- docker
- poetry
Install poetry here:
poetry env use 3.11
poetry install
This poetry is used for manage local dev enviroment.
./script/start-docker.sh
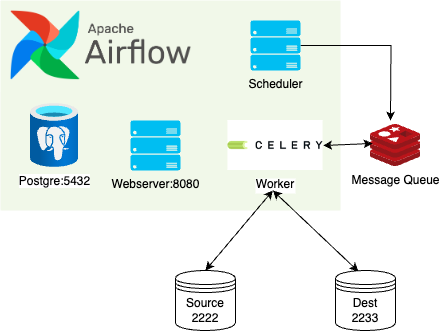
Access airflow UI at localhost:8008
Access flower UI at localhost:5555
Airflow Admin Username/Password: airflow/airflow
SSH Port of source: 2222 SSH Port of targer: 2233
Test for sftp server
sftp -P 2222 airflow@localhost
sftp -P 2233 airflow@localhost
- I did not consider the security of pipeline.
In file dags/file_transfer_dag.py
Operator FileTransferOperator in plugins/file_transfer_plugin/operators/file_transfer_operator.py
This is a basis Operator in Airflow to solving minimize problems transfer from source SFTP server to another SFTP server.
This operator will flaws when we have large number of files + files that have larges. If this happen Airflow Executor will face I/O blocking task and on hold all queue task until this operator resolve.
This is an attempt to solve larges number of file problem
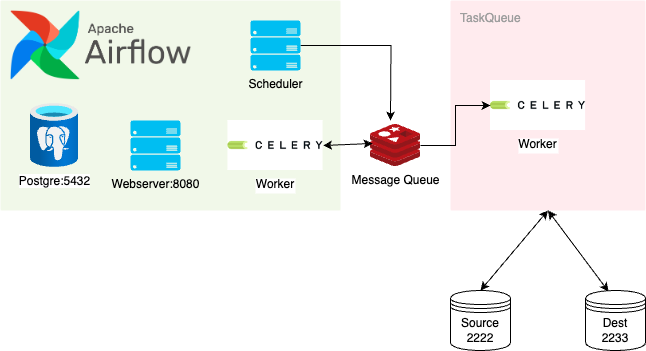
- In this project, I used Celery as TaskQueue (another celery server not Airflow) to show how we could dedicated small transfer task for another TaskQueue system.
- In realitiy, we could apply this pattern for any kind of TaskQueue / or custom server API.
Note: I do not prefer to use dynamic dags because it will break the structure of DAG day by day. Therefore very hard to monitor.
TODO: Code
This is an attempt to solve large file problem
- The large file will be divided into small one and processed like two difference files in pipeline.
- E.g: file_1.txt = 1G. We will divide into 100MB chunks: file_1_.txt.divided.000001, ... , file_1_.txt.divided.000010
- Files will be transfer to target system ( the larger number of file are resolve with scaling task queue).
- Another task will merge all divided file in target file system.
In previous approach the pipeline has two cons:
- The number of files increase overtime, thus the speed and memory used by pipeline is also increase. E.g: in first day: number of file in source is 3, the pipeline will scan all 3 file and compare with files target ( may be 0 ) . In the next day, the file increase to 6 -> we need to scan 6-3 files. Therefore, in the Tth day, the pipeline will process T*(avg_file_per_day).
- Pipeline is not idempotent: In every call, the output of pipeline is changed -> Hard to tracking bug and backfill data.
So to fix those cons, we could considering using date partition style in file structure:
- On March 1st, 2024:
sftp://<source>/a/b/c/file_1.txt->sftp://<source>/a/b/c/2024/03/01/file_1.txt - On March 2nd, 2024,
sftp://<source>/a/b/c/file_1.txt->sftp://<source>/a/b/c/2024/03/02/file_2.txt..etc..
Or if it is not possible, we can consider to clone data in source/a/b/c to source/a/b/c/temp/2024/03/01/*.txt by scaning date add in source/a/b/c . The old file within 30 days will be truncate and move to legacy path source/a/b/c/old_data for backfill purpose.