The project goal is to create a machine learning pipeline to classify disaster events from a dataset provided by Figure Eight containing real messages. The final outcome is a web app where an emergency worker can enter a new message and get classification results in different categories.
- Python3
- Machine Learning Libraries:
NumPy,Pandas,Scikit-Learn - Natural Language Process Libraries:
nltk - SQLlite Database Libraries:
SQLalchemy - Model Loading and Saving Library:
Pickle - Web App and Data Visualization:
Flask,Plotly
-
Run the following commands in the project's root directory to set up your database and model.
- To run ETL pipeline that cleans data and stores in database
python data/process_data.py data/disaster_messages.csv data/disaster_categories.csv data/disaster_response.db - To run ML pipeline that trains classifier and saves
python models/train_classifier.py data/disaster_response.db models/classifier.pkl
- To run ETL pipeline that cleans data and stores in database
-
Run the following command in the app's directory to run your web app.
python run.py -
Go to http://0.0.0.0:3001/ to see the web app.
The notebooks folder contains two jupyter notebooks that help you understand how the pipeline scripts are built step by step:
- ETL Pipeline Preparation: Loads the datasets, merges them, cleans the data and stores them in a SQLite database.
- ML Pipeline Preparation: Loads the dataset from SQLite database, splits data into train and test set, builds a text preprocessing and ML pipeline, trains and tunes models using GridSearch (SVM, Random Forest), outputs reults on the test set and exports the final model as a pickle file.
Python scripts:
data/process_data.py- ETL pipelinemodels/train_classifier.py- ML Pipelineapp/run.py- Flask Web App
Datasets:
- messages.csv: Contains the id, message and genre, i.e. the method (direct, social, ...) the message was sent.
- categories.csv: Contains the id and the categories (related, offer, medical assistance..) the message belonges to.
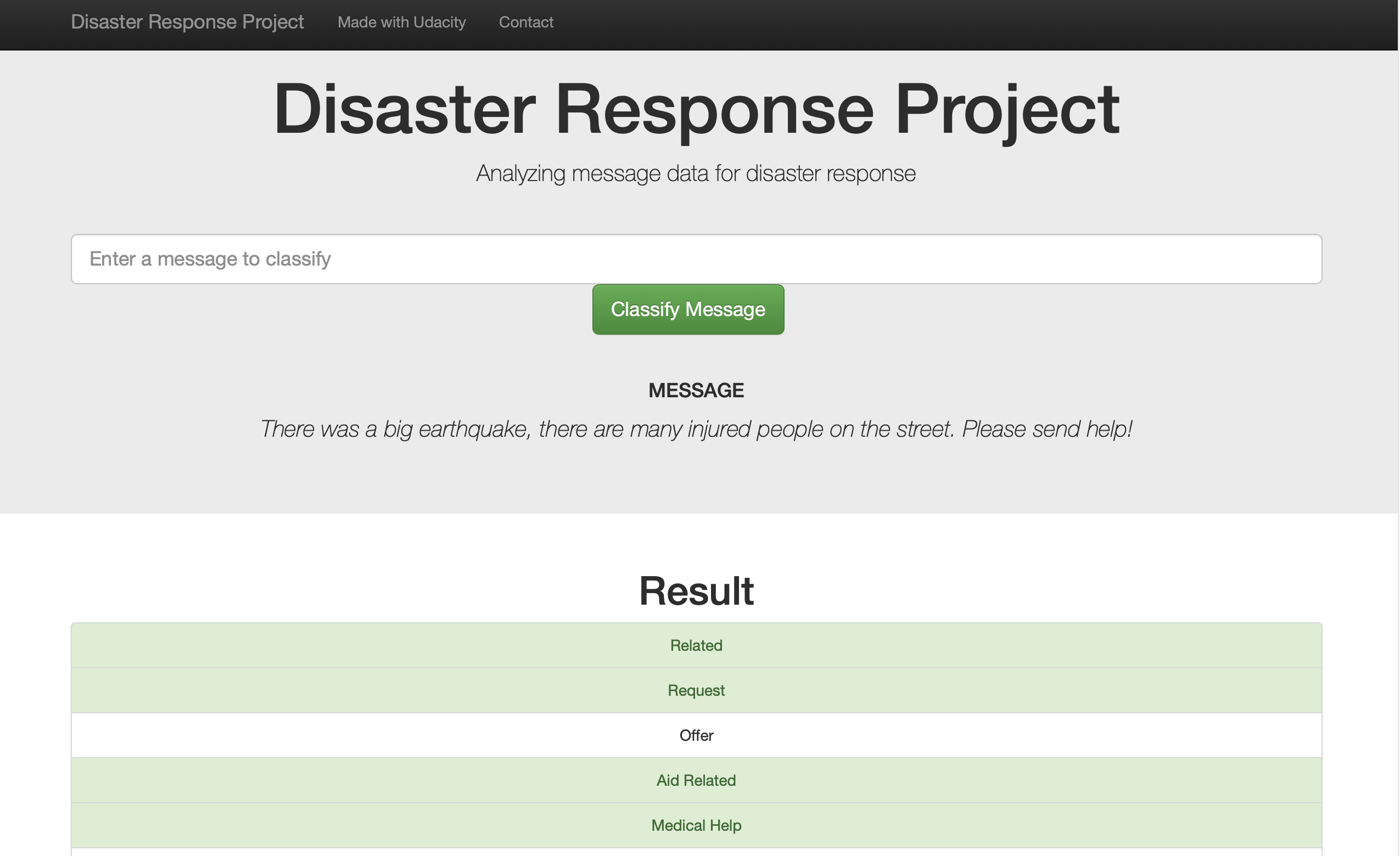
The final output of the project is an interactive web app that takes a message from the user as an input and then classifies it into the respective categories.
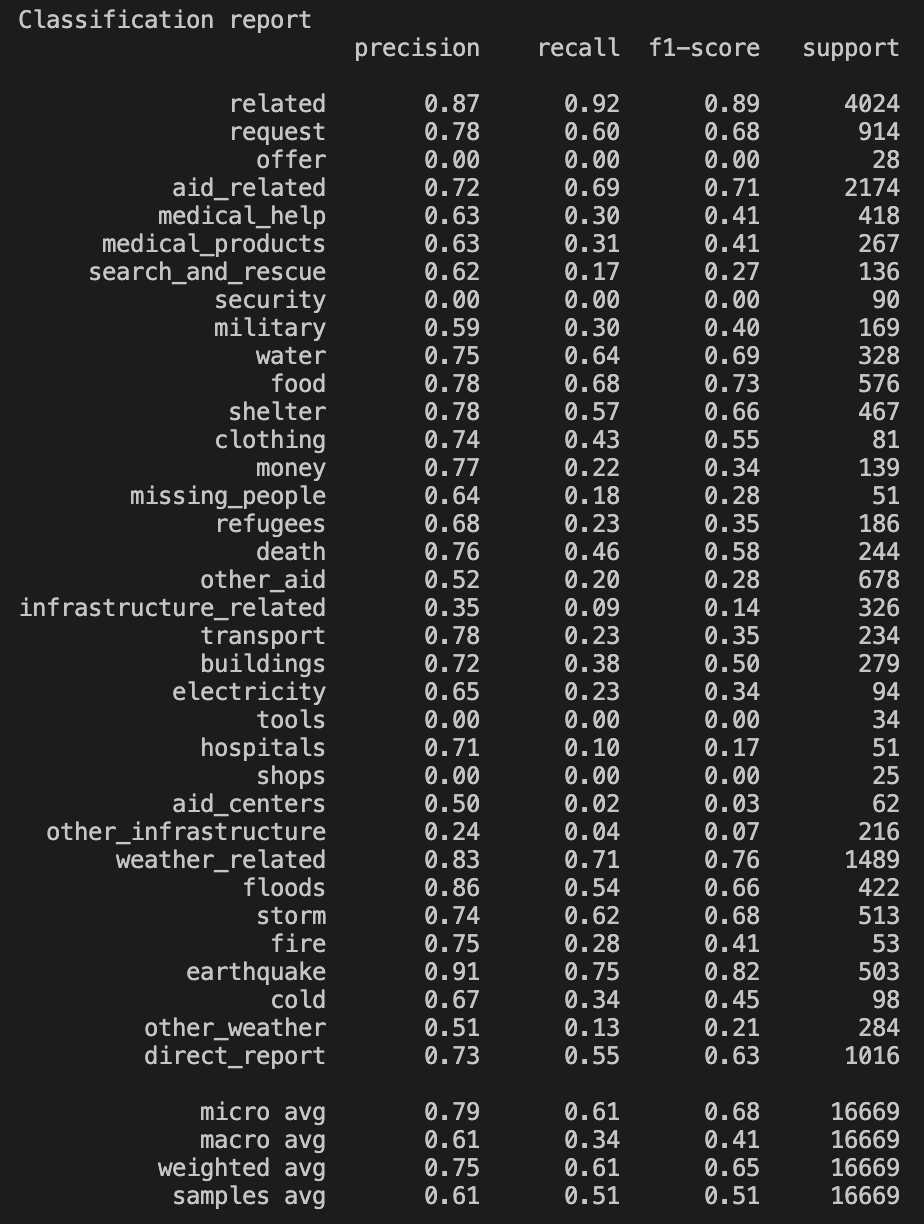
Classification Report running a Linear Support Vector Machines Classifier.
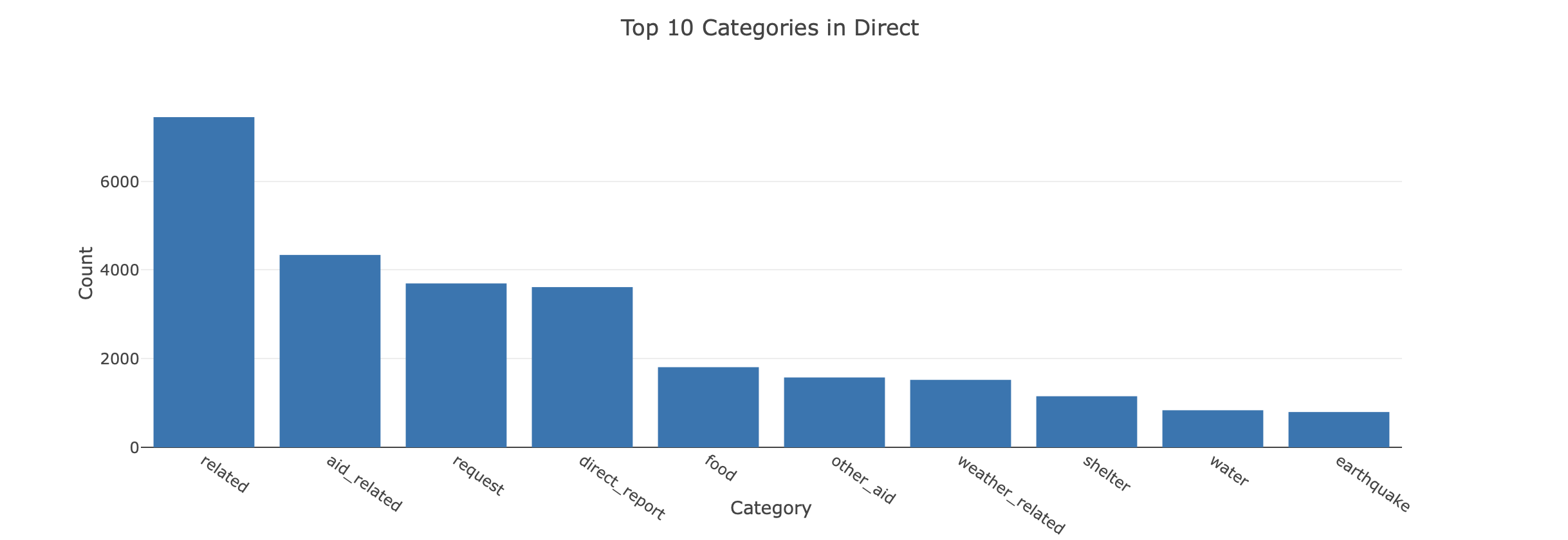
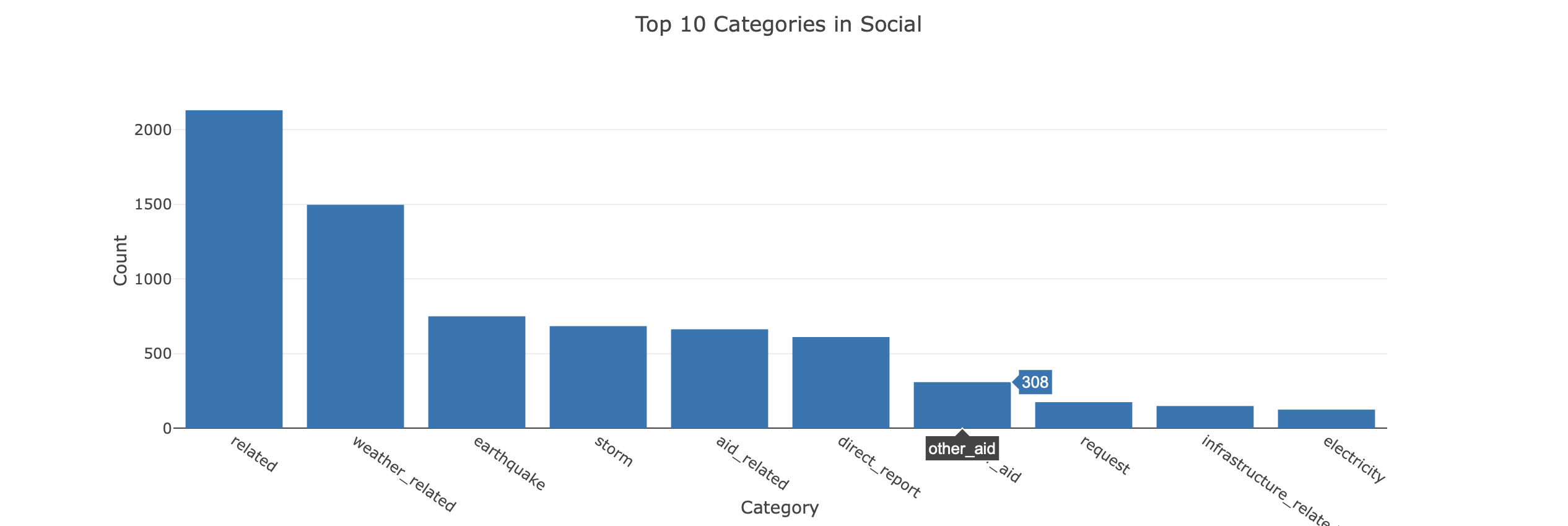
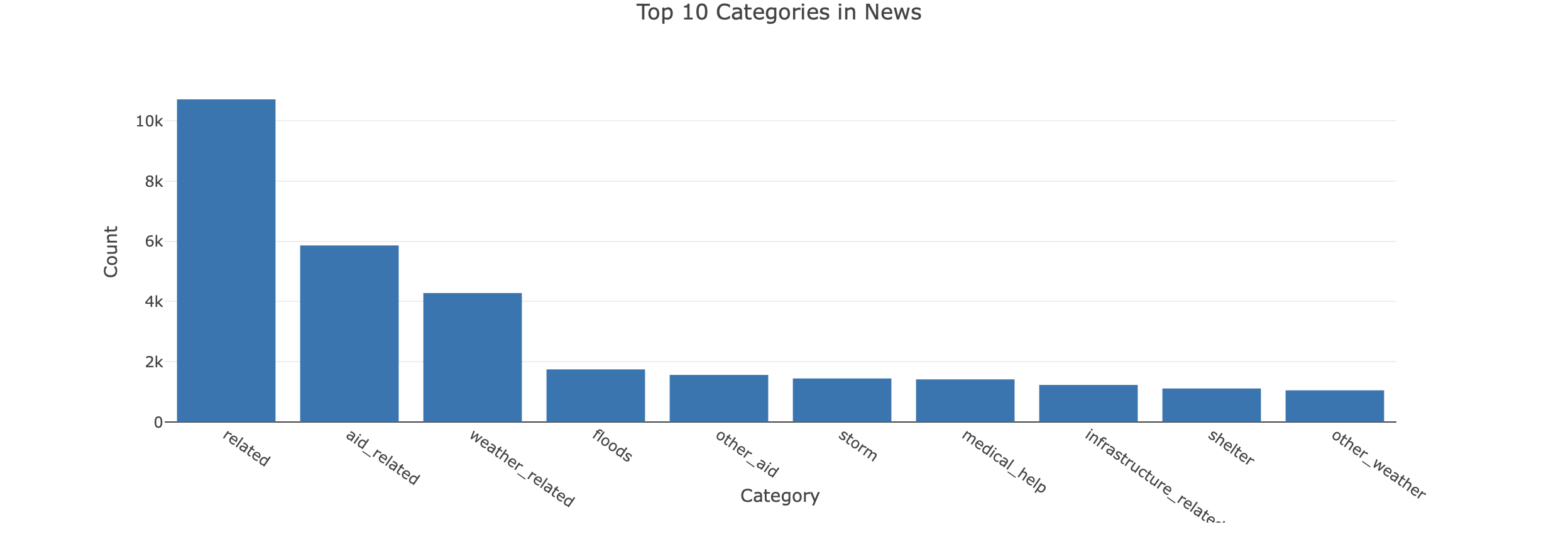
Distribution of Top 10 Categories by Genre
The dataset has highly imbalanced classes, i.e. there is an uniqual representation of classes. This affects the ML algorithms because the probability that the instances belong to the majority class is significantly high, so the algorithms are more likely to classify new observations to the majority class.
Possible approaches to address imbalanced data are:
- Boosting the predictive performance on minority class, using recognition-based learning or cost-sensitive learning.
- Resampling the data (over-sampling, under-sampling, SMOTE).
This project has been completed as part of the Data Science Nanodegree on Udacity. The data was collected by Figure Eight and provided by Udacity.