Class Name ID 四資管四 王浚科 B10709028 Date : 2021-10-30
實做 Source Code
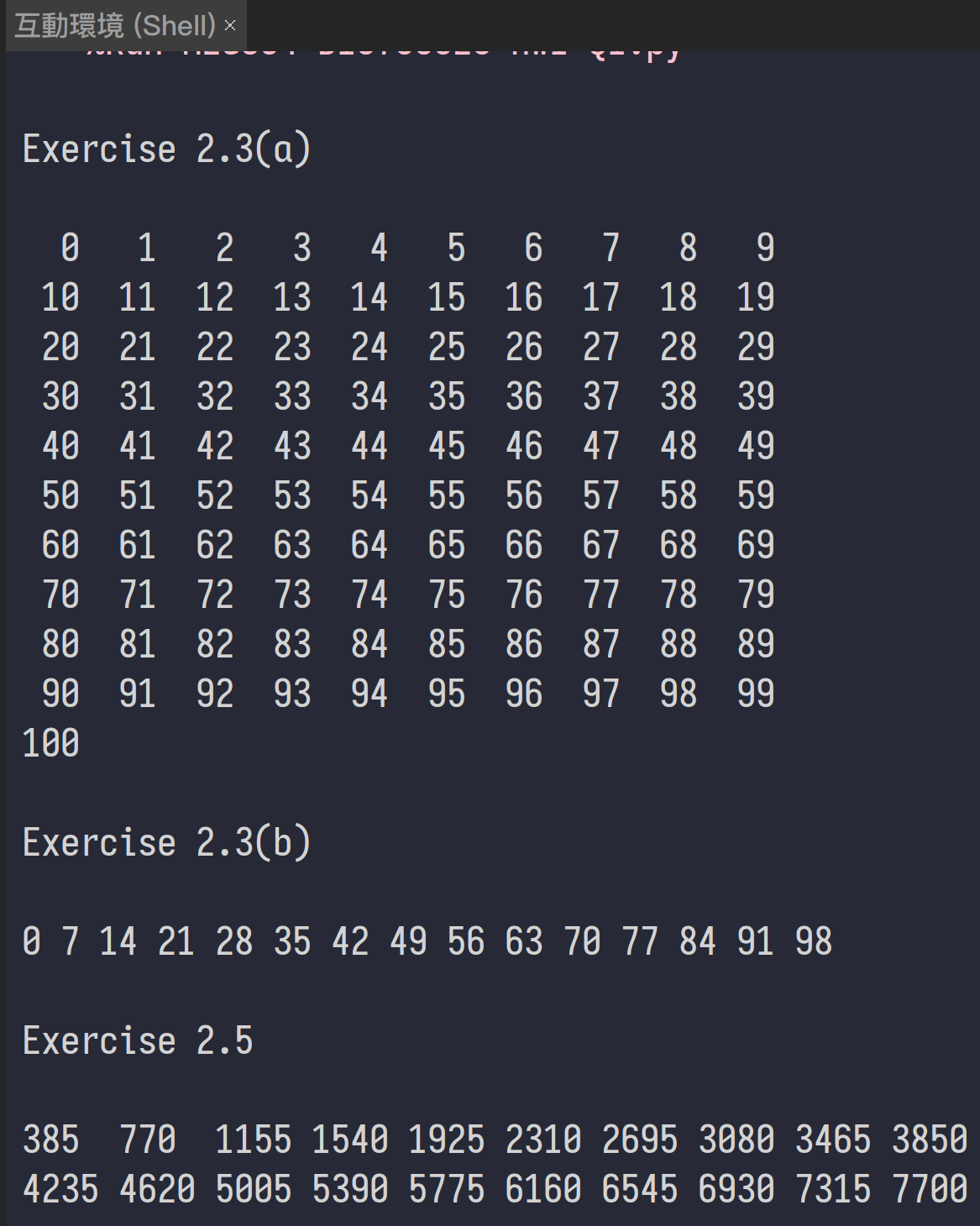
def Exercise23a():
i: int = 0
while (i <= 100):
# Pretty Print
if (((i+1) % 10) == 0):
print(f"{i:>3}")
else:
print(f"{i:>3}", end=" ")
i = i + 1
def Exercise23b():
i: int = 0
while (i <= 100):
# Pretty Print
if ((i % 7) == 0):
print(i, end=" ")
i = i + 1
def Exercise25():
numberFound: int = 0
x: int = 11
while (numberFound < 20):
if (((x % 5) == 0) and ((x % 7) == 0) and ((x % 11) == 0)):
# Pretty Print
if (((numberFound + 1) % 10) == 0):
print(f"{x:<4}")
else:
print(f"{x:<4}", end=" ")
numberFound = numberFound + 1
x = x + 1
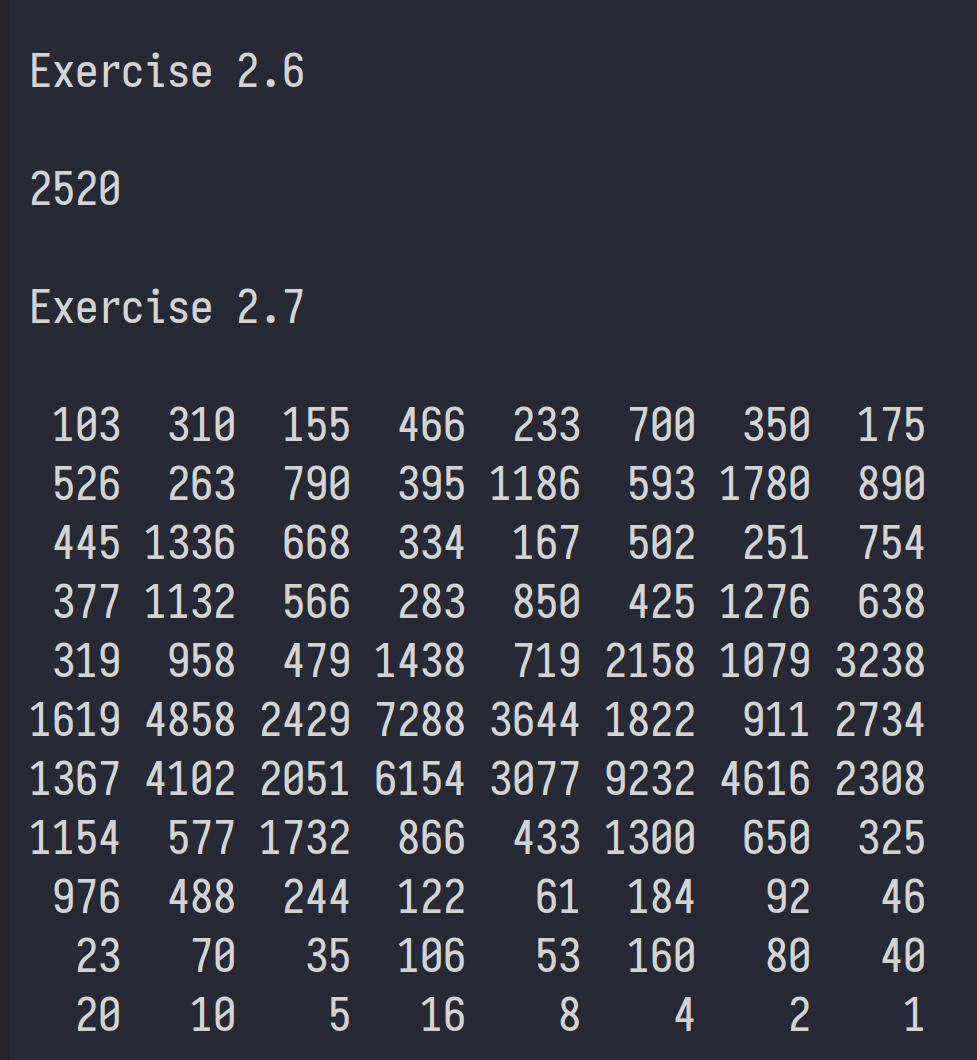
def Exercise26():
numberFound: int = 0
i: int = 10
while (numberFound < 1):
if (((i % 7) == 0) and ((i % 8) == 0)
and ((i % 9) == 0) and ((i % 10) == 0)):
print(i)
numberFound = numberFound + 1
i = i + 1
def Exercise27():
numberFound: int = 0
i: int = 103
print(f"{i:>4}", end=" ")
while (i != 1):
numberFound = numberFound + 1
if ((i % 2) == 0):
i = i // 2
elif ((i % 2) == 1):
i = 3 * i + 1
# Pretty Print
if (((numberFound + 1) % 8) == 0):
print(f"{i:>4}")
else:
print(f"{i:>4}", end=" ")
# More Code in "Source Code" Link file.除了 Print statement 改為 function 之外,也用了 f-string Source Code
def SieveOfEratosthenes(n):
prime = [True for i in range(n + 1)]
p = 2
while (p * p <= n):
if (prime[p] == True):
for i in range(p * 2, n + 1, p):
prime[i] = False
p += 1
prime[0] = False
prime[1] = False
for p in range(n + 1):
if prime[p]:
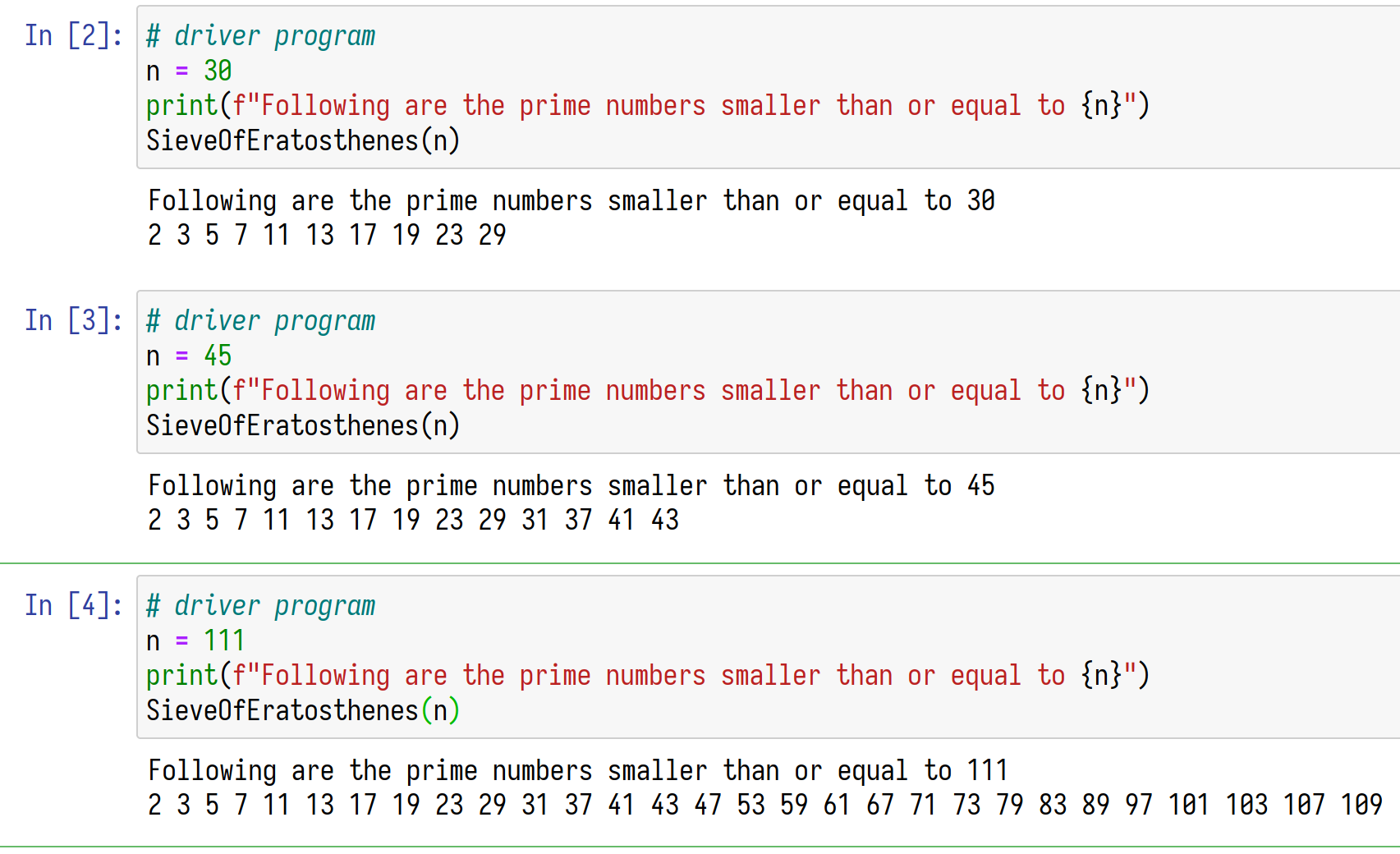
print(p, end=" ")# driver program
n = 30
print(f"Following are the prime numbers smaller than or equal to {n}")
SieveOfEratosthenes(n)# driver program
n = 45
print(f"Following are the prime numbers smaller than or equal to {n}")
SieveOfEratosthenes(n)# driver program
n = 111
print(f"Following are the prime numbers smaller than or equal to {n}")
SieveOfEratosthenes(n)使用型別註釋,統一使用 float,只允許0至100之間的數字進入 List,使用 f-string 輸出有限小數點 Source Code
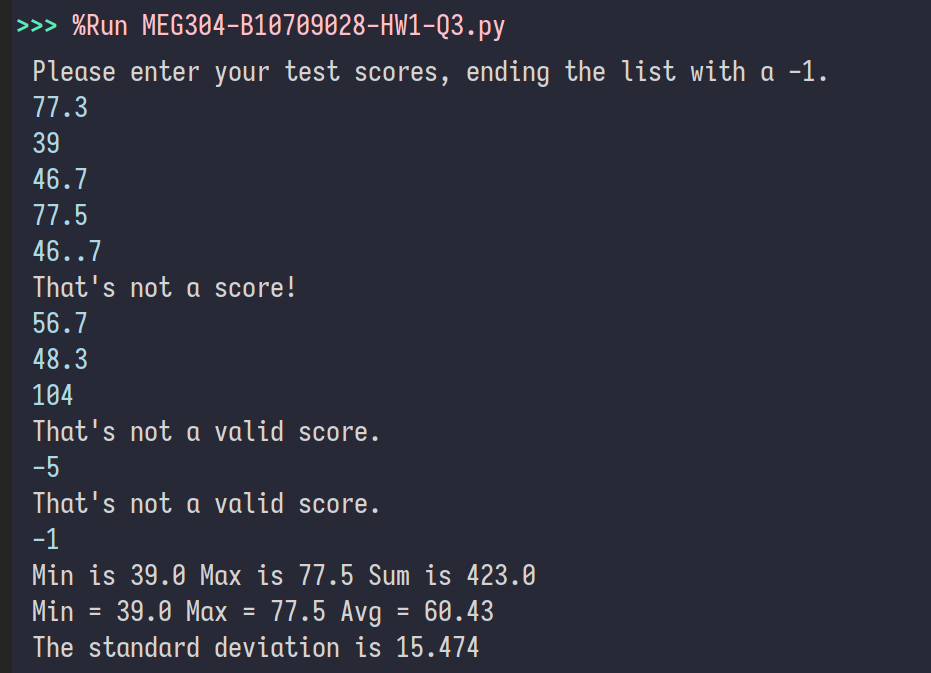
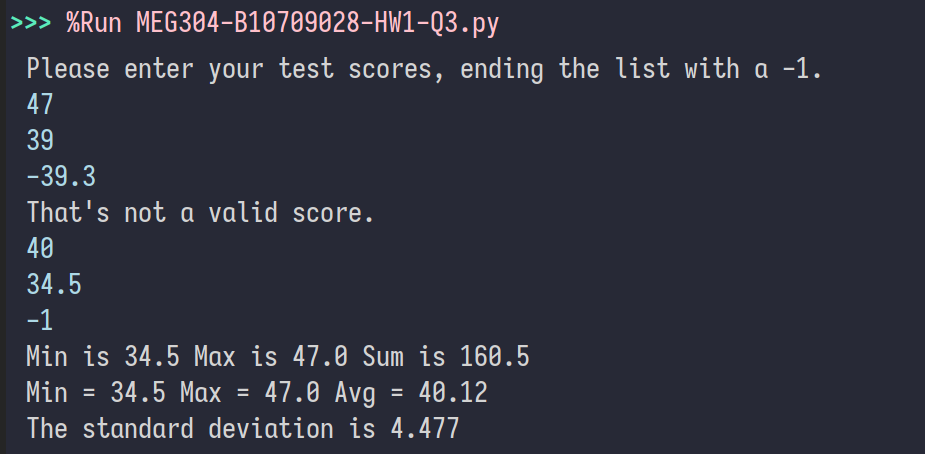
import math
from typing import List
scores: List[float] = []
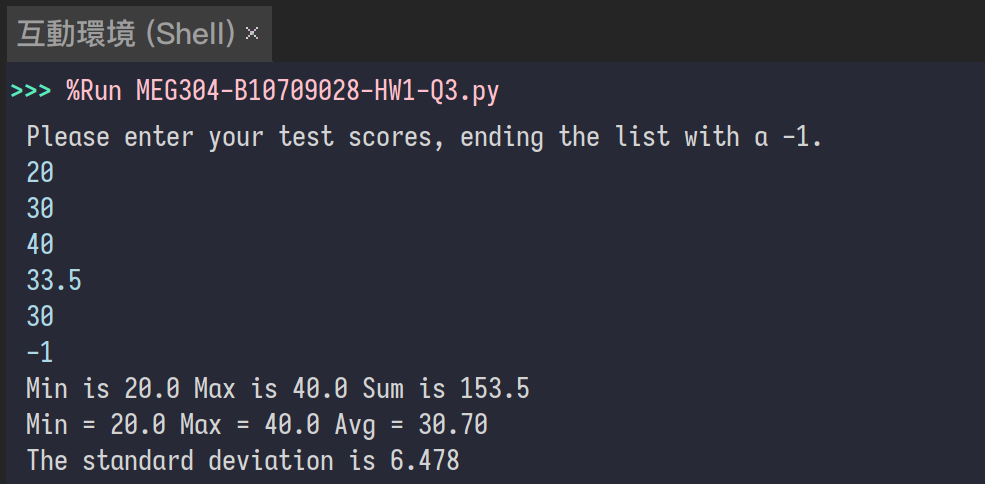
print("Please enter your test scores, ending the list with a -1.")
try:
curscore: float = float(input(""))
except ValueError:
print("That's not a score!")
while curscore != -1:
if (0 <= curscore <= 100):
scores.append(curscore)
else:
print("That's not a valid score.")
try:
curscore: float = float(input(""))
except ValueError:
print("That's not a score!")
total = 0
minimum = scores[0]
maximum = scores[0]
for i in range(len(scores)):
total = total + scores[i]
if scores[i] < minimum:
minimum = scores[i]
if scores[i] > maximum:
maximum = scores[i]
avg = total/len(scores)
print(f"Min is {min(scores)} Max is {max(scores)} Sum is {sum(scores)}")
print(f"Min = {minimum} Max = {maximum} Avg = {total/len(scores):.2f}")
varsum = 0
for x in scores:
varsum = varsum + ((x-avg)**2)
print(f"The standard deviation is {math.sqrt(varsum/len(scores)):.3f}")使用型別註釋,可使用 int 或 float,先允許 >0 的數字,再篩選 A, B, C, D, F 等級,使用 f-string 輸出 Source Code
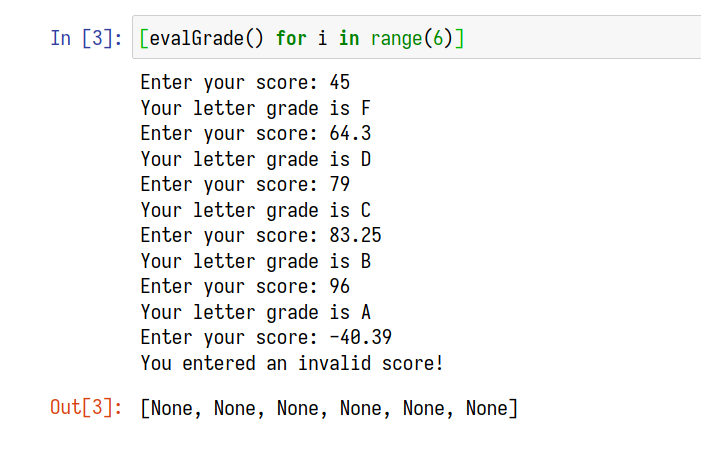
from typing import Union
def grade(score: Union[int, float]):
if 90 <= score <= 100:
return "A"
elif 80 <= score < 90:
return "B"
elif 70 <= score < 80:
return "C"
elif 60 <= score < 70:
return "D"
elif 0 <= score < 60:
return "F"def evalGrade():
score: Union[int, float] = eval(input("Enter your score: "))
if (score >= 0):
print(f"Your letter grade is {grade(score)}")
else:
print("You entered an invalid score!")[evalGrade() for i in range(6)]使用型別註釋,只使用 int ,只允許 int 的數字,再篩選四個等級,使用 f-string 輸出 Source Code
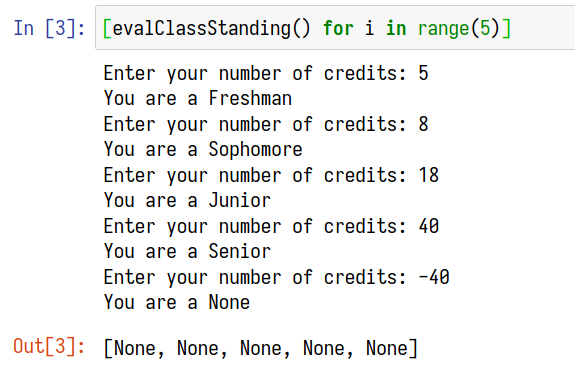
def classStanding(credits: int):
if 0 <= credits < 7:
return "Freshman"
elif 7 <= credits < 16:
return "Sophomore"
elif 16 <= credits < 26:
return "Junior"
elif credits >= 26:
return "Senior"def evalClassStanding():
try:
c: int = int(input("Enter your number of credits: "))
except ValueError:
print("That's not a credit!")
print(f"You are a {classStanding(c)}")[evalClassStanding() for i in range(5)]使用型別註釋,只使用 float,使用 f-string 輸出有限小數點 Source Code
def babysittingBill(sTime: float, eTime: float):
# Ending time can go up to 24. Afterwards, it becomes a new day with a new bill.
if (eTime < 0 or eTime > 24
or sTime < 0 or sTime > 24):
print("Ending and starting times shall be between 0 and 24.")
return -1
if eTime < sTime:
print("Ending time cannot be less than starting time!")
return -1
if eTime <= 21:
total_bill = (eTime - sTime) * 2.5
else:
total_bill = ((eTime - 21) * 1.75) + ((21 - sTime) * 2.5)
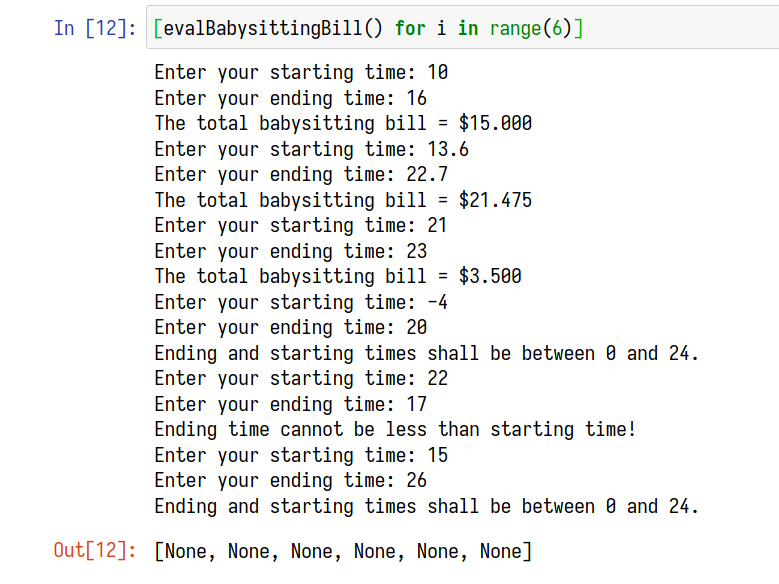
return total_billdef evalBabysittingBill():
st: float = float(input("Enter your starting time: "))
et: float = float(input("Enter your ending time: "))
if ((type(st) is float) and
(type(et) is float)):
bill = babysittingBill(st, et)
if bill != -1:
print(f"The total babysitting bill = ${bill:.3f}")
else:
print("You can only enter numerics!")[evalBabysittingBill() for i in range(6)]A123456xxx => 1 * 1 + 0 * 9 + 1 * 8 + 2 * 7 + 3 * 6 + 4 * 5 + 5 * 4 + 6 * 3 + $x_1$ (X1) * 2 + $x_2$ (X2) * 1 + $x_3$ (X3)
A1:
$x_1$ =$x_2$ =$x_3$ => 4 *$x_1$ + 99 ≡ 0 (mod 10) => 無解,因為4的倍數加上99永遠不會是10的倍數(尾數相加必需為0)A2:
$x_1$ =$x_2$ ≠$x_3$ => 3 *$x_1$ +$x_3$ + 99 ≡ 0 (mod 10) => 唯一解$x_1$ =$x_2$ = 7,$x_3$ = 0A3:
$x_1$ =$x_3$ ≠$x_2$ => 3 *$x_1$ +$x_2$ + 99 ≡ 0 (mod 10) => 唯一解$x_1$ =$x_3$ = 7,$x_2$ = 0A4:
$x_1$ ≠$x_2$ =$x_3$ => 2 *$x_1$ + 2 *$x_2$ + 99 ≡ 0 (mod 10) => 無解, 2 *$x_1$ 或 2 *$x_2$ 尾數必需為1A5:
$x_1$ ≠$x_2$ ≠$x_3$ => 2 *$x_1$ +$x_2$ +$x_3$ + 99 ≡ 0 (mod 10) => 19 組解,令$x_2$ = 1 or$x_3$ = 1,{ 0 … 9 } 皆可帶入$x_1$
D10xxyyyy4 => 1 * 1 + 3 * 9 + 1 * 8 + 0 * 7 + $x_1$ (X1) * 6 + $x_2$ (X2) * 5 + $y_1$ (y1) * 4 + $y_2$ (y2) * 3 + $y_3$ (y3) * 2 + $y_4$ (y4) * 1 + 4
B1:
$x_1$ =$x_2$ ,$y_1$ =$y_2$ =$y_3$ =$y_4$ => 11 *$x_1$ + 10 *$y_1$ + 40 ≡ 0 (mod 10) => 10組解,當$x_1$ = 0 時,$y_1$ ∈ { 0 … 9 }B2:
$x_1$ ≠$x_2$ ,$y_1$ =$y_2$ =$y_3$ =$y_4$ => 6 *$x_1$ + 5 *$x_2$ + 10 *$y_1$ + 40 ≡ 0 (mod 10) =>$x_1$ 必為 0 or 5,$x_2$ 必為 { 0, 2, 4, 6, 8 },$y_1$ ∈ { 0 … 9 },共 2 * 5 * 10 = 100 組組合B3:
$x_1$ =$x_2$ ,$y_1$ ≠$y_2$ ≠$y_3$ ≠$y_4$ => 11 *$x_1$ + 4 *$y_1$ + 3 *$y_2$ + 2 *$y_3$ +$y_4$ + 40 ≡ 0 (mod 10)
假設 A, B 式有相同解,即 A:
xy = "67" 並非正確的組合