Learning Diverse and Discriminative Representations via the Principle of Maximal Coding Rate Reduction
This repository is the official implementation of
ReduNet: A White-box Deep Network from the Principle of Maximizing Rate Reduction (2021)
by Kwan Ho Ryan Chan* (UC Berkeley), Yaodong Yu* (UC Berkeley), Chong You* (UC Berkeley), Haozhi Qi (UC Berkeley), John Wright (Columbia), and Yi Ma (UC Berkeley), and
by Yaodong Yu* (UC Berkeley), Kwan Ho Ryan Chan* (UC Berkeley), Chong You (UC Berkeley), Chaobing Song (UC Berkeley) and Yi Ma (UC Berkeley).
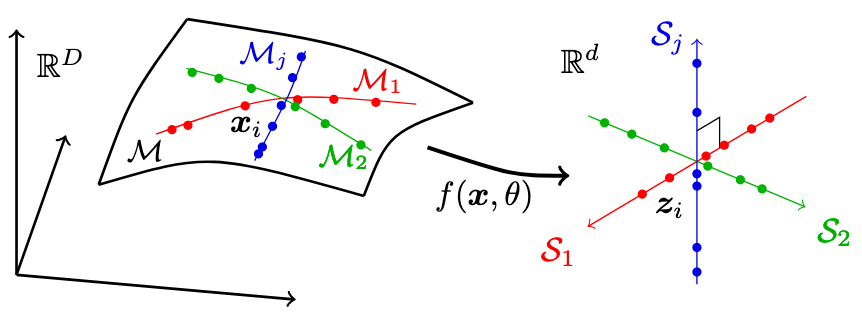
Our goal is to learn a mapping that maps the high-dimensional data that lies in a low-dimensional manifold to low-dimensional subspaces with the following three properties:
- Between-Class Discriminative: Features of samples from different classes/clusters should be highly uncorrelatedand belong to different low-dimensional linear subspaces
- Within-Class Compressible: Features of samples from the same class/cluster should be relatively correlated in a sense that they belong to a low-dimensional linear subspace
- Maximally Diverse Representation: Dimension (or variance) of features for each class/cluster should beas large as possibleas long as they stay uncorrelated from the other classes
To achieve this, we propose an objective function called Maximal Coding Rate Reduction (MCR2). In our paper, we provide not only theoretical guarantees to the desired properties upon convergence, but also practical properties such as robustness to label corruption and empirical results such as state-of-the-art unsupervised clustering performance. For more details on algorithm design, please refer to our paper.
- This codebase is written for
python3. - To install necessary python packages, run
pip install -r requirements.txt.
- All functions used in training can be found in
train_func.py, which includes:load_checkpoint(...),load_trainset(...), etc. For implementation details please refer to docstring. - Code for training are in the following files:
train_sup.pyandtrain_selfsup.py. Each has its own command options. - Augmentations is used in unsupervised and contrastive setting. Check
augmentloader.pyfor implementation details.
usage: train_sup.py [-h] [--arch ARCH] [--fd FD] [--data DATA] [--epo EPO]
[--bs BS] [--lr LR] [--mom MOM] [--wd WD] [--gam1 GAM1]
[--gam2 GAM2] [--eps EPS] [--lcr LCR] [--lcs LCS]
[--tail TAIL] [--transform TRANSFORM]
[--save_dir SAVE_DIR] [--data_dir DATA_DIR]
[--pretrain_dir PRETRAIN_DIR]
[--pretrain_epo PRETRAIN_EPO]
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
--arch ARCH architecture for deep neural network (default: resnet18)
--fd FD dimension of feature dimension (default: 128)
--data DATA dataset for training (default: CIFAR10)
--epo EPO number of epochs for training (default: 500)
--bs BS input batch size for training (default: 1000)
--lr LR learning rate (default: 0.0001)
--mom MOM momentum (default: 0.9)
--wd WD weight decay (default: 5e-4)
--gam1 GAM1 gamma1 for tuning empirical loss (default: 1.)
--gam2 GAM2 gamma2 for tuning empirical loss (default: 1.)
--eps EPS eps squared (default: 0.5)
--lcr LCR label corruption ratio (default: 0)
--lcs LCS label corruption seed for index randomization (default: 10)
--tail TAIL extra information to add to folder name
--transform TRANSFORM transform applied to trainset (default: default
--save_dir SAVE_DIR base directory for saving PyTorch model. (default: ./saved_models/)
--data_dir DATA_DIR base directory for saving PyTorch model. (default: ./data/)
--pretrain_dir PRETRAIN_DIR load pretrained checkpoint for assigning labels
--pretrain_epo PRETRAIN_EPO load pretrained epoch for assigning labels
Examples at a later section.
usage: train_selfsup.py [-h] [--arch ARCH] [--fd FD] [--data DATA] [--epo EPO]
[--bs BS] [--aug AUG] [--lr LR] [--mom MOM] [--wd WD]
[--gam1 GAM1] [--gam2 GAM2] [--eps EPS] [--tail TAIL]
[--transform TRANSFORM] [--sampler SAMPLER]
[--pretrain_dir PRETRAIN_DIR]
[--pretrain_epo PRETRAIN_EPO] [--save_dir SAVE_DIR]
[--data_dir DATA_DIR]
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
--arch ARCH architecture for deep neural network (default: resnet18)
--fd FD dimension of feature dimension (default: 32)
--data DATA dataset for training (default: CIFAR10)
--epo EPO number of epochs for training (default: 50)
--bs BS input batch size for training (default: 1000)
--aug AUG number of augmentations per mini-batch (default: 49)
--lr LR learning rate (default: 0.001)
--mom MOM momentum (default: 0.9)
--wd WD weight decay (default: 5e-4)
--gam1 GAM1 gamma1 for tuning empirical loss (default: 1.0)
--gam2 GAM2 gamma2 for tuning empirical loss (default: 10)
--eps EPS eps squared (default: 2)
--tail TAIL extra information to add to folder name
--transform TRANSFORM transform applied to trainset (default: default
--sampler SAMPLER sampler used in augmentloader (default: random
--pretrain_dir PRETRAIN_DIR load pretrained checkpoint for assigning labels
--pretrain_epo PRETRAIN_EPO load pretrained epoch for assigning labels
--save_dir SAVE_DIR base directory for saving PyTorch model. (default: ./saved_models/)
--data_dir DATA_DIR base directory for saving PyTorch model. (default: ./data/)
Examples at a later section.
Testing methods available are: svm, knn, nearsub, kmeans, ensc. Each method also has options for testing hyperparameters, such as --k for top k components in kNN. Methods can also be chained. Checkpoint can also be specified using --epoch option. Please refer to evaluate.py and cluster.py and for more implementation details.
- Command Options
usage: evaluate.py [-h] [--model_dir MODEL_DIR] [--svm] [--knn] [--nearsub]
[--kmeans] [--ensc] [--epoch EPOCH] [--k K] [--n N]
[--gam GAM] [--tau TAU] [--n_comp N_COMP] [--save]
[--data_dir DATA_DIR]
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
--model_dir MODEL_DIR base directory for saving PyTorch model.
--svm evaluate using SVM
--knn evaluate using kNN measuring cosine similarity
--nearsub evaluate using Nearest Subspace
--kmeans evaluate using KMeans
--ensc evaluate using Elastic Net Subspace Clustering
--epoch EPOCH which epoch for evaluation
--k K top k components for kNN
--n N number of clusters for cluster (default: 10)
--gam GAM gamma paramter for subspace clustering (default: 100)
--tau TAU tau paramter for subspace clustering (default: 1.0)
--n_comp N_COMP number of components for PCA (default: 30)
--save save labels
--data_dir DATA_DIR path to dataset
- An example for evaluation:
$ python3 evaluate.py --knn --nearsub --k 10 --model_dir saved_models/sup_resnet18+128_cifar10_epo500_bs1000_lr0.001_mom0.9_wd0.0005_gam11.0_gam210.0_eps0.5_lcr0
, which runs kNN with top 10 components and nearest subspace on the latest checkpoint in model_dir.
- (Extracting Features as .zip) To extract the features, use
extract.py. - (Plotting figures) Plot functions are located in
plot.py. Plots will be saved in(model_dir)/figures/ - (Reproduce Results in Paper)
$ python3 train_sup.py --arch resnet18 --data cifar10 --fd 128 --epo 500 --bs 1000 --eps 0.5 --gam1 1 --gam2 1 --lr 0.01 --lcr 0.0
$ python3 train_sup.py --arch resnet18 --data cifar10 --fd 128 --epo 500 --bs 1000 --eps 0.5 --gam1 1 --gam2 1 --lr 0.01 --lcr 0.1
$ python3 train_sup.py --arch resnet18 --data cifar10 --fd 128 --epo 500 --bs 1000 --eps 0.5 --gam1 1 --gam2 1 --lr 0.01 --lcr 0.2
$ python3 train_sup.py --arch resnet18 --data cifar10 --fd 128 --epo 500 --bs 1000 --eps 0.5 --gam1 1 --gam2 1 --lr 0.01 --lcr 0.3
$ python3 train_sup.py --arch resnet18 --data cifar10 --fd 128 --epo 500 --bs 1000 --eps 0.5 --gam1 1 --gam2 1 --lr 0.01 --lcr 0.4
$ python3 train_sup.py --arch resnet18 --data cifar10 --fd 128 --epo 500 --bs 1000 --eps 0.5 --gam1 1 --gam2 1 --lr 0.01 --lcr 0.5
$ python3 train_selfsup.py --arch resnet18ctrl --data cifar10 --fd 128 --epo 100 --bs 1000 --eps 0.5 --gam1 20 --gam2 0.05 --lr 0.1 --aug 50 --transform cifar
$ python3 train_selfsup.py --arch resnet18ctrl --data cifar100 --fd 128 --epo 100 --bs 1000 --eps 0.5 --gam1 20 --gam2 0.05 --lr 0.1 --aug 50 --transform cifar
$ python3 train_selfsup.py --arch resnet18stl --data stl10 --fd 128 --epo 100 --bs 1000 --eps 0.5 --gam1 20 --gam2 0.05 --lr 0.1 --aug 50 --transform stl10
For technical details and full experimental results, please check the paper. If you have used our work in your own, please consider citing:
@article{yu2020learning,
title={Learning diverse and discriminative representations via the principle of maximal coding rate reduction},
author={Yu, Yaodong and Chan, Kwan Ho Ryan and You, Chong and Song, Chaobing and Ma, Yi},
journal={Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems},
volume={33},
year={2020}
}
- This README is formatted based on paperswithcode.
- Feel free to post issues via Github.
Please contact ryanchankh@berkeley.edu and yyu@eecs.berkeley.edu if you have any question on the codes.