FLIM-Builder
This is the official repository of the software FLIM-Builder. FLIM-Builder provides an interface for training FLIM-based CNNs. In FLIM Builder, the user can define the network architecture, load and annotate the dataset, train the CNN using FLIM, see each kernel's activation (an manually select them if desired), and run on the validation set.
Installing
Requirements
GCC 4.9+ (build-essential)
ATLAS (libatlas-base-dev)
LAPACK (liblapack-dev)
BLAS (libopenblas-dev)
Qt 6.3.1+
For running with GPU:
Install cuda-toolkit from NVIDIA
Compiling
To generate a Makefile, simply run:
qmake FLIMBuilder.pro <OPTIONS=use_gpu>
Add the optional OPTIONS=use_gpu flag for enabling GPU (you must have cuda-toolkit working)
Then, run:
make .
How to use
(Considering Navigating FLIMBuilder, the module you should interact with for every action is in parenthesis.)
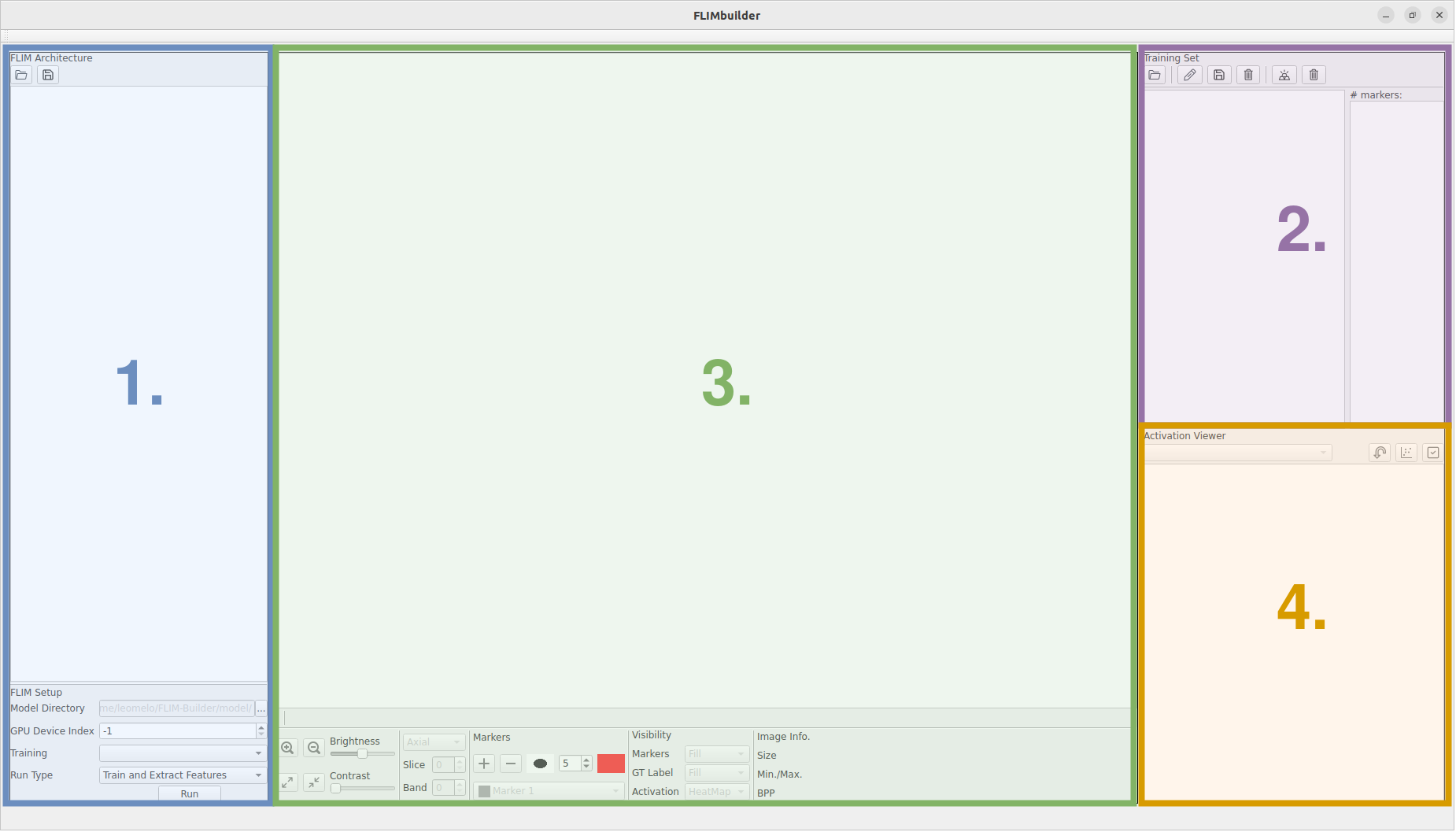
A simple step-by-step without much user interaction would be:
a) Define a CNN architecture and a folder to save the model (1.);
b) Load a dataset (2.);
c) Load/add scribbles to the training images (2./3.);
d) Train and execute all layers (1.);
e) Load the validation/test data (2.);
f) Run the learned model (1.).
Navigating FLIMBuilder
We splitted FLIMBuilder in four parts to present them separately.
(a) Load an architecture setup;
(b) Area to change the archictecture file;
(c) Save the architecture file;
(d) Set directory to save the model and the results;
(e) Define which device to run the model (-1 for CPU);
(f) Define which layer to train/run;
(g) Select whether to train, run or both;
(h) Run the model with all set configurations.
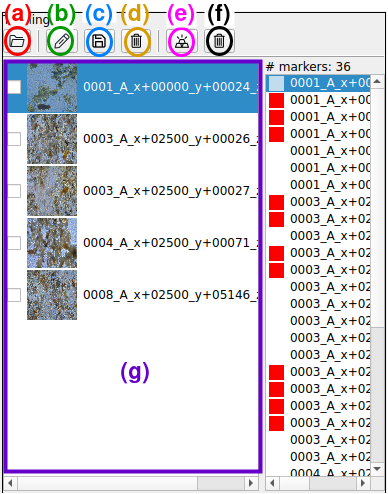
(a) Load Image dataset;
(b) Load previously saved scribbles;
(c) Save new scribbles;
(d) Delete all scribbles;
(e) Load pixel-wise ground-truth;
(f) Unload pixel-wise ground-truth;
(g) Look at dataset images
(Double-click one to select it for annotation or to see its activations).
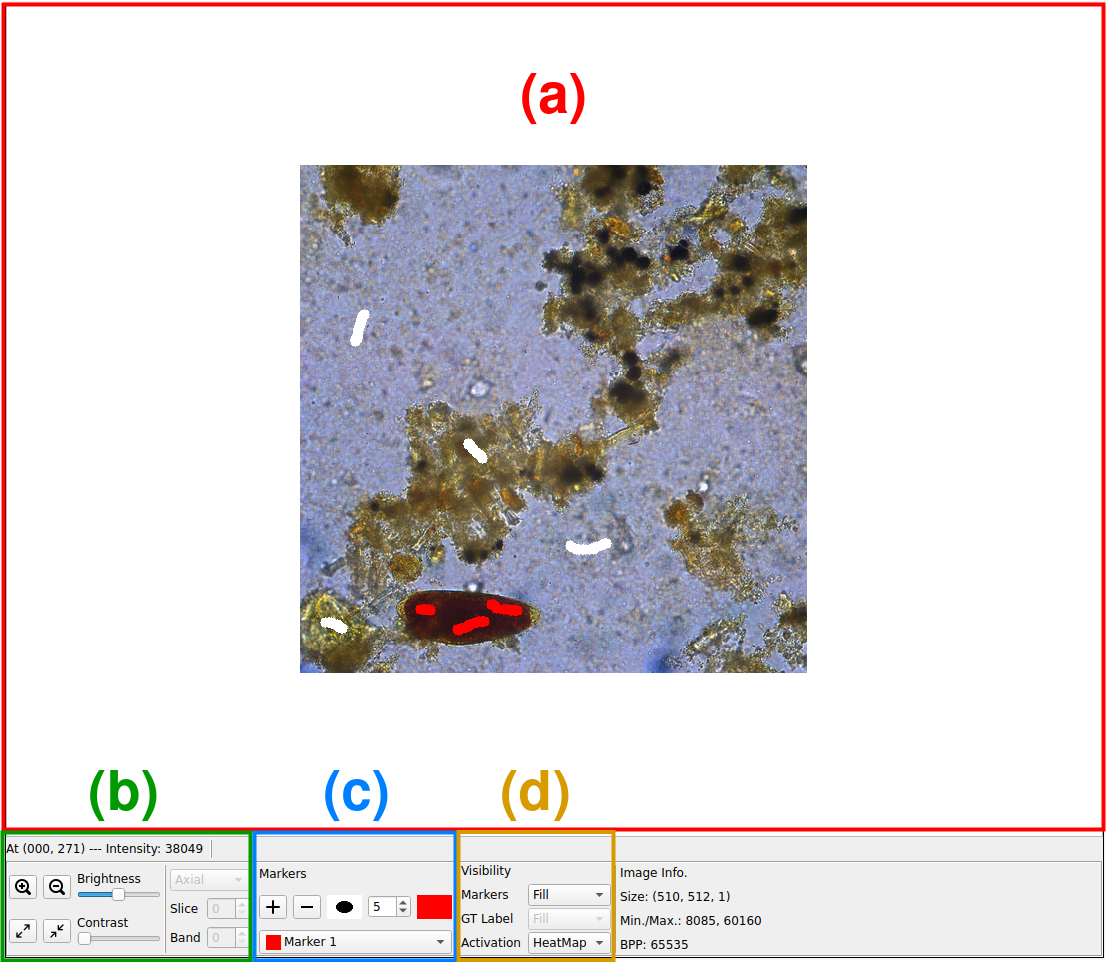
(a) Image pannel to view images and activatios and add scribbles;
(b) Image manipulation options
(c) Marker options to change their size or label
(d) Visualization and annotation options.
(a) Layer Selection
(b) Invert the activations of selected kernels
(c) Visualize projection the kernels' feature space using TSNe
(d) Confirm a kernel selection (removes all other kernels).
(e) Kernel panel
(Double-click kernels to look at its ativation in the image panel (3.). Also, click on the check-boxes to select kernels.