EasyPeasy is a Swift framework that lets you create Auto Layout constraints programmatically without headaches and never ending boilerplate code. Besides the basics, EasyPeasy resolves most of the constraint conflicts for you and lets you attach to a constraint conditional closures that are evaluated before applying a constraint, this lets you apply (or not) a constraint depending on platform, size classes, orientation... or the state of your controller, easy peasy!
In this quick tour through EasyPeasy we assume that you already know the advantages and disadvantages of the different Auto Layout APIs and therefore you won't see here a comparison of the code side by side, just read and decide whether EasyPeasy is for you or not.
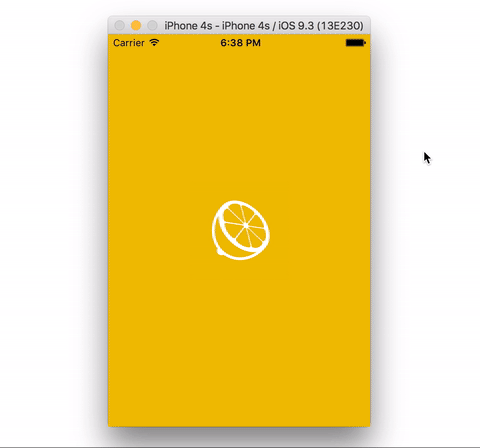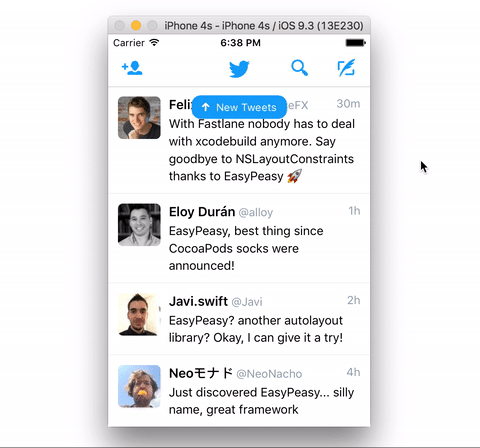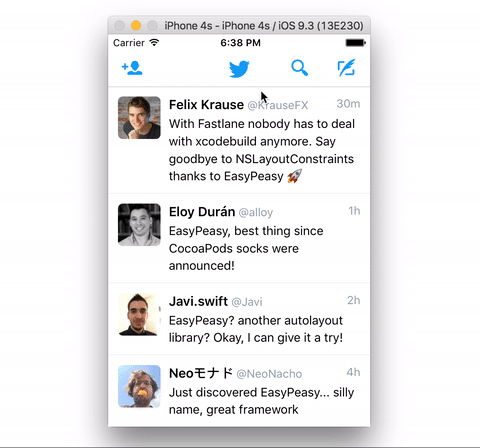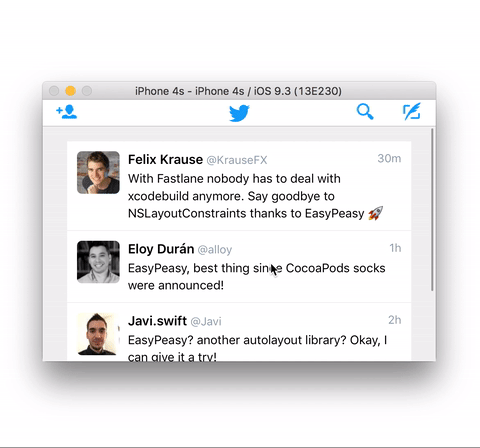
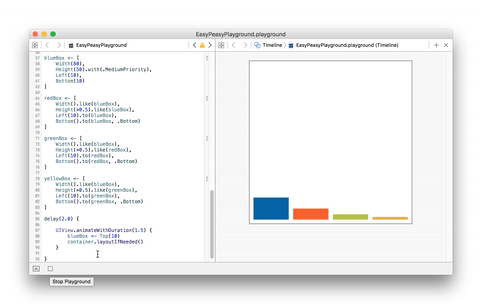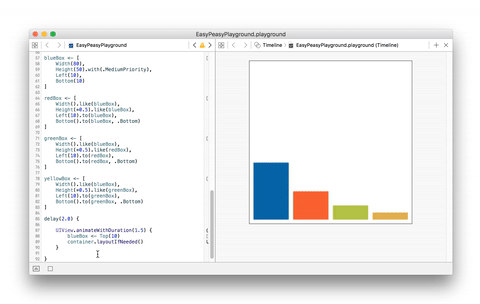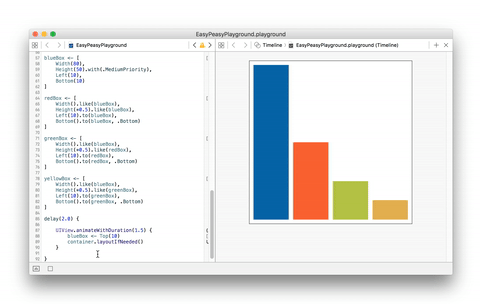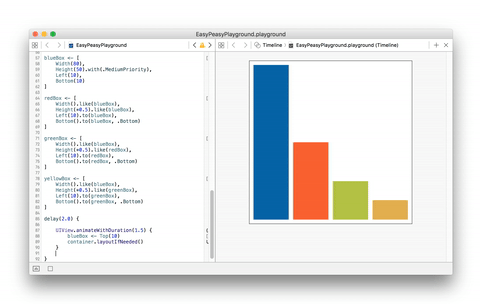
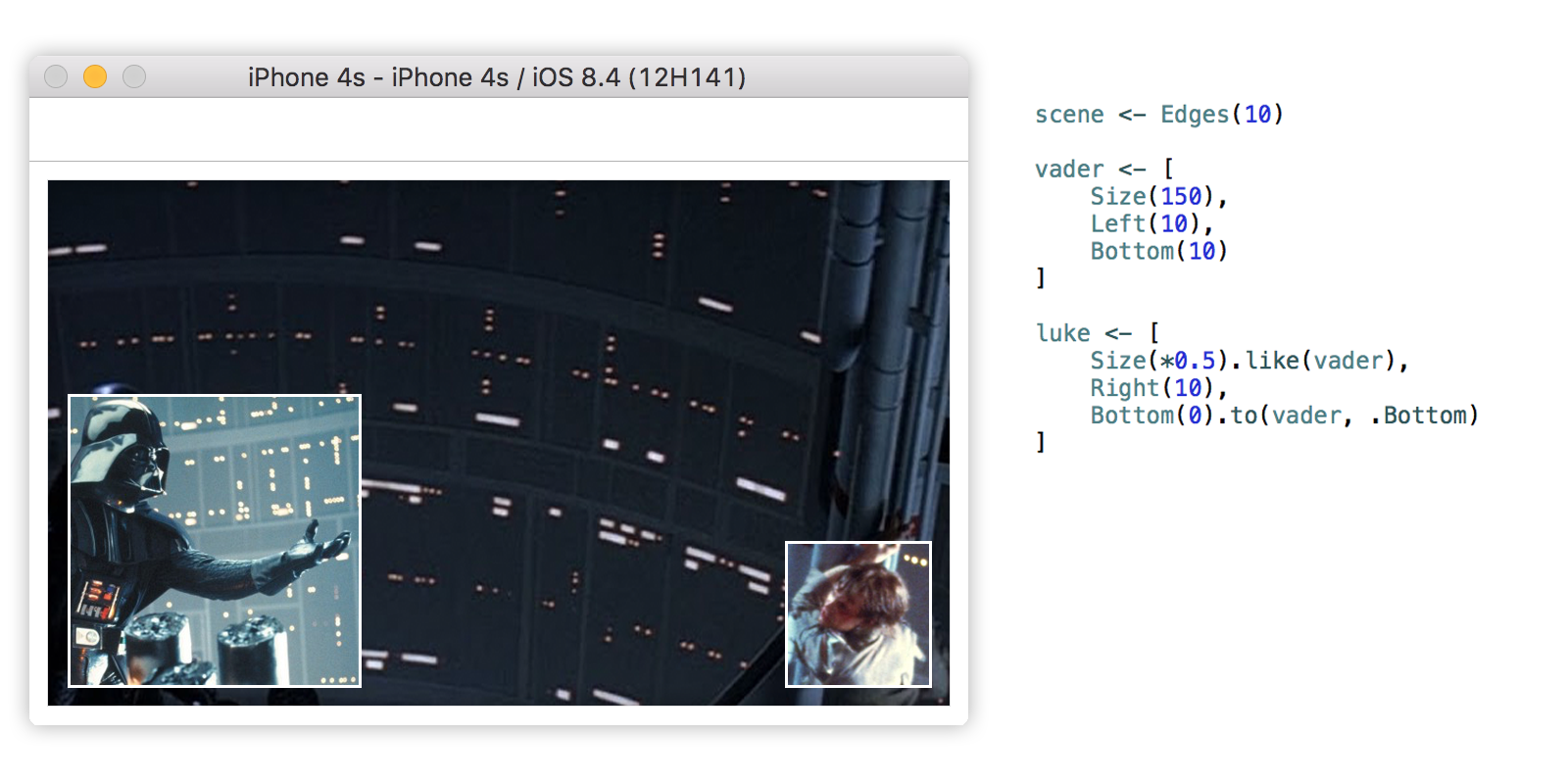
The example below is quite simple but shows how effortless its implementation
result using EasyPeasy.
EasyPeasy is available through CocoaPods. To install it, simply add the following line to your Podfile:
pod "EasyPeasy"For now EasyPeasy is only compatible with iOS 8 and above, although we aim to make it compatible with OS X. The framework has been tested with Xcode 7 and Swift 2.0, however don't hesitate to report any issues you may find with different versions.
EasyPeasy is a set of position and dimension attributes that you can apply
to your views. For instance, to set a width of 200px to a view you would create
an attribute of class Width with a constant value of 200, then the attribute
is applied to the view by using the custom apply operator <-.
myView <- Width(200)Because our view without height is nothing we can apply multiple attributes at once as follows:
myView <- [
Width(200),
Height(120)
]In the previous example, two attributes have been applied and therefore two constraints
created and added: a width constraint with constant = 200 and a height constraint
with constant = 120.
Without really knowing it, we have just created an EasyPeasy Constant
struct containing the constant and the relation of a NSLayoutConstraint.
That relation is a Modifier and EasyPeasy provides four different modifiers:
.EqualTo: the equivalent ofNSLayoutRelationEqual, it's created like in our previous example.Width(200).GreaterThanOrEqualTo: the equivalent ofNSLayoutRelationGreaterThanOrEqual, it's created as easy as thisWidth(>=200)and it means that our view has a width greater than or equal to 200px..LessThanOrEqualTo: the equivalent ofNSLayoutRelationLessThanOrEqualis created as followsWidth(<=200)..MultipliedBy: this modifier is a bit particular as it does not match anyNSLayoutRelation, instead, this modifier replaces themultiplierproperty of aNSLayoutConstraint. It's created like thisWidth(*2)and means that the width of our view is two times something, we will mention later how to establish the relationship with that something.
EasyPeasy provides as many Attribute classes as attributes NSLayoutConstraint
have, plus something that we have called CompoundAttributes (we will explain these
attributes later).
There are just two dimension attributes Width and Height. You can create an
Auto Layout relationship between your view DimensionAttribute and another view
by using the method func like(view: UIView) -> Self. Example:
contentLabel <- Width().like(headerView)That line of code will create a constraint that sets a width for contentLabel
equal to the headerView width.
The table below shows the different position attributes available. Because they
behave like the NSLayoutConstraint attributes, you can find a complete
description of them in the Apple docs.
| Attribute | Attribute | Attribute | Attribute |
|---|---|---|---|
| Left | Right | Top | Bottom |
| Leading | Trailing | CenterX | CenterY |
| LeftMargin | RightMargin | TopMargin | BottomMargin |
| LeadingMargin | TrailingMargin | CenterXWithinMargins | CenterYWithinMargins |
| FirstBaseline | LastBaseline | -- | -- |
As well as the DimensionAttributes have the like: method to establish
Auto Layout relationships, you can use a similar method to do the same with
PositionAttributes. This method is:
func to(view: UIView, _ attribute: ReferenceAttribute? = nil) -> SelfThe example below positions contentLabel 10px under headerView with the same
left margin as headerView.
contentLabel <- [
Top(10).to(headerView),
Left().to(headerView, .Left)
]These attributes are the ones that create multiple DimensionAttributes or
PositionAttributes under the hood. For example, the Size attribute will create
a Width and a Height attributes with their width and height
NSLayoutConstraints respectively.
These are the CompoundAttributes available:
Size: As mentioned before this attribute will apply aWidthand aHeightattribute to the view. It can be initialized in many ways and depending on that the result may change. These are some examples:
// Apply width = 0 and height = 0 constraints
view <- Size()
// Apply width = referenceView.width and height = referenceView.height constraints
view <- Size().like(referenceView)
// Apply width = 100 and height = 100 constraints
view <- Size(100)
// Apply width = 200 and height = 100 constraints
view <- Size(CGSize(width: 200, height: 100))Edges: This attribute createsLeft,Right,TopandBottomattributes at once. Examples:
// Apply left = 0, right = 0, top = 0 and bottom = 0 constraints to its superview
view <- Edges()
// Apply left = 10, right = 10, top = 10 and bottom = 10 constraints to its superview
view <- Edges(10)
// Apply left = 10, right = 10, top = 5 and bottom = 5 constraints to its superview
view <- Edges(UIEdgeInsets(top: 5, left: 10, bottom: 5, right: 10))Center: It createsCenterXandCenterYattributes. Examples:
// Apply centerX = 0 and centerY = 0 constraints to its superview
view <- Center()
// Apply centerX = 10 and centerY = 10 constraints to its superview
view <- Center(10)
// Apply centerX = 0 and centerY = 50 constraints to its superview
view <- Center(CGPoint(x: 0, y: 50))Margins: This attribute createsLeftMargin,RightMargin,TopMarginandBottomMarginattributes at once. Examples:
// Apply leftMargin = 0, rightMargin = 0, topMargin = 0 and bottomMargin = 0 constraints to its superview
view <- Margins()
// Apply leftMargin = 10, rightMargin = 10, topMargin = 10 and bottomMargin = 10 constraints to its superview
view <- Margins(10)
// Apply leftMargin = 10, rightMargin = 10, topMargin = 5 and bottomMargin = 5 constraints to its superview
view <- Margins(UIEdgeInsets(top: 5, left: 10, bottom: 5, right: 10))CenterWithinMargins: It createsCenterXWithinMarginsandCenterYWithinMarginsattributes. Examples:
// Apply centerXWithinMargins = 0 and centerYWithinMargins = 0 constraints to its superview
view <- CenterWithinMargins()
// Apply centerXWithinMargins = 10 and centerYWithinMargins = 10 constraints to its superview
view <- CenterWithinMargins(10)
// Apply centerXWithinMargins = 0 and centerYWithinMargins = 50 constraints to its superview
view <- CenterWithinMargins(CGPoint(x: 0, y: 50))The Priority enum does the same function as UILayoutPriority and it's shaped
by four cases:
-
LowPriority: it creates an Auto Layout priority withFloatvalue1. -
MediumPriority: it creates an Auto Layout priority withFloatvalue500. -
HighPriority: it creates an Auto Layout priority withFloatvalue1000. -
CustomPriority: it specifies the Auto Layout priority defined by the developer in the case associated valuevalue. Example:.CustomPriority(value: 750.0)
In order to apply any of these priorities to an Attribute, the method
.with(priority: Priority) must be used. The following example gives an
UILayoutPriority of 500 to the Top Attribute applied to view:
view <- Top(>=50).with(.MediumPriority)One of the peculiarities of EasyPeasy is the usage of Conditions or closures
that evaluate whether a constraint should be applied or not to the view.
The method when(condition: Condition) sets the Condition closure to an Attribute.
There is plenty of use cases, the example below shows how to apply different constraints depending on the device:
view <- [
Top(10),
Bottom(10),
Width(250),
Left(10).when { Device() == .iPad },
CenterX(0).when { Device() == .iPhone }
]Note: the global function Device() in the example above is not implemented in
the framework.
These Condition closures can be re-evaluated during the lifecycle of an UIView,
to do so you just need to call the UIView convenience method easy_reload().
view.easy_reload()Bare in mind that these Condition closures are stored in properties therefore
you need to capture those variables you access within the closure. For example:
descriptionLabel <- [
Height(100).when { weak self in
return self?.expandDescriptionLabel ?? false
}
]Finally but not less important in this section we will explain how to interact
with Attributes once they have been applied to an UIView using the <-
operator.
We briefly mentioned in the introductory section that EasyPeasy solves most
of the constraint conflicts and it's true. Usually, in order to update a constraint
or the constant of a constraint you have to keep a reference to your
NSLayoutConstraint and update the constant when needed. With EasyPeasy you
just need to apply another Attribute to your UIView of the same or different
type. In the example below we have two methods, the one in which we setup our
constraints viewDidLoad() and a method in which we want to update the Top
attribute of our headerView.
func viewDidLoad() {
super.viewDidLoad()
headerView <- [
Top(0),
Left(0),
Right(0),
Height(60)
]
}
func didTapButton(sender: UIButton?) {
headerView <- Top(100)
}That's it! we have updated our Top constraint without caring about keeping
references or installing/uninstalling new constraints.
However, there is some cases in which EasyPeasy cannot prevent a conflict (at
least for now). This is when multiple constraints cannot be satisfied, i.e. existing
a Left and Right constraints it's also applied a Width constraint (all of them
with the same priority). But EasyPeasy is smart enough to prevent conflicts,
i.e. when replacing a Left and Right attributes with a CenterX attribute.
EasyPeasy provides a method extending UIView that clears all the constraints
installed in an UIView by the framework. This method is func easy_clear().
view.easy_clear()Animating constraints with EasyPeasy is very straightforward, just apply one
or more Attributes to your view within an animation block and you are ready to
go, without worrying about constraint conflicts. Example:
UIView.animateWithDuration(0.3) {
view <- Top(10)
view.layoutIfNeeded()
}Don't forget to clone the repository and run the example project to see EasyPeasy in action.
Note: the messages in the demo app aren't real and the appearance of those Twitter accounts no more than a tribute to some kickass developers :)
Alternatively, you can play with EasyPeasy cloning the Playground project available here.
EasyPeasy is a well documented framework and therefore all the documented classes and methods are available in Cocoadocs.
Carlos Vidal - @carlostify
EasyPeasy is available under the MIT license. See the LICENSE file for more info.