The CNTK Wiki has all information on CNTK including setup, examples, etc.
Give us feedback through these channels.
2017-01-10. CNTK for Windows supports Visual 2015 If you pull or merge the master branch, CNTK will now require Visual Studio 2015 to build on Windows. There are two ways to move your development environment to Visual Studio 2015:
Migrate VS2013 to VS2015: This gives you a fine grained control over where components are installed
Script driven setup: This gives you an mostly automated migration to Visual Studio 2015
2016-12-22. V 2.0 Beta 7 Release Highlights of this Release:
- Python API behaviour is changed to be more strict.
- New Examples and Tutorials (Artistic Style Transfer and GoogLeNet (Inception V3) ).
- New version of CNTK Evaluation library NuGet Package.
- CNTK Background Improvements.
See more in the Release Notes Get the Release from the CNTK Releases page
2016-12-13. V 2.0 Beta 6 Release Highlights of this Release:
- Both Windows and Linux packages are now created using NVIDIA CUDA 8.0 toolkit.
- Linux version now supports Python 3.5 (Windows support is coming soon).
- Support for training on one-hot and sparse arrays via NumPy.
- New Examples and Tutorials: Video action recognition, Finance Timeseries with Pandas/Numpy, Neural Character Language Models
- Stability Improvements and bug fixes.
See more in the Release Notes Get the Release from the CNTK Releases page
2016-11-25. V 2.0 Beta 5 Release Highlights of this Release:
- The Windows binary packages are now created using the NVIDIA CUDA 8 toolkit, see the release notes for details. The CNTK-Linux binary packages are still built with CUDA 7.5. The Linux support for Cuda8 will follow shortly!
- Performance enhancements for evaluation of bitmap images through the new
EvaluateRgbImagefunction in the managed Eval API. - A new version of the CNTK Nuget package is available.
- Stability Improvements and bug fixes, i.e. decreased memory footprint in CNTK Text Format deserializer.
- We continue to improve documentation and tutorials on an ongoing basis, in this release we added a Sequence-to-Sequence tutorial.
See more in the Release Notes Get the Release from the CNTK Releases page
2016-11-21. V 2.0 Beta 4 Release Highlights of this Release:
- New ASGD/Hogwild! training using Microsoft’s Parameter Server (Project Multiverso)
- Distributed Scenarios now supported in CNTK Python API
- New Memory Compression mode to reduce memory usage on GPU
- CNTK Docker image with 1bit-SGD support
- Stability Improvements and bug fixes
See more in the Release Notes Get the Release from the CNTK Releases page
The Microsoft Cognitive Toolkit (https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/research/product/cognitive-toolkit/), is a unified deep-learning toolkit that describes neural networks as a series of computational steps via a directed graph. In this directed graph, leaf nodes represent input values or network parameters, while other nodes represent matrix operations upon their inputs. CNTK allows to easily realize and combine popular model types such as feed-forward DNNs, convolutional nets (CNNs), and recurrent networks (RNNs/LSTMs). It implements stochastic gradient descent (SGD, error backpropagation) learning with automatic differentiation and parallelization across multiple GPUs and servers. CNTK has been available under an open-source license since April 2015. It is our hope that the community will take advantage of CNTK to share ideas more quickly through the exchange of open source working code.
Wiki: Go to the CNTK Wiki for all information on CNTK including setup, examples, etc.
License: See LICENSE.md in the root of this repository for the full license information.
Tutorial: Microsoft Computational Network Toolkit (CNTK) @ NIPS 2015 Workshops
Blogs:
- Microsoft Computational Network Toolkit offers most efficient distributed deep learning computational performance
- Microsoft researchers win ImageNet computer vision challenge (December 2015)
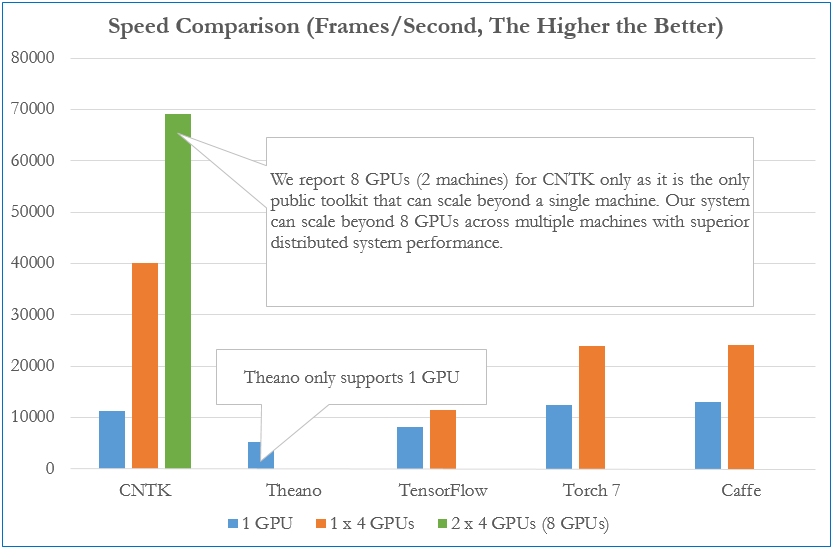
The figure below compares processing speed (frames processed per second) of CNTK to that of four other well-known toolkits. The configuration uses a fully connected 4-layer neural network (see our benchmark scripts) and an effective mini batch size (8192). All results were obtained on the same hardware with the respective latest public software versions as of Dec 3, 2015.
If you used this toolkit or part of it to do your research, please cite the work as:
Amit Agarwal, Eldar Akchurin, Chris Basoglu, Guoguo Chen, Scott Cyphers, Jasha Droppo, Adam Eversole, Brian Guenter, Mark Hillebrand, T. Ryan Hoens, Xuedong Huang, Zhiheng Huang, Vladimir Ivanov, Alexey Kamenev, Philipp Kranen, Oleksii Kuchaiev, Wolfgang Manousek, Avner May, Bhaskar Mitra, Olivier Nano, Gaizka Navarro, Alexey Orlov, Hari Parthasarathi, Baolin Peng, Marko Radmilac, Alexey Reznichenko, Frank Seide, Michael L. Seltzer, Malcolm Slaney, Andreas Stolcke, Huaming Wang, Yongqiang Wang, Kaisheng Yao, Dong Yu, Yu Zhang, Geoffrey Zweig (in alphabetical order), "An Introduction to Computational Networks and the Computational Network Toolkit", Microsoft Technical Report MSR-TR-2014-112, 2014.
CNTK is in active use at Microsoft and constantly evolving. There will be bugs.
This project has adopted the Microsoft Open Source Code of Conduct. For more information see the Code of Conduct FAQ or contact opencode@microsoft.com with any additional questions or comments.