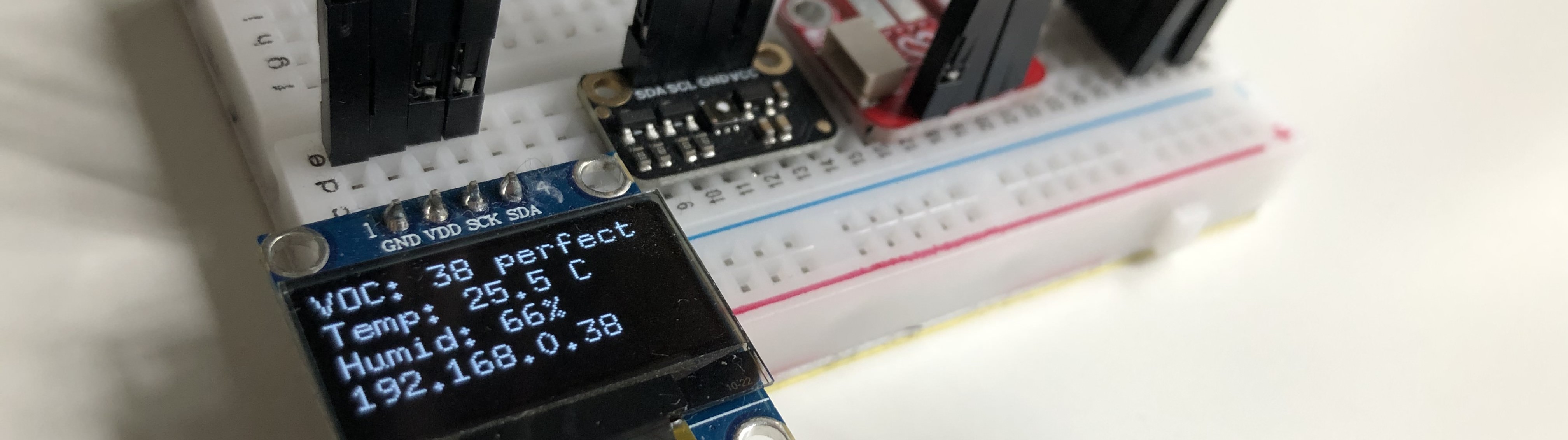
SHT40 is a capacitive-type humidity and temperature sensor. It measures the relative humidity in the range of 0 - 100 %RH with a precision of ±1% and temperature in the range of -40 °C - 125 °C with a precision < ±0.1 °C.
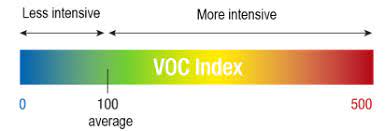
The setup utilizes Adafruit SGP40 Air Quality Sensor. The sensor uses the aforementioned temperature and humidity sensor to provide data for the computation of compensated VOC index. The index is computed using Sensirion VOC algorithm. The algorithm outputs a natural number in the range [0, 500 signalizing indoor air quality. Values below 100 indicate a typical indoor gas composition, while values above 100 indicate deteriorated air quality.
A database is necessary for measurement storage. Please, run a Postgresql DB before installing the server application, for example using Docker:
docker run --name pv191-server-postgres --user postgres -e POSTGRES_PASSWORD=mysecretpassword -d -p 5432:5432 --restart always postgresAfter the DB server is running, and you've created a database for the application, specify the connection URL in the server unit file (You have to do this step after you've installed the server).
The server application is provided as a Debian package. The server runs as a systemd service upon installation.
wget https://github.com/KristianMika/pv191-smart-home-server/releases/download/v0.1.0/smart-home-server_0.1.0_arm64.deb
sudo apt-get install ./smart-home-server_0.1.0_arm64.debTo set up a reverse Nginx proxy, follow the official installation guide or use the official Nginx Docker image. The configuration file is provided in ./nginx.conf. Please, note you'll have to generate keys and certificates specified in the configuration file.
Nginx is necessary even if you are not planning on exposing the service to the Internet, as the proxy is used to wrap the traffic in https. Some features, such as notifications, require the https protocol.
In case you are exposing the service to the Internet, consider installing a firewall.
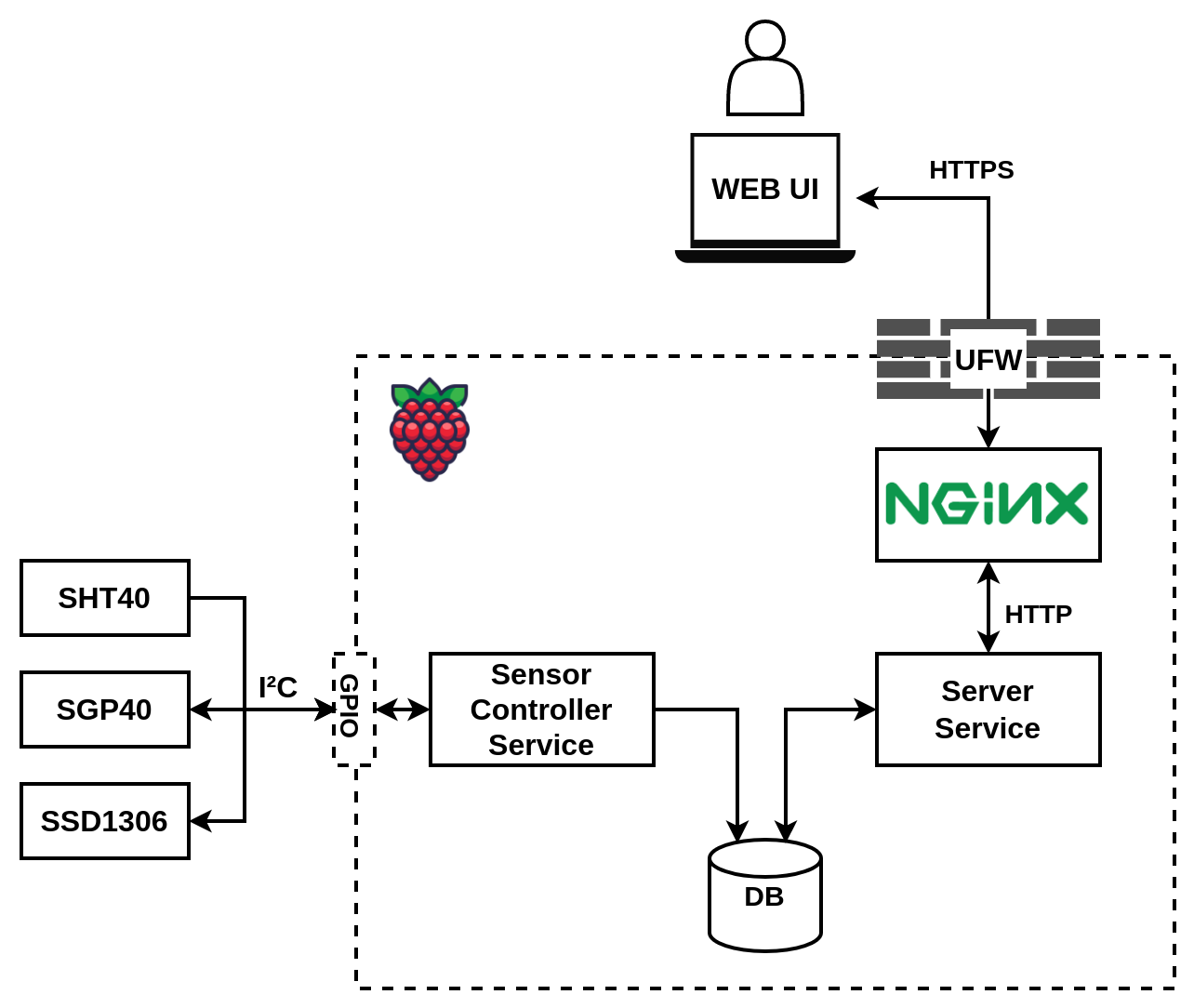
The application consists of 2 services:
- The sensor-controller service samples sensors in user-specified intervals and stores measurements in the database
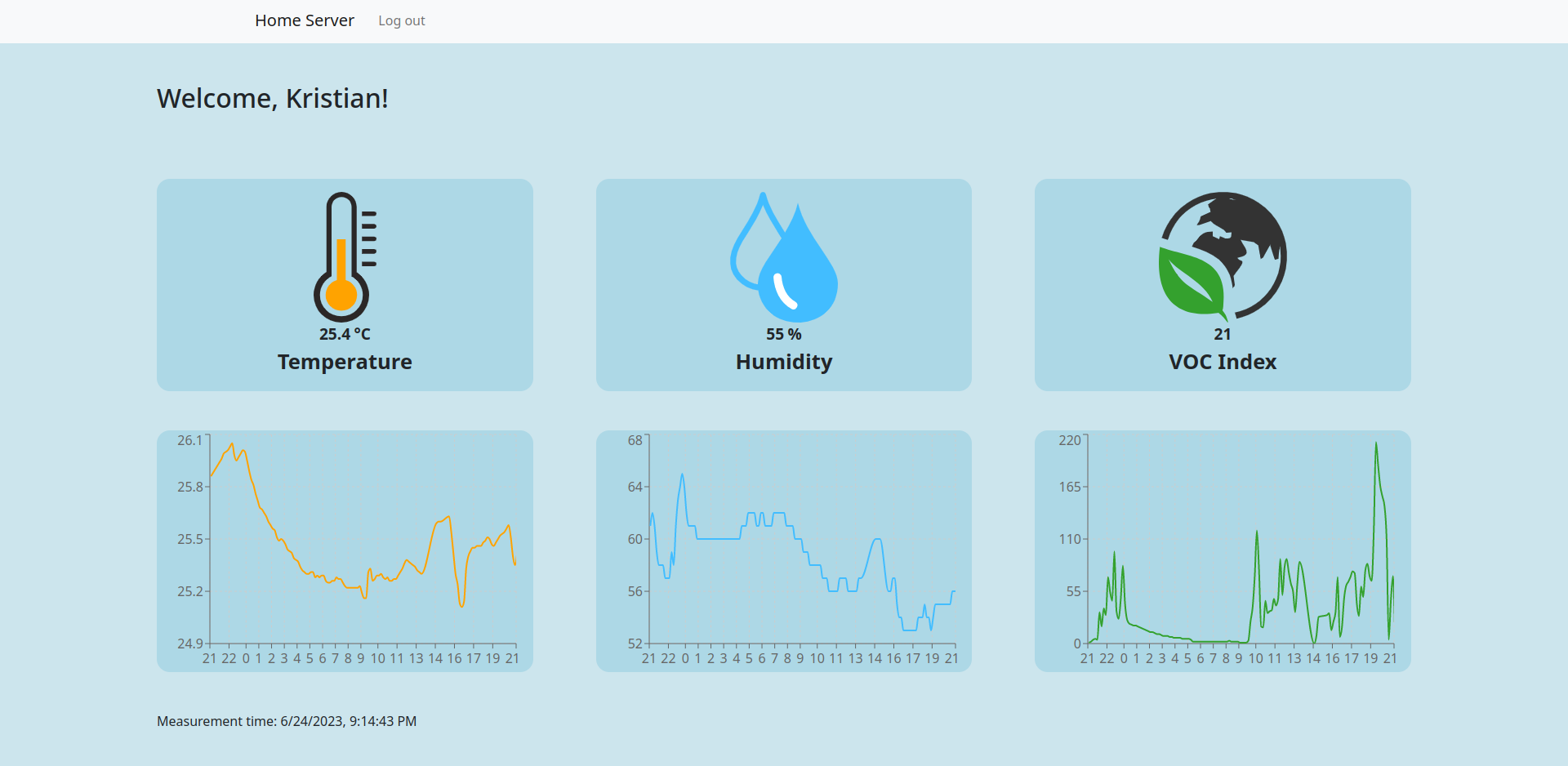
- The server service serves the UI page and exposes API that, after the user has authenticated, provides measurements from the DB.