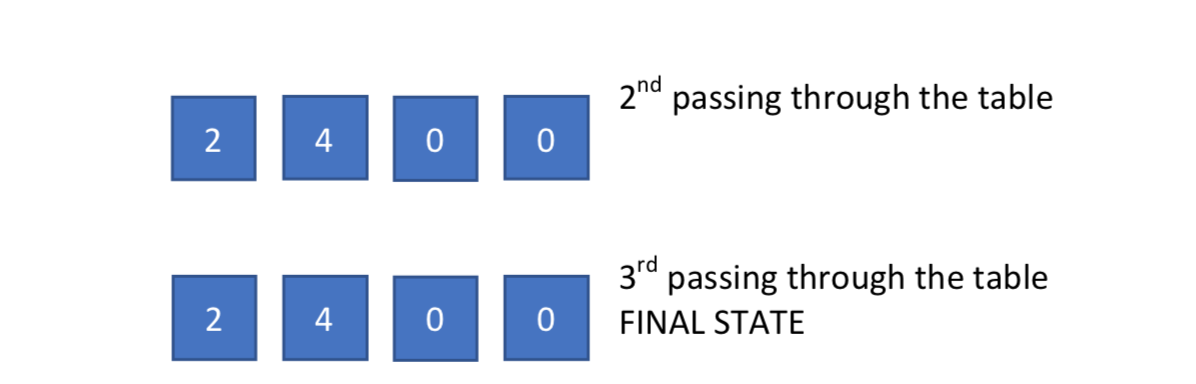
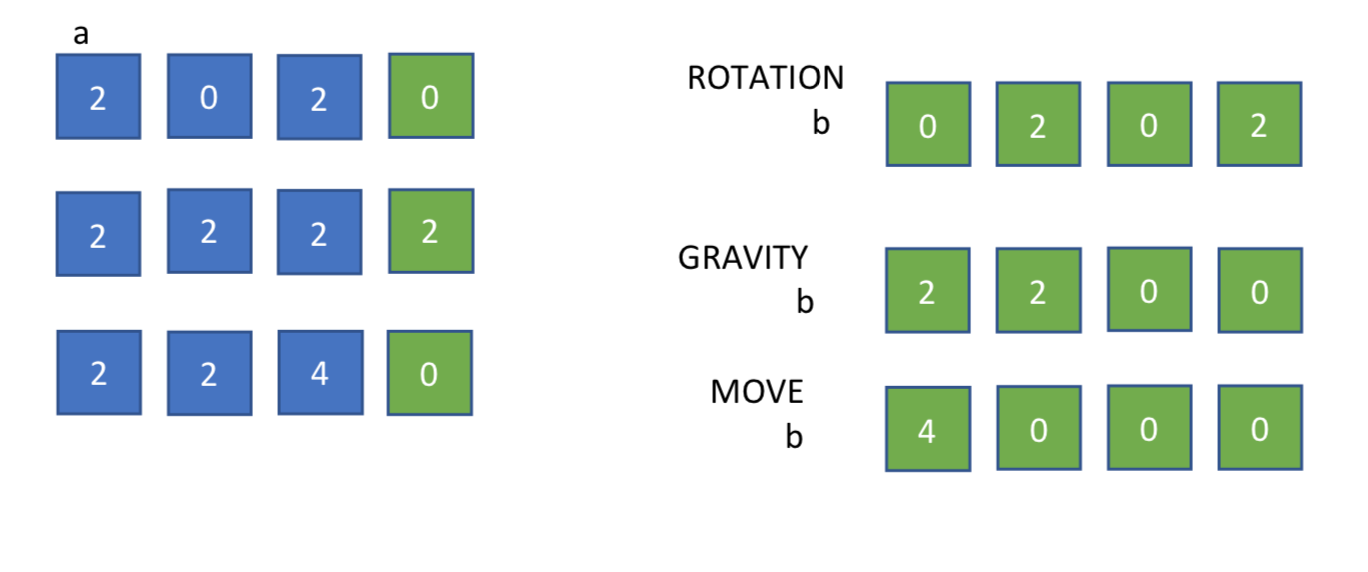
Gravity / Rotation The Gravity function is designed to swift all elements to the left and eliminates possible not needed zeros in between. It passes through the one-dimensional table three times. Every time, it checks every element with the next, starting from the start of the array. If the element is zero and the next element is not zero element then we swap the elements of the table. For instance,
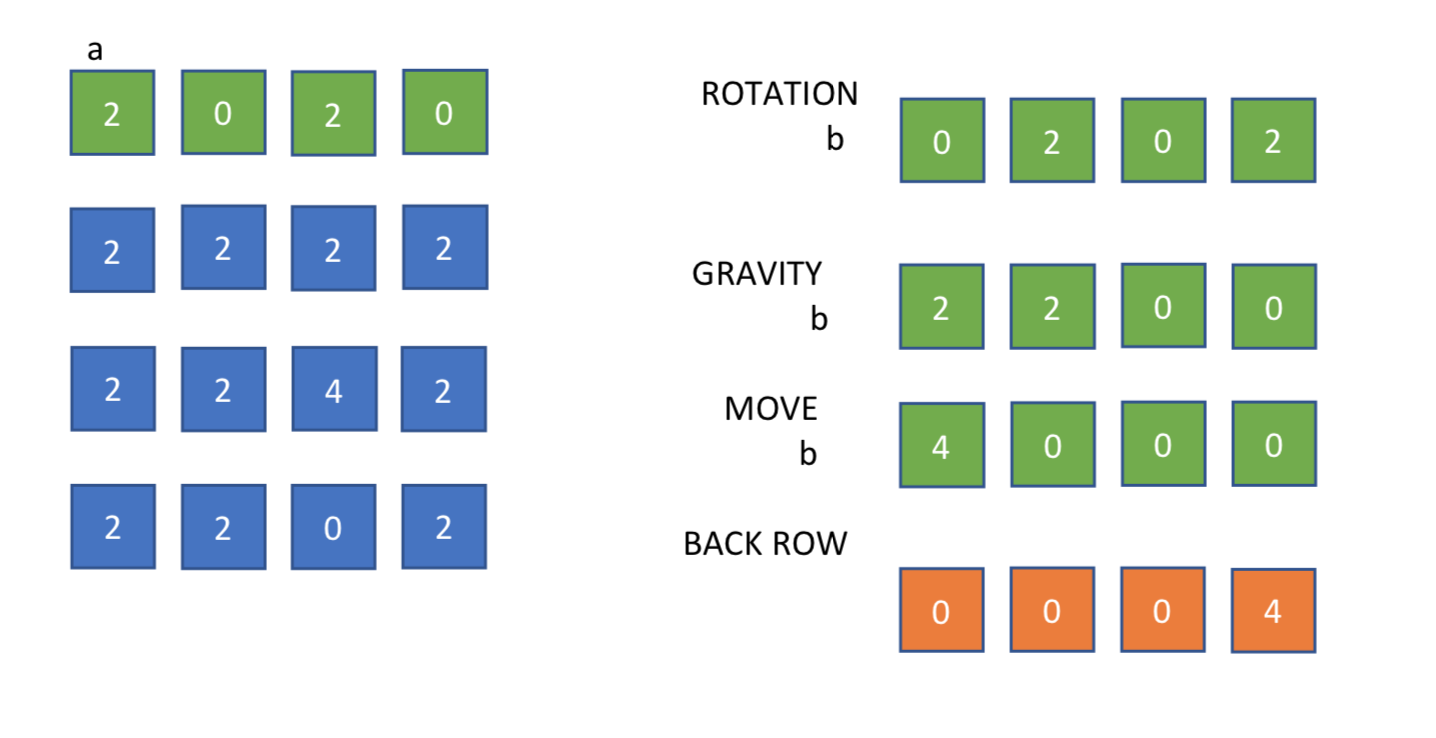
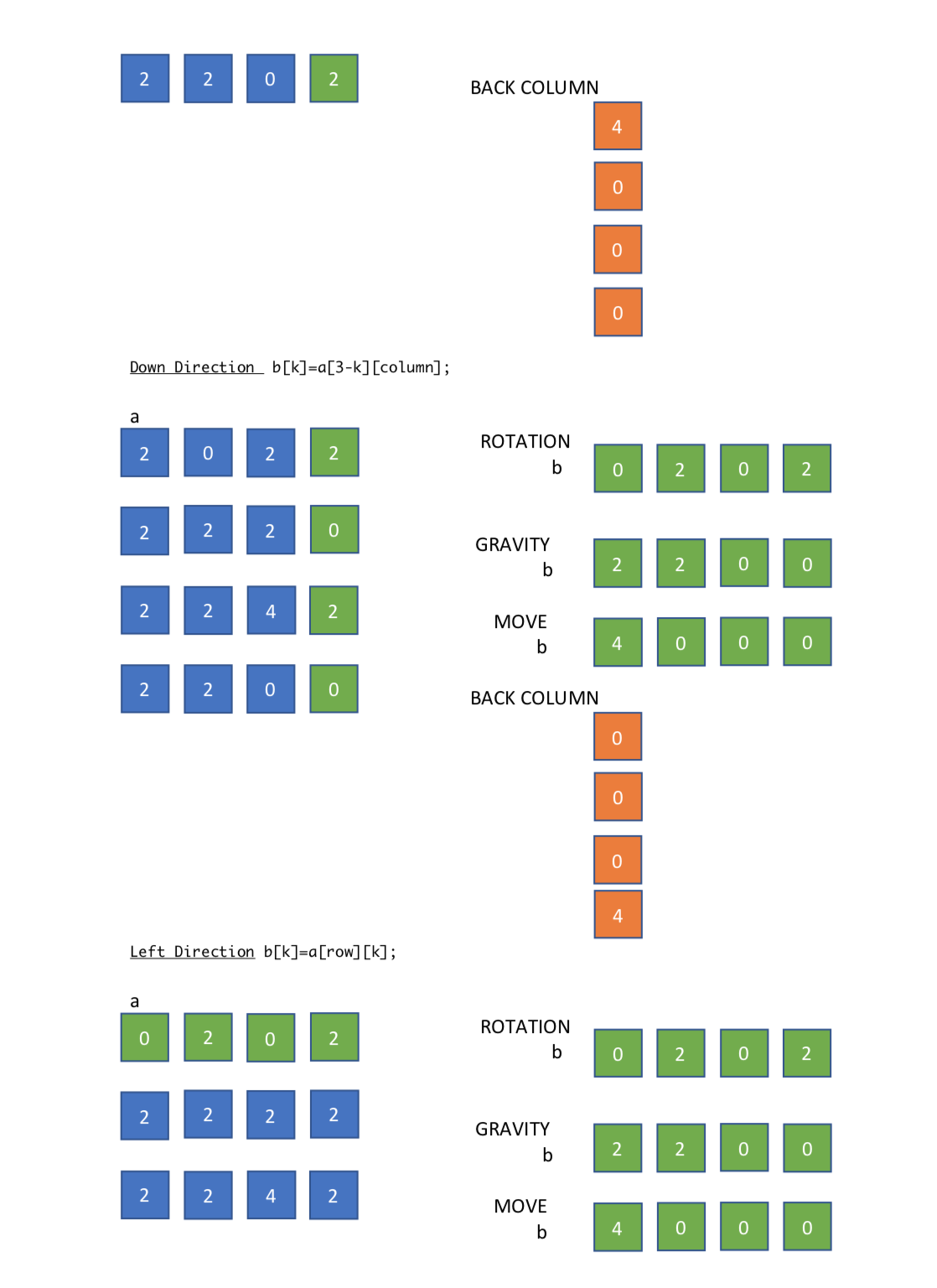
The Rotation function rotates one line of my 4x4 table (row or column) as it was supposed to move on the left. Then the Gravity and Move functions do the swift and the additions. More specifically,
Right Direction b[k]=a[row][3-k];
Up Direction b[k]=a[k][column];