tcrgrapher
R package for identifying condition associated T cell clonotypes
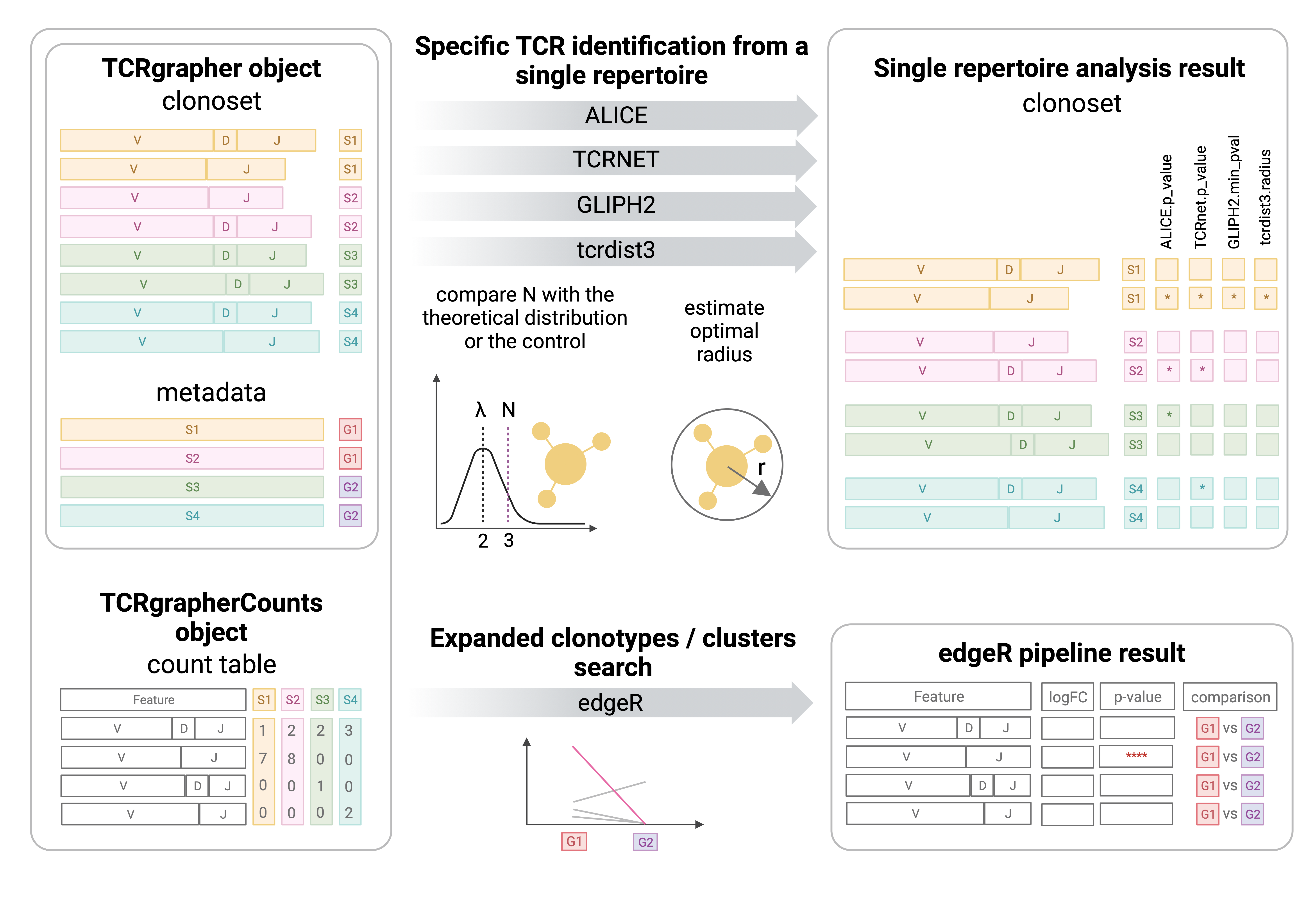
TCR repertoires and metadata, if it is presented, are stored in the S4 TCRgrapher object. A search for specific TCR identification can be performed by ALICE, TCRNET, GLIPH2 and tcrdist3. The output is the same object with additional columns in the repertoire. The edgeR pipeline uses the TCRgrapherCounts object as an input, which is an extension of the TCRgrapher object. The TCRgrapherCounts constructor creates a count table where each column corresponds to one sample and each row corresponds to a unique feature. The feature can be a unique amino acid sequence or a combination of amino acid sequences and V or V and J segments. It can also be a connectivity component of the graph where every node is a feature and edges connect neighbors. The output file provides all pairwise comparisons between groups and a comparison of every group with all others. The picture is created with BioRender.com.
Installation
install.packages('devtools')
library(devtools)
# to install the develop version
devtools::install_github("KseniaMIPT/tcrgrapher")Data loading
Data are stored in a TCRgrapher object. TCRgrapher is a S4 class that can be constructed by calling the TCRgrapher( ) function. TCRgrapher contains clonoset and metadata as data.tables.
There are three ways to initialize an object.
(1) Specify the path to the one file without metadata
If the path for only one file is specified, metadata will be produced automatically and will contain one row and two columns: "file" and "sample_id". Clonoset will have and additional column "sample_id" with one unique value and a column "clone_id" with an unique id for every row. Positions of "count", "cdr3nt", "cdr3aa", "V gene", "J gene" clonoset's columns must be specified.
# See ?TCRgrapher
TCRgrObject <- TCRgrapher(file_path, 1, 3, 4, 5, 7) # positions of clonoset's columns
# if you have MIXCR data, you need to delete scores from V and J columns
TCRgrObject <- TCRgrapher(file_path, 4, 16, 18, 8, 10)
clonoset(TCRgrObject)$bestVGene <- sapply(str_split(clonoset(TCRgrObject)$bestVGene, '\\*'), function(x) x[[1]])
clonoset(TCRgrObject)$bestJGene <- sapply(str_split(clonoset(TCRgrObject)$bestJGene, '\\*'), function(x) x[[1]])(2) Specify the path to the directory with files without metadata
If the path for the directory with files is specified and metadata is not specified, metadata will be produced automatically and will have a number of rows equal to the number of samples in the directory. All files will be merged into one data.table with additional columns "sample_id" and "clone_id" with unique ids for every row. Positions of "count", "cdr3nt", "cdr3aa", "V gene", "J gene" clonoset's columns must be specified.
TCRgrObject <- TCRgrapher(dir_path, 1, 3, 4, 5, 7)(3) Specify the path to the directory with files and metadata
If the path for the directory with files and the path to the metadata are specified, only files from the metadata column "file" will be taken into consideration. Clonosets will be merged into one data.table with additional columns "sample_id" and "clone_id" with unique ids for every row. Values in the "sample_id" column will be the same as in the "sample_id" metadata column. Positions of "count", "cdr3nt", "cdr3aa", "V gene", "J gene" clonoset's columns and "file", "sampl_id" metadata's columns must be specified.
TCRgrObject <- TCRgrapher(dir_path, 1, 3, 4, 5, 7, # positions of clonoset's columns
metadata_path, 1, 2) # positions of metadtata's columns# get metadata
metadata(TCRgrObject)
# get clonoset
clonoset(TCRgrObject)
# add column
clonoset(TCRgrObject)$col <- your_vector
# subsetting (correct subsetting is important for edgeR analysis)
subset(TCRgrObject, vector_with_sample_ids_to_keep)
# get edges if htey are present
edges(TCRgrObject)ALICE pipeline
To calculate generation probability, TCRgrapher can use OLGA or SONIA.
For detailed information about OLGA, please visit https://github.com/statbiophys/OLGA.
OLGA can be installed using pip or pip3.
pip install olgaFor detailed information about SONIA, please visit https://github.com/statbiophys/SONIA
SONIA is a Python 2.7/3.6 software. It is available on PyPI and can be downloaded and installed through pip:
pip install soniaALICE_pipeline The function takes a TCRgrapher object as an input and performs
neighborhood enrichment analysis using the ALICE algorithm. You can find default
parameters and possible options below.
TCRgrObject <- ALICE_pipeline(TCRgrObject, Q_val = 6.27, cores = 1, thres_counts = 1,
N_neighbors_thres = 1, p_adjust_method = "BH",
chain = 'mouseTRB', stats = 'OLGA', model= '-')- TCRgrObject - TCRgrapher object that contains a clonotype table
- Q - Selection factor. 1/Q sequences pass selection in a thymus. The default value for mice is 6.27. If a human model is taken and Q is not changed manually, Q = 27 is used
- cores - number of used cores, 1 by default
- thres_counts - Only sequences with a number of counts above this threshold are taken into account
- N_neighbors_thres - Only sequences with a number of neighbors above the threshold are used to calculate generation probability
- p_adjust_method - One of the methods from p.adjust in the stats package. Possible options: "bonferroni", "holm", "hochberg", "hommel", "BH" or "fdr", "BY", "none". "BH" is a default method.
- chain - statistical model selection. Possible options: "mouseTRB", "humanTRB" and "humanTRA".
- stats - a tool that will be used for generation probability calculation. Possible options: "OLGA", "SONIA". "SONIA" also calculates Q for every sequence.
- model - the standard OLGA generation probability model is used by default. To set your generation probability model, write "set_custom_model_VDJ <path_to_folder_with_model>". A generation probability model is usually IGOR output. A folder should contain the following files: V_gene_CDR3_anchors.csv, J_gene_CDR3_anchors.csv, model_marginals.txt, and model_params.txt. Some models can be found in the folder "model".
The function returns a TCRgrapher object with the same clonotype table as the input, filtered by the number of counts and the number of neighbors with additional columns. Additional columns include the following
- D - The number of clonoset neighbors. Neighbor is a similar sequence with one mismatch
- VJ_n_total - Number of unique sequences with the given VJ combination
- Pgen - Probability to be generated, computed by OLGA
- Pgen_sum_corr - The sum of Pgen of all sequences similar to the given with one mismatch
- Pgen_by_VJ - conditional probability. The sum of probabilities to be generated with the given VJ combination
- p_val - p value under the null hypothesis that the number of sequence's neighbors is not more than in the random model
- p_adjust - p value with multiple testing correction
Additional functions for ALICE analysis
pval_with_abundance(clonoset) The function takes the output of the ALICE_pipeline
function and adjusts the p-value, taking into account the abundance of every clonotype.
There are two additional columns in the output depending on count normalization:
"pval_with_abundance_log2_counts" - Log2 is used for count normalization;
"pval_with_abundance_counts" - no count normalization.
edgeR analysis
edgeR_pipeline The function performs statistical analysis by edgeR to
identify significantly expanded clonotypes. First, it filters the data using
relatively mild conditions that better suit TCR repertoire data. Second, it
normalizes counts and estimates dispersion by standard edgeR methods. Finally,
it performs all pairwise comparisons between groups and compares each group vs.
all others using the GLM and QL F-test.
To use the edgeR_pipeline function, you should create a TCRgrapherCounts object.
TCRgrapherCounts is a subclass of TCRgrapher with additional slots: count_table
and feature_info. Count data could be aggregated in the following ways. First,
clonotypes with the same amino acid sequences and V gene would be merged together
using the default parameters TCRgrapherCounts(TCRgrObject). Second,
clonotypes with the same amino acid sequences and VJ combination would be merged
together using the j_jene parameter TCRgrapherCounts(TCRgrObject, j_gene = TRUE).
Third, clonotypes with the same amino acid sequences regardless of VJ would be merged.
TCRgrapherCounts(TCRgrObject, v_gene = FALSE, j_gene = FALSE). Finally,
clonotypes from the same connectivity component found by the make_TCR_graph and
find_TCR_components functions would be grouped together by running
TCRgrapherCounts(TCRgrObject, cluster_id = TRUE)
Metadata must contain a column that specifies levels of comparison. The name of the column is the second parameter of the edgeR_pipeline function.
# EdgeR installation
if (!require("BiocManager", quietly = TRUE))
install.packages("BiocManager")
BiocManager::install("edgeR")
# documentation
?TCRgrapherCounts
library(edgeR)
# load the data
TCRgrObject <- TCRgrapher(dir_path, 1, 3, 4, 5, 7, metadata_path, 1, 2)
# create a count table with aggregation by V segments
TCRgrCounts <- TCRgrapherCounts(TCRgrObject) # v_gene = TRUE by default
# run EdgeR pipeline
edgeR_res <- edgeR_pipeline(TCRgrCounts, your_comparison)
# group by V segmentss and clusters
TCRgrCounts_cl <- TCRgrapherCounts(TCRgrObject, cluster_id == TRUE)
edgeR_res_cl <- edgeR_pipeline(TCRgrCounts_cl, your_comparison)
# see the composition of the clusters
feature_info(TCRgrCounts_cl)
# see count table
count_table(TCRgrCounts_cl)
# see edges
edges(TCRgrCounts_cl)
# find 'vs all' comparisons that are consistent with pairwise comparisons
edgeR_res_filtered <- filter_edgeR_res(edgeR_res)
edgeR_res_p_all_filter <- edgeR_res_p_all_filter[consistent == TRUE &
the_worst_pairwise_p < 0.5 &
FDR < 0.1 &]Wilcox pipeline for searching of expanded clonotypes
The pipeline is similar to the edgeR_piplene but uses wilcox test for group comparison. It is not sensitive for the outliers. For more details see ?wilcox_pipeline and ?filter_wilcox_res.
Typical actions:
library(stats)
# data loading in case of mixcr
TCRgrObject <- TCRgrapher(dir_path, 4, 16, 18, 8, 10, metadata_path, 1, 2)
clonoset(TCRgrObject)$bestVGene <- sapply(str_split(clonoset(TCRgrObject)$bestVGene, '\\*'), function(x) x[[1]])
clonoset(TCRgrObject)$bestJGene <- sapply(str_split(clonoset(TCRgrObject)$bestJGene, '\\*'), function(x) x[[1]])
# create a count table for clusters of clonotypes and aggregation by V segments
TCRgrCounts <- TCRgrapherCounts(TCRgrObject, cluster_id = TRUE) # v_gene = TRUE by default
# run wilcox_pipeline
wilcox_res <- wilcox_pipeline(TCRgrCounts, your_comparison)
# find 'vs all' comparisons that are consistent with pairwise comparisons
wilcox_res_filtered <- filter_wilcox_res(wilcox_res)
# filter by p_value
wilcox_res_filtered <- wilcox_res_filtered[p_value_greater < 0.1]
# create a heatmap using ComplexHeatmap library
if (!require("BiocManager", quietly = TRUE))
install.packages("BiocManager")
BiocManager::install("ComplexHeatmap")
library(ComplexHeatmap)
ph <- heatmap_expanded(TCRgrCounts, wilcox_res_filtered)
phTCRNET pipeline
TCRgrObject <- run_TCRNET(TCRgrObject, background_path, command = 'vdjtools')
# documentation
?run_TCRNETTCRdist3 pipeline
library(reticulate)
TCRgrObject <- calc_TCRdist3_radius(TCRgrObject)
# documentation
?calc_TCRdist3_radiusAdditional functions
make_TCR_graph(clonoset, v_gene = TRUE, j_gene = FALSE)
The function makes a graph from a clonoset table with the igraph package. Every
node of the graph is a unique clonotype from the table (one line). Edges connect
clonotypes with one amino acid mismatch or identical clonotypes if they were in
separate lines. If 'v_gene' and 'j_gene' are TRUE, edges connect only clonotypes
with the same V gene or VJ combination.
For more information ?make_TCR_graph
find_TCR_components(clonoset, graph) The function takes a clonoset table
and make_TCR_graph output and returns the same clonoset table with an additional
column "cluster_id". All clusters of neighbors with one mismatch have a unique id.
For more information ?find_TCR_components
find_TCR_components_by_bfs(TCRgrObject) The function searches for connectivity
components of the graph, where every node is a clonotype with a unique clone_id
and edges connect clonotypes that differ by one amino acid mismatch. It returns
the same TCRgrapher object with list of edges and with additional column cluster_id
in the clonoset table. The fastest way to find TCR components. For more information
?find_TCR_components_by_bfs
bfs_for_TCRs The function searches for all neighbors of the source (src)
clonotype. A neighbor is a clonotype that differs by one amino acid mismatch.
For more information ?bfs_for_TCRs
make_gen_model The function uses the IGoR software to infer a new generation
model. IGoR should be installed. The recommended version is v1.3.0. The function
takes the path to the file with non-functional nucleotide CDR3 sequences and writes
a generation model based on these sequences to the working directory. For more
information ?make_gen_model. To use more features, one can use IGoR directly.
See the documentation at https://qmarcou.github.io/IGoR/#version.
References
- Pogorelyy, M. V. et al. Detecting T cell receptors involved in immune responses from single repertoire snapshots. PLoS Biol. 17, e3000314 (2019).
- Sethna, Z., Elhanati, Y., Callan, C. G., Walczak, A. M. & Mora, T. OLGA: fast computation of generation probabilities of B- and T-cell receptor amino acid sequences and motifs. Bioinformatics 35, 2974–2981 (2019).
- Isacchini G, Walczak AM, Mora T, Nourmohammad A. Deep generative selection models of T and B cell receptor repertoires with soNNia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021 Apr 6;118(14):e2023141118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2023141118. PMID: 33795515; PMCID: PMC8040596.
- Elhanati Y, Sethna Z, Callan CG Jr, Mora T, Walczak AM. Predicting the spectrum of TCR repertoire sharing with a data-driven model of recombination. Immunol Rev. 2018 Jul;284(1):167-179. doi: 10.1111/imr.12665. PMID: 29944757; PMCID: PMC6033145.
- Pogorelyy, M. V. & Shugay, M. A Framework for Annotation of Antigen Specificities in High-Throughput T-Cell Repertoire Sequencing Studies. Front. Immunol. 10, 2159 (2019).
- Mayer-Blackwell, K. et al. TCR meta-clonotypes for biomarker discovery with tcrdist3: identification of public, HLA-restricted SARS-CoV-2 associated TCR features. bioRxiv (2021) doi:10.1101/2020.12.24.424260.
- Huang, H., Wang, C., Rubelt, F., Scriba, T. J. & Davis, M. M. Analyzing the Mycobacterium tuberculosis immune response by T-cell receptor clustering with GLIPH2 and genome-wide antigen screening. Nat. Biotechnol. 38, 1194–1202 (2020).