=> not meant to be a guide but just an overview of Docker Tutorial for Beginners === https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=pTFZFxd4hOI <=
What is Docker? Virtual MAchines vs Containers Architecture of Docker Installing Docker Development Workflow
Is a platform for building, running and shipping app, so your application works the same wy in other computers.
this solves common issues
- one or more files missing in diff computers
- softWare version
- diff config
it works sending a package with all the needed fils (including soft version, configs, etc.)
we can remove the applications on our dev machines and it will be saved in docker (kind of a github)
// NutShell //
consistently build, rund, and ship applications across multiple devices
Container => an isolated environment for running applications VM => virtual Machines => An abstraction of a machine (physical HardWare)
VM use hypervisor like virtual box
VM benefits : run applicaiton isolations inside a VM, we can have 2 VM with 2 diff apps, using the same dependencies VM Problems => Each vm need a full-blown OS + Slow starts + resource intensive (since it takes hardware sources)
==== Containers ====
Benefits:
- allow running multiple apps in insolation
- are lightweight
- USe OS of the host
- start wuickly
- need less hadware resources
Client ====> Docker engine rest API
Containers are Process and use the Kernel of the host (kernel => OS)
we can run Win/linux containers in Windows only linux continers in linux and Linux vm in MAc
~ docker version ==> shows the version of docker
we manually download and install = > https://docs.docker.com/get-docker/
we needed to set up the window's subsystem to have Virtual MAchine platform as well as Windows Subsystem for linux -- https://acesse.dev/XWbRG <
GEt started information ==> https://docs.docker.com/guides/get-started/
Application => dockerize it (add DockerFile) => will contain everything that it needs to run => creates an image that we then sent to a container => start the container
instead of running the app locally (my-App) we do it trough docker (docker run ...)
DEV => Registry => test/prod we github client computer ==== simplification
instructions<
- Starts with an OS
- Install Node
- Copy app files
- Run node app.js
docker build -t Docker . > build the docker file thing (image) we wont see it
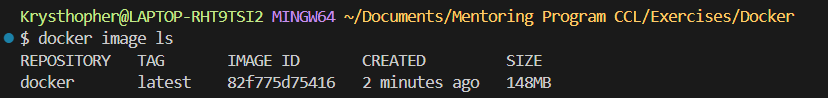
docker image ls => as in git basic commands ls is list items so here is the images
since the image contains alpine linux, node, it has a 148mb data
docker run [image name] => this will run the docker file, just like Node
VM machine online to play with docker > https://labs.play-with-docker.com/p/cp153pgl2o9000frn6sg
alt + enter => makes it bigger
docker pull krysthecoder/[name] > just like github this will pull the image
the docker file = is basically a doc with instructions like the typeScript config file
Docker is built on basic linux commands most tutorials are based on linux commands
Linux ==> Open sources Linux distributions => versions
- ubuntu
- debian
- alpine
- fedora
- Centos
==== we will use ubuntu on this notepad ====
we look for the offical image at => https://hub.docker.com/
instead of docker pull ubuntu => docker run ubuntu
docker ps -a => list the container/process
docker run -it ubuntu => it for interactable
basics commands
- echo hello
- whoami
- echo $0
- history
- apt
< apt uses the package intalled and we can work with it >
apt install => will look for what its inside apt update => wil update out package list apt list => list what we have available to install
Files are saved in a tree form
/bin-boot-dev-etc-hom-root-lib-var-proc
in linux everything is a file
[navigating-file-system]
lst = list cd = change directory / use relative - cd boot
[manipulate-file]
mv = rename files folders or change then => mv file1 renamed touch = create stuff rm = delete function rm -r = delete recursevely
nano file1.txt = will create a file
cat [file] = will show the content more [file] = will work like cat but its better for large files less [file] = will work even better as it allow us to got and and down head -n 5 [file] = will show the first few lines in this case 5
cat file1.txt > file2.txt == the > will redirect the content 1 to another file