The emsarray package provides a common interface
for working with the many model geometry conventions used at CSIRO.
It enhances xarray Datasets
and provides a set of common operations for manipulating datasets.
To use, open the dataset using the emsarray.open_dataset() function
and use the dataset.ems attribute:
import emsarray
from shapely.geometry import Point
dataset = emsarray.tutorial.open_dataset('gbr4')
capricorn_group = Point(151.869, -23.386)
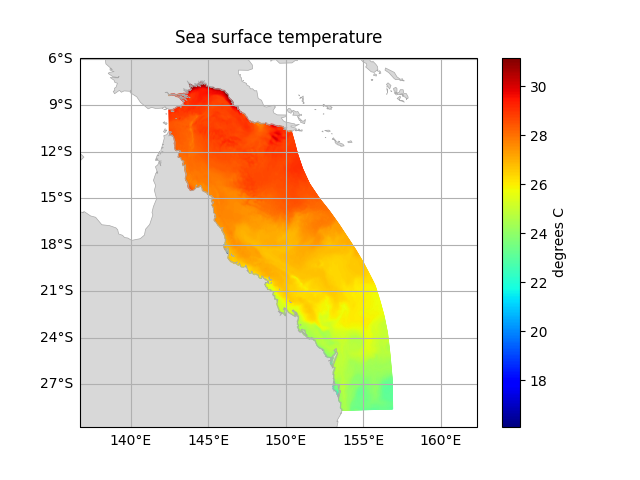
point_data = dataset.ems.select_point(capricorn_group)Some methods take a DataArray as a parameter:
# Plot the sea surface temperature for time = 0
temp = dataset['temp'].isel(time=0, k=-1)
dataset.ems.plot(temp)A number of operations provide further functionality to manipulate datasets, export geometry, and select subsets of data:
from emsarray.operations import geometry
geometry.write_geojson(dataset, './gbr4.geojson')
geometry.write_shapefile(dataset, './gbr4.shp')Examples of using emsarray are available in the emsarray-notebooks repository.
You can explore these notebooks online with Binder.
To get set up for development, make a virtual environment and install the dependencies:
$ python3 -m venv
$ source venv/bin/activate
$ pip install --upgrade pip>=21.3
$ pip install -e . -r continuous-integration/requirements.txtTo run the tests, install and run tox:
$ python3 -m venv
$ source venv/bin/activate
$ pip install --upgrade pip>=21.3 tox
$ toxThe documentation for the current stable version of emsarray is available on Read The Docs.
To build the documentation, install the development requirements as above and invoke Sphinx:
$ make -C docs/ htmlWhile updating or adding to the documentation,
run the live target to automatically rebuild the docs whenever anything changes.
This will serve the documentation via a livereload server.
$ make -C docs/ liveYou can the view the docs at http://localhost:5500