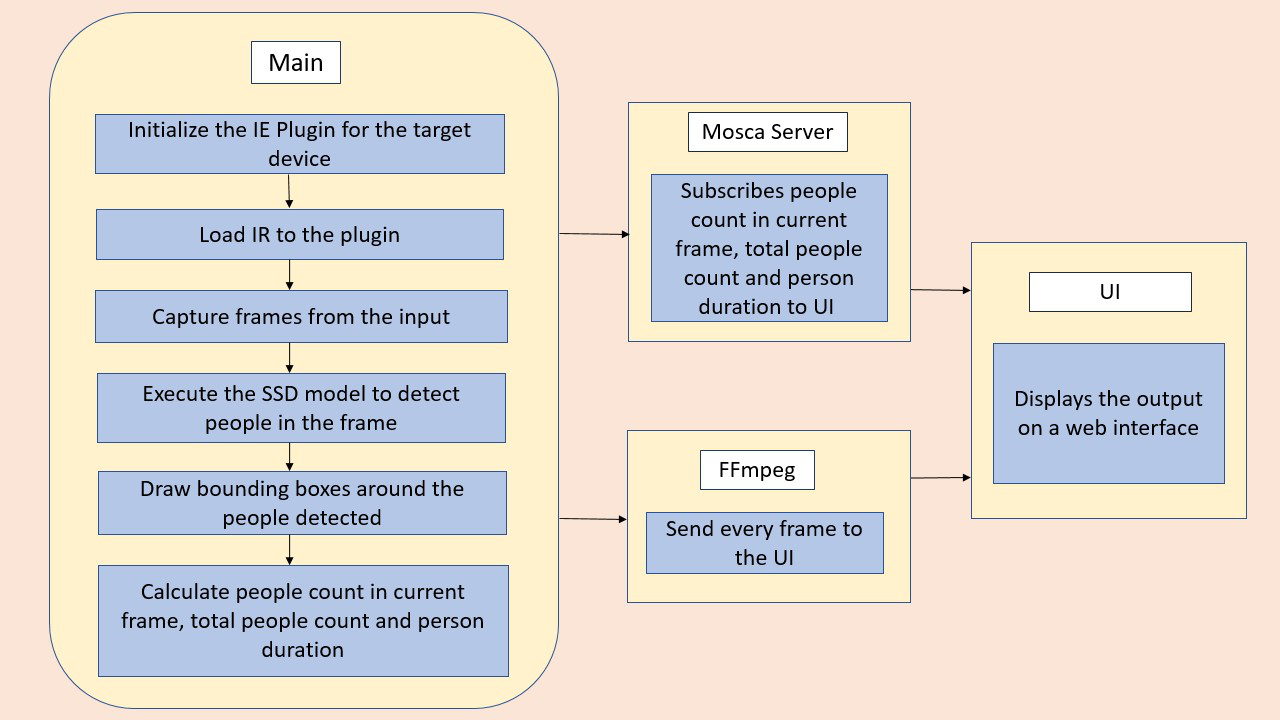
This project servers as a proof of concept for developing smart IoT solution using IntelOpen VINO software tools and Intel Hardware. The Objective of the app is to detect people in a designated area, provide the number of people in the frame, average duration of the people in the frame and total count. The app should count the number of people in the current frame, the duration that a person is in the frame (time elapsed between entering and exiting a frame) and the total count of people. It then sends the data to a local web server using the Paho MQTT Python package.
A link to the demo of the application is
- 6th to 10th generation Intel® Core™ processor with Iris® Pro graphics or Intel® HD Graphics.
- OR use of Intel® Neural Compute Stick 2 (NCS2)
- OR Udacity classroom workspace for the related course
- Intel® Distribution of OpenVINO™ toolkit 2019 R3 release
- Node v6.17.1
- Npm v3.10.10
- CMake
- MQTT Mosca server
Utilize the classroom workspace, or refer to the relevant instructions for your operating system for this step.
Utilize the classroom workspace, or refer to the relevant instructions for your operating system for this step.
There are three components that need to be running in separate terminals for this application to work:
- MQTT Mosca server
- Node.js* Web server
- FFmpeg server
From the main directory:
-
For MQTT/Mosca server:
cd webservice/server npm install -
For Web server:
cd ../ui npm installNote: If any configuration errors occur in mosca server or Web server while using npm install, use the below commands:
sudo npm install npm -g rm -rf node_modules npm cache clean npm config set registry "http://registry.npmjs.org" npm install
For this project faster_rcnn_inception_v2_coco model is used from the tensorflow model detection zoo.
Downloading the model from the GitHub repository of Tensorflow Object Detection Model Zoo by the following command:
wget http://download.tensorflow.org/models/object_detection/faster_rcnn_inception_v2_coco_2018_01_28.tar.gz
Extracting the tar.gz file by the following command:
tar -xvf faster_rcnn_inception_v2_coco_2018_01_28.tar.gz
Changing the directory to the extracted folder of the downloaded model: cd faster_rcnn_inception_v2_coco_2018_01_28 The model can’t be the existing models provided by Intel as a part of the Udacity acceptance criteria of the Nanodegree project. So, converting the TensorFlow model to Intermediate Representation (IR) or OpenVINO IR format. The command used is given below:
python /opt/intel/openvino/deployment_tools/model_optimizer/mo.py --input_model model/faster_rcnn_inception_v2_coco_2018_01_28/frozen_inference_graph.pb --tensorflow_object_detection_api_pipeline_config pipeline.config --reverse_input_channels --tensorflow_use_custom_operations_config /opt/intel/openvino/deployment_tools/model_optimizer/extensions/front/tf/faster_rcnn_support.json
From the main directory:
cd webservice/server/node-server
node ./server.js
You should see the following message, if successful:
Mosca server started.
Open new terminal and run below commands.
cd webservice/ui
npm run dev
You should see the following message in the terminal.
webpack: Compiled successfully
Open new terminal and run the below commands.
sudo ffserver -f ./ffmpeg/server.conf
Open a new terminal to run the code.
You must configure the environment to use the Intel® Distribution of OpenVINO™ toolkit one time per session by running the following command:
source /opt/intel/openvino/bin/setupvars.sh -pyver 3.5
You should also be able to run the application with Python 3.6, although newer versions of Python will not work with the app.
When running Intel® Distribution of OpenVINO™ toolkit Python applications on the CPU, the CPU extension library is required. This can be found at:
/opt/intel/openvino/deployment_tools/inference_engine/lib/intel64/
Depending on whether you are using Linux or Mac, the filename will be either libcpu_extension_sse4.so or libcpu_extension.dylib, respectively. (The Linux filename may be different if you are using a AVX architecture)
Though by default application runs on CPU, this can also be explicitly specified by -d CPU command-line argument:
python main.py -i resources/Pedestrian_Detect_2_1_1.mp4 -m your-model.xml -l /opt/intel/openvino/deployment_tools/inference_engine/lib/intel64/libcpu_extension_sse4.so -d CPU -pt 0.6 | ffmpeg -v warning -f rawvideo -pixel_format bgr24 -video_size 768x432 -framerate 24 -i - http://0.0.0.0:3004/fac.ffm
If you are in the classroom workspace, use the “Open App” button to view the output. If working locally, to see the output on a web based interface, open the link http://0.0.0.0:3004 in a browser.
This project is implemented using faster_rcnn_inception_v2_coco_2018_01_28 which gives output in terms of bounding boxes on personal identification.
The custom layer is contained within Intel Open VINO toolkit, in the tensorfloe section namely "faster_rcnn_support.json"
Tensorflow Object detection model zoo provide a collection of detection models pre-trained on the COCO dataset, the Kitti dataset, the Open Images dataset, the AVA v2.1 dataset and the iNaturalist Species Detection Dataset.
For this project I have tested ssd_inception_v2_coco_2018_01_28, faster_rcnn_inception_v2_coco_2018_01_28, ssd_mobilenet_v2_coco_2018_03_29 models from the tenforflow modelzoo. Finally, found that faster faster_rcnn_inception_v2 seems to give results of person identification.
Some of the potential use cases of the people counter app are:
-
The application could be used to detect number of people in an area and therefore could potentially applied to scene where there is a retriction on the number of people in a particular area - In this time of COVID-19, this application can be used where there is restriction every applied in public places
-
The second application could be to monitor intruders in restricted areas and danger zones
-
Since the application can be installed in devices with small form factor, this could be intalled in 4 wheel vehicles and Aeroplanes. This could then give information for security in case of theft or hijack.
Lighting, model accuracy, and camera focal length/image size have different effects on a deployed edge model. The potential effects of each of these are as follows...
[This heading is only required if a suitable model was not found after trying out at least three different models. However, you may also use this heading to detail how you converted a successful model.]
In investigating potential people counter models, I tried each of the following three models:
- Model 1: [ssd_inception_v2_coco_2018_01_28]
- Model Source
- converted the model to an Intermediate Representation with the following arguments
python /opt/intel/openvino/deployment_tools/model_optimizer/mo.py --input_model model/ssd_inception_v2_coco_2018_01_28/frozen_inference_graph.pb --tensorflow_object_detection_api_pipeline_config model/ssd_inception_v2_coco_2018_01_28/pipeline.config --reverse_input_channels --tensorflow_use_custom_operations_config /opt/intel/openvino/deployment_tools/model_optimizer/extensions/front/tf/ssd_v2_support.json
-
The model was insufficient for the app because it didn't give the sufficient results of detecting people in the frame.
-
I tried to improve the model for the app by changing the threshold of detection in the range 0.3 to 0.6, still the reults were not proper.
-
Model 2: [ssd_mobilenet_v2]
- Model Source
- I converted the model to an Intermediate Representation with the following arguments
python /opt/intel/openvino/deployment_tools/model_optimizer/mo_tf.py --input_model model/ssd_mobilenet_v2_coco_2018_03_29/frozen_inference_graph.pb --tensorflow_object_detection_api_pipeline_config model/ssd_mobilenet_v2_coco_2018_03_29/pipeline.config --tensorflow_use_custom_operations_config /opt/intel/openvino/deployment_tools/model_optimizer/extensions/front/tf/ssd_v2_support.json --reverse_input_channel
The model is run using the following command without connecting to the MQTT server as client :
python main.py -i resources/Pedestrian_Detect_2_1_1.mp4 -m model/ssd_mobilenet_v2_coco_2018_03_29/frozen_inference_graph.xml -l /opt/intel/openvino/deployment_tools/inference_engine/lib/intel64/libcpu_extension_sse4.so -d CPU -pt 0.6
-
The model was sufficient as it gives sufficient reults when run in command line without integrating to the app, however the model seems to fail on integration with the application.
-
Model 3: [faster_rcnn_inception_v2_coco_2018_01_28]
- Model Source
- I converted the model to an Intermediate Representation with the following arguments
python /opt/intel/openvino/deployment_tools/model_optimizer/mo_tf.py --input_model model/faster_rcnn_inception_v2_coco_2018_01_28/frozen_inference_graph.pb --tensorflow_object_detection_api_pipeline_config model/faster_rcnn_inception_v2_coco_2018_01_28/pipeline.config --tensorflow_use_custom_operations_config /opt/intel/openvino/deployment_tools/model_optimizer/extensions/front/tf/ssd_v2_support.json --reverse_input_channel
- The model ran successfully on the command line without connecting to the MQTT server and also after integration with the app
- The model was run with the following command
python main.py -i resources/Pedestrian_Detect_2_1_1.mp4 -m model/faster_rcnn_inception_v2_coco_2018_01_28/frozen_inference_graph.xml -l /opt/intel/openvino/deployment_tools/inference_engine/lib/intel64/libcpu_extension_sse4.so -d CPU -pt 0.6
| Model | Latency ( µs) | Memory (mb) |
|---|---|---|
| Faster_rcnn_inception_v2_coco (TF) | 1281 | 562 |
| Faster_rcnn_inception_v2_coco (OpenVINO) | 889 | 282 |