- This Java micro-server project demonstrates proficiency in microservices architecture and RESTful APIs for managing e-commerce inventory. It showcases the ability to create, retrieve, update, and delete inventory items using HTTP-based communication and data persistence.
- Features
- Requirements
- Getting Started
- API Endpoints
- Database
- Authentication
- Error Handling
- Entity Mapping: JPA entities for Supplier, Stock, Order, and OrderItem with defined relationships.
- Inventory Management API: CRUD operations for entities, stock management, and order management.
- Security: Implementation of Spring Security for restricted access and authentication mechanisms.
- Production-Ready Considerations: Error handling, validation, logging, and monitoring functionalities.
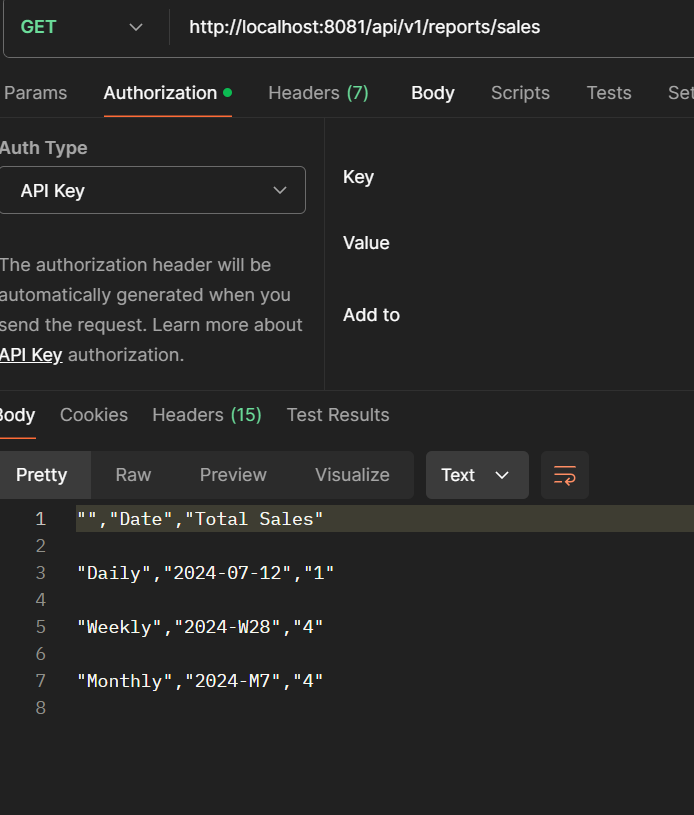
- Additional Functionalities: Low stock alerts, order status updates, and inventory reports.
- Java 17 or higher
- Maven 3.9 or higher
- PostgresSql 16 or higher
- Clone the repository:
- Navigate to the project and set up application.properties:
- cd fs17_java_inventory_service/src/main/resources
spring.application.name=inventory
# Setup postgres
spring.datasource.url=your database url
spring.datasource.username=your database username
spring.datasource.password=your database password
spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto=update
spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.dialect=org.hibernate.dialect.PostgreSQLDialect
logging.level.root=INFO
logging.level.org.springframework.web=DEBUG
logging.level.org.springframework.security=DEBUG
logging.level.org.hibernate.SQL=DEBUG
logging.level.org.hibernate.type.descriptor.sql.BasicBinder=TRACE
spring.config.import = env.properties
server.port=8081
# Email service
spring.mail.host=smtp.gmail.com
spring.mail.port=587
spring.mail.username=your email address
spring.mail.password=${EMAIL_PASSWORD}
spring.mail.properties.mail.smtp.auth=true
spring.mail.properties.mail.smtp.starttls.enable=true
# Monitoring
management.endpoints.web.exposure.include=*
management.endpoint.health.show-details=always
- Set up the environment variables (see Environment Variables).
- create .env file
SECRET_API_KEY=your api key
EMAIL_PASSWORD=your email password
- Maven installation
mvn clean install
- Run the server and should now be running on http://localhost:8081
- Suppliers
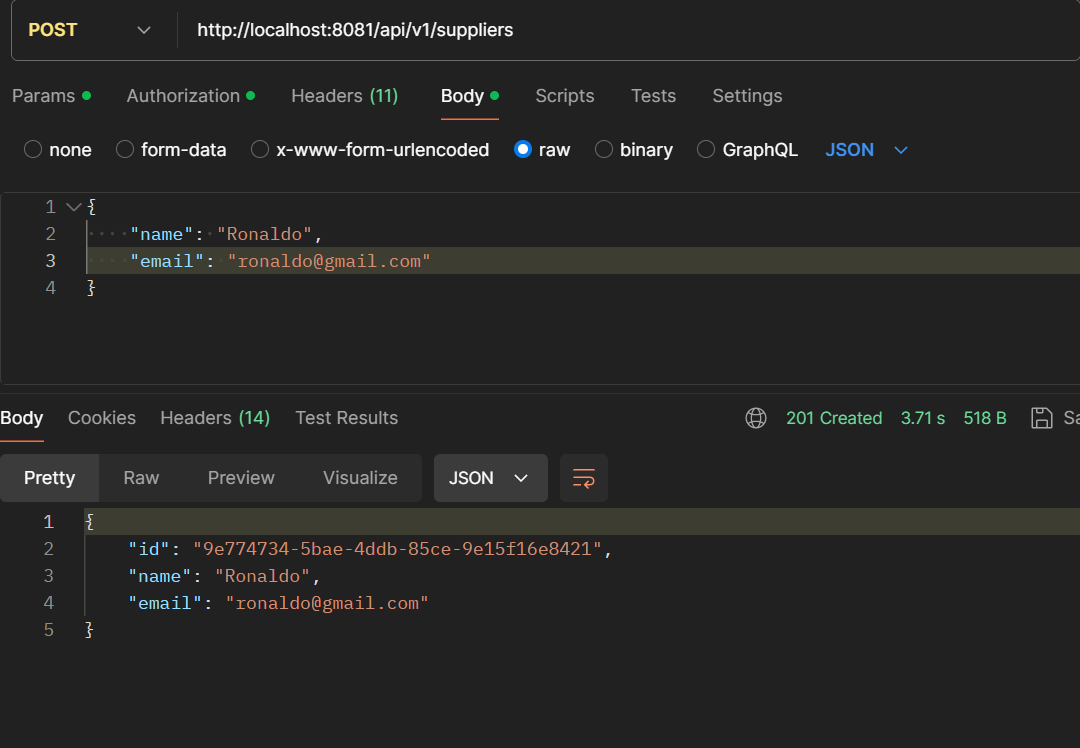
- POST /api/v1/suppliers: Create a new supplier.
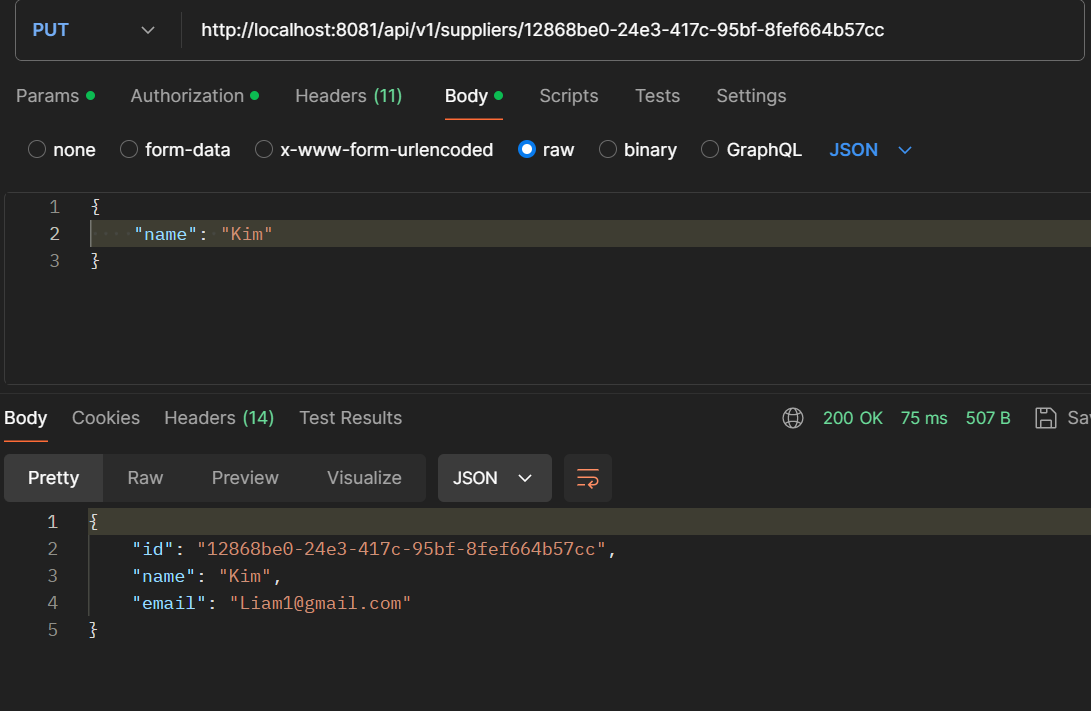
- PUT /api/v1/suppliers/{id}: Update supplier.
- GET /api/v1/suppliers: Get all suppliers.
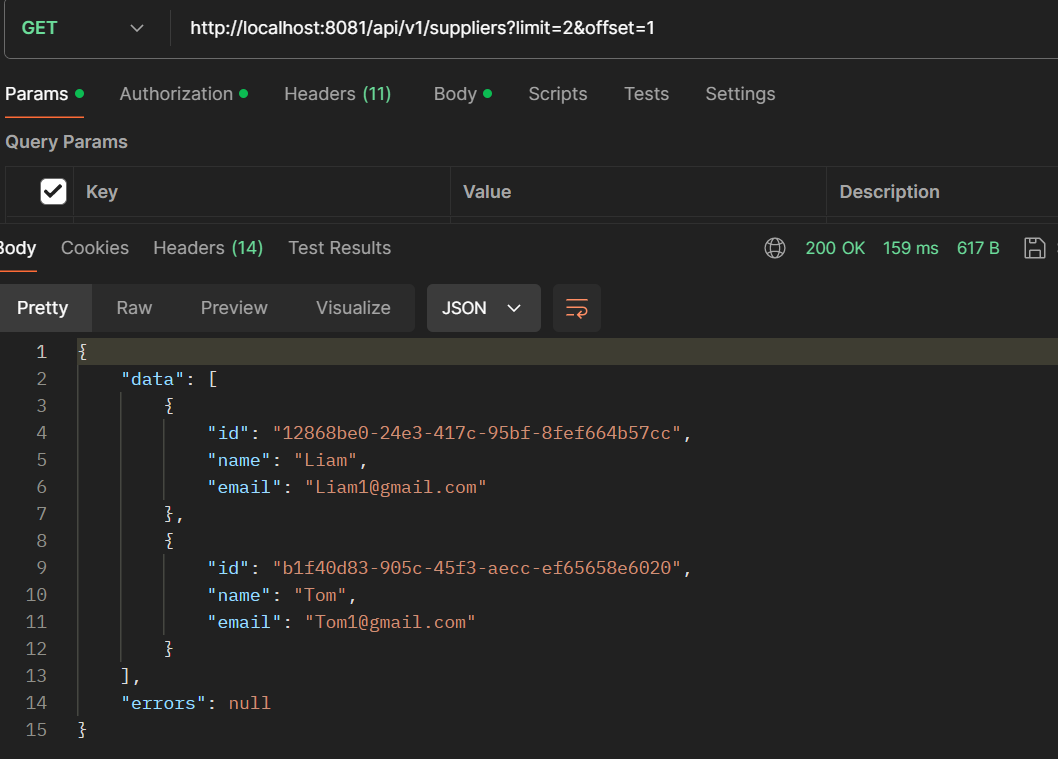
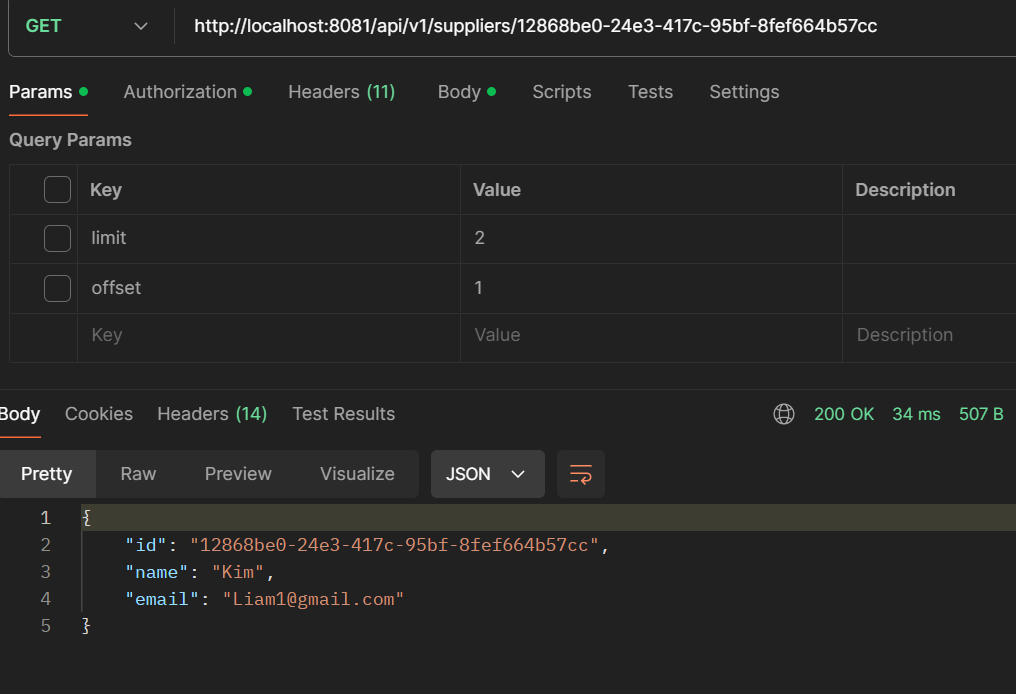
- GET /api/v1/suppliers/{id}: Get a single supplier.
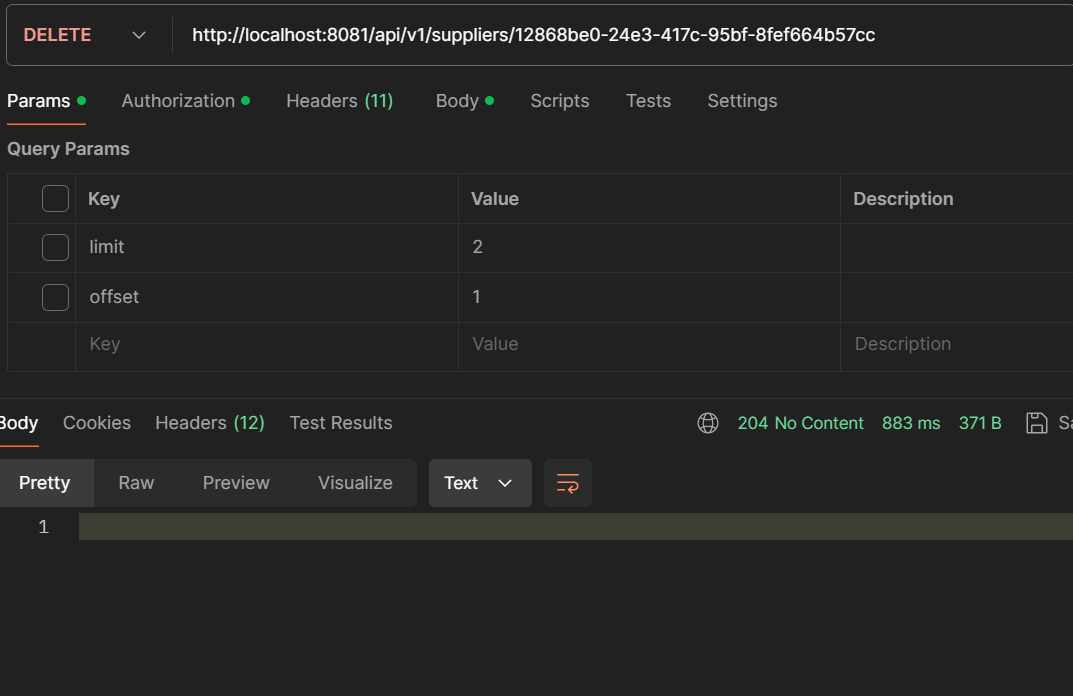
- DELETE /api/v1/suppliers/{id}: Delete a supplier.
- Stocks
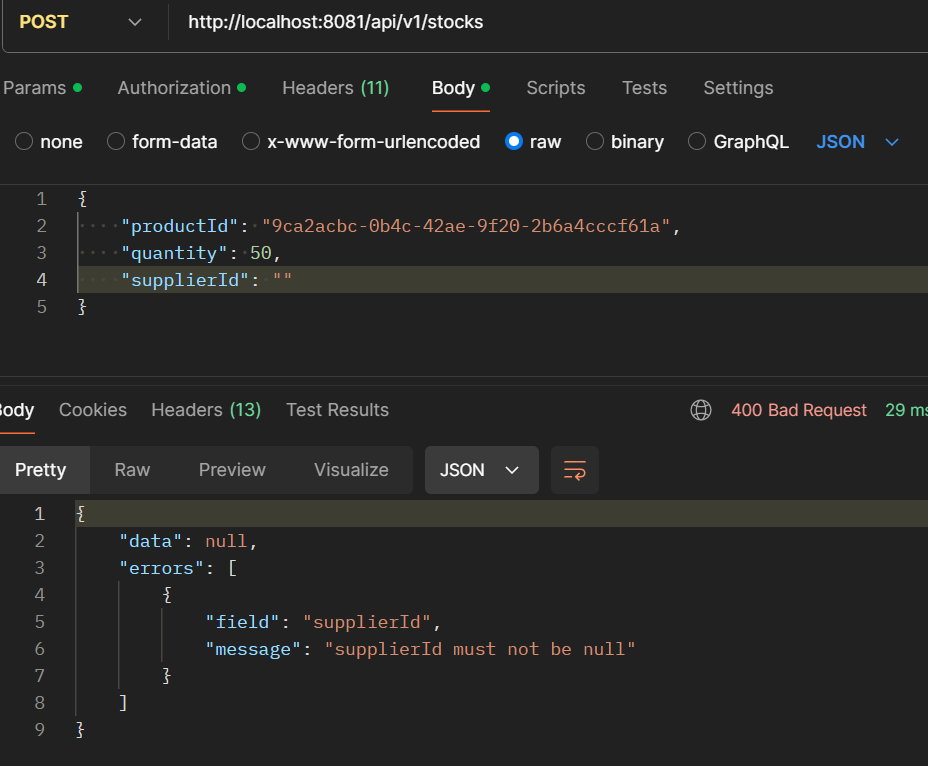
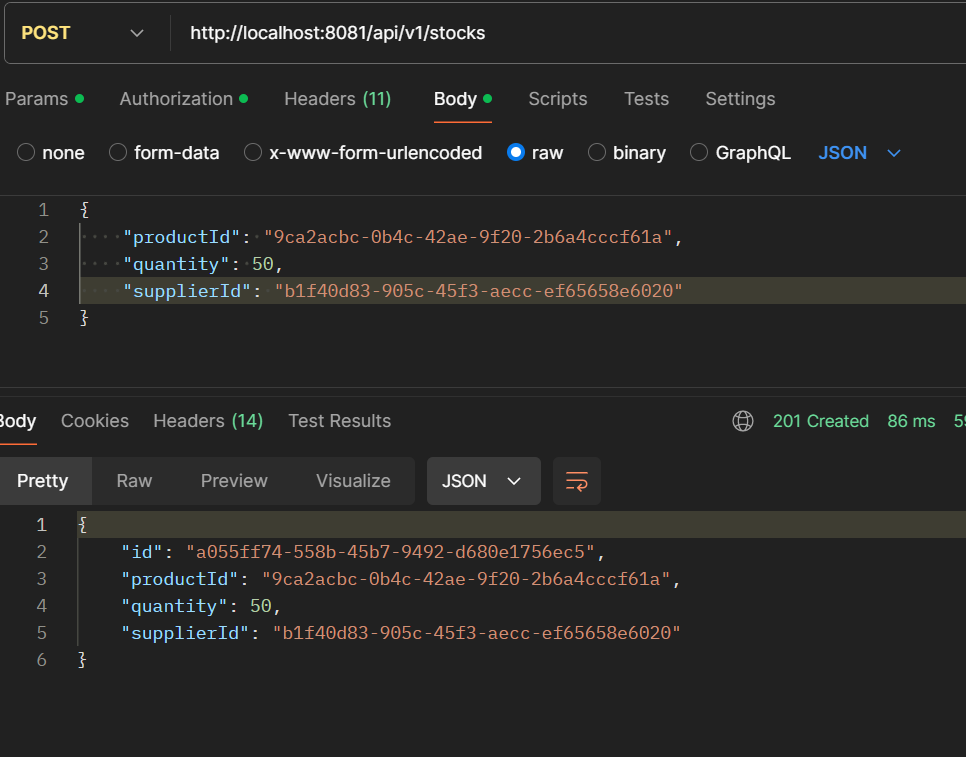
- POST /api/v1/stocks: Create a new stock.
- PUT /api/v1/stocks/{id}: Update stock.
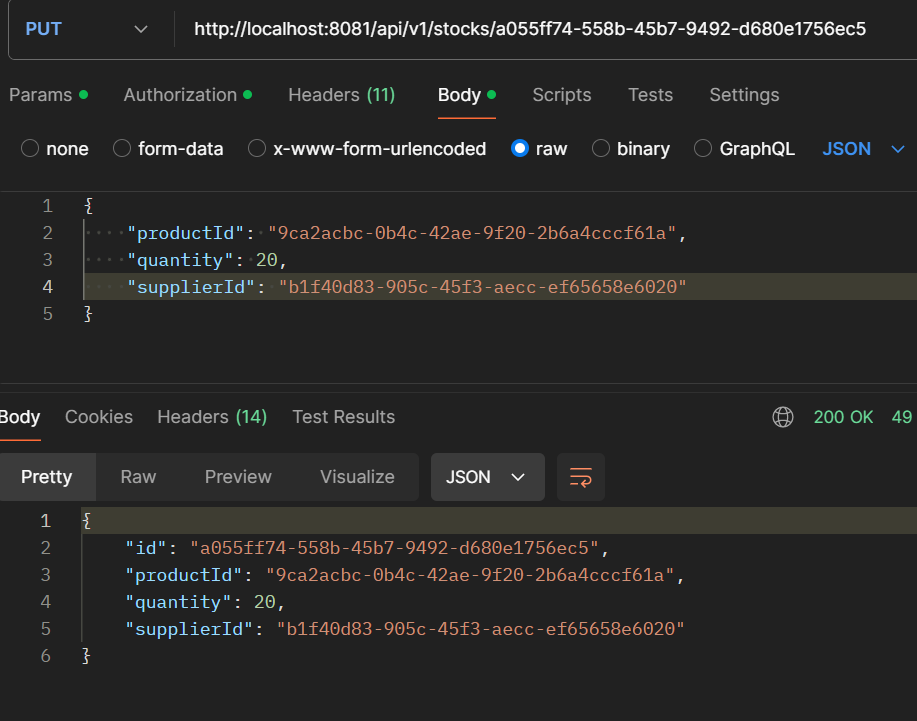
- GET /api/v1/suppliers: Get all stocks.
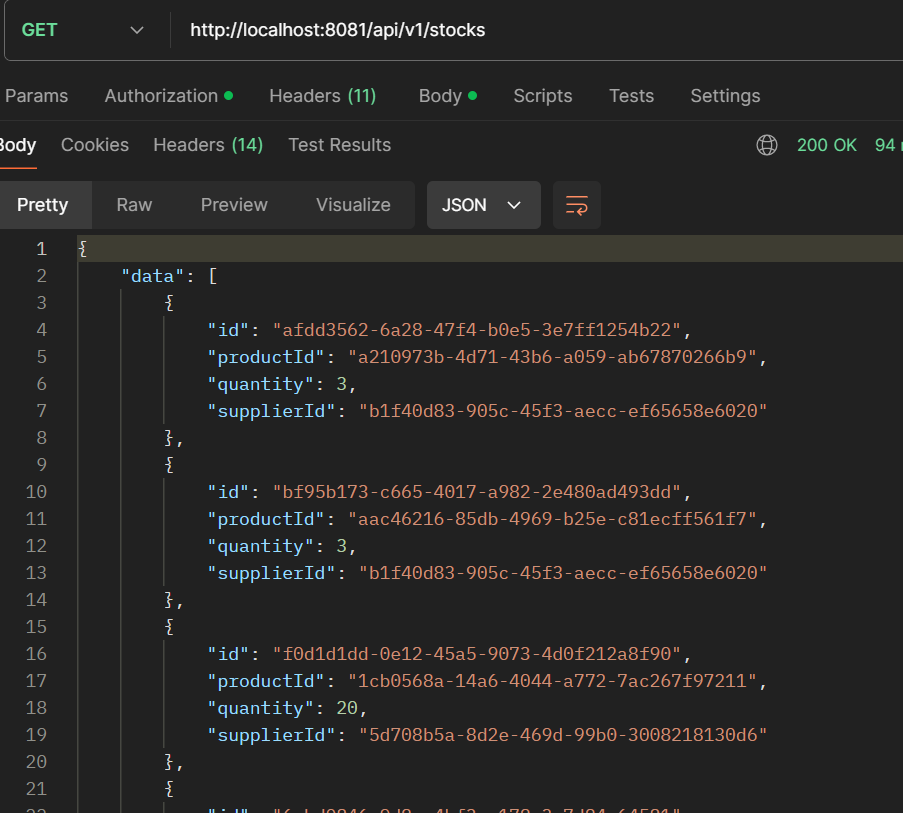
- GET /api/v1/stocks/{id}: Get a single stock.
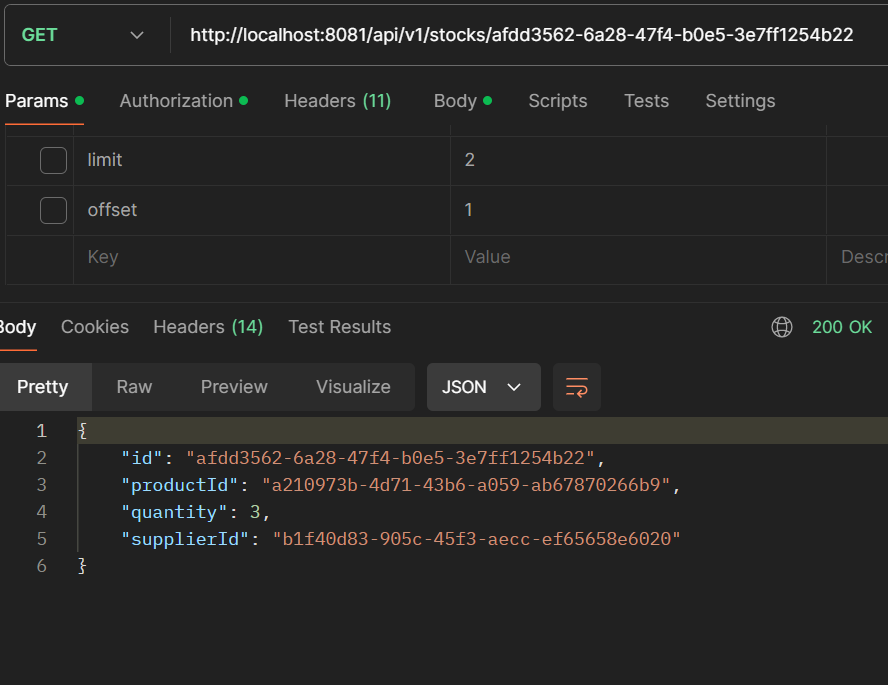
- DELETE /api/v1/stocks/{id}: Delete a stock.
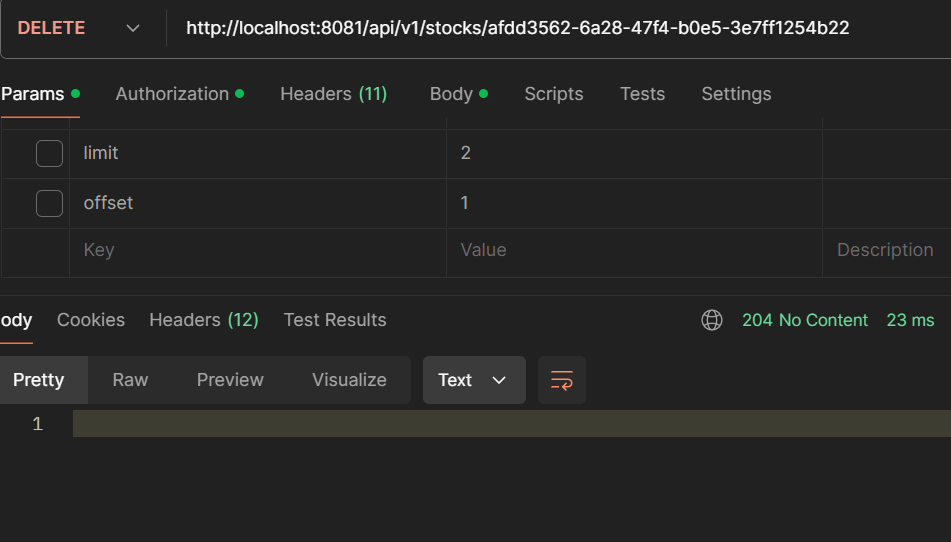
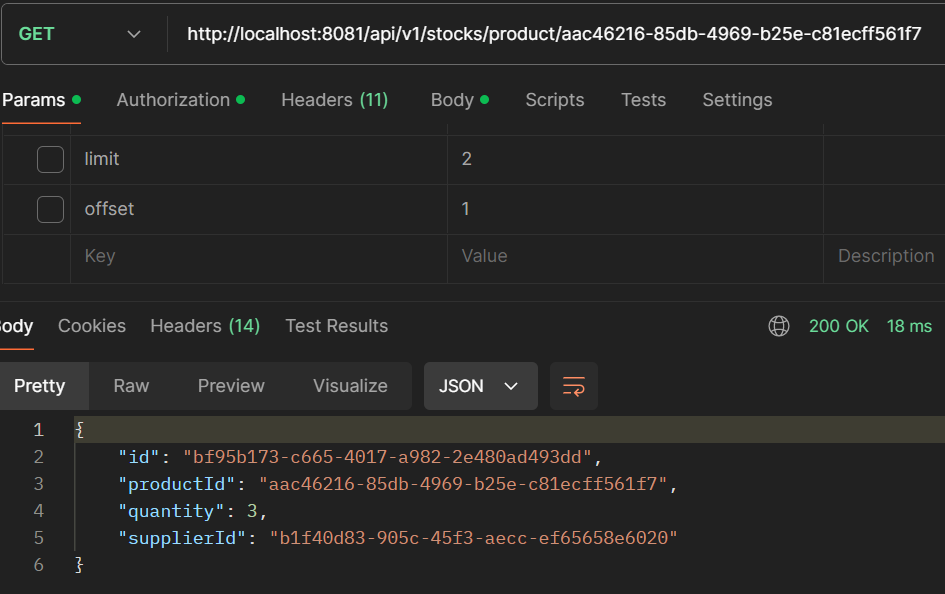
- GET /api/v1/stocks/product/{productId}: Get a stock by productId.
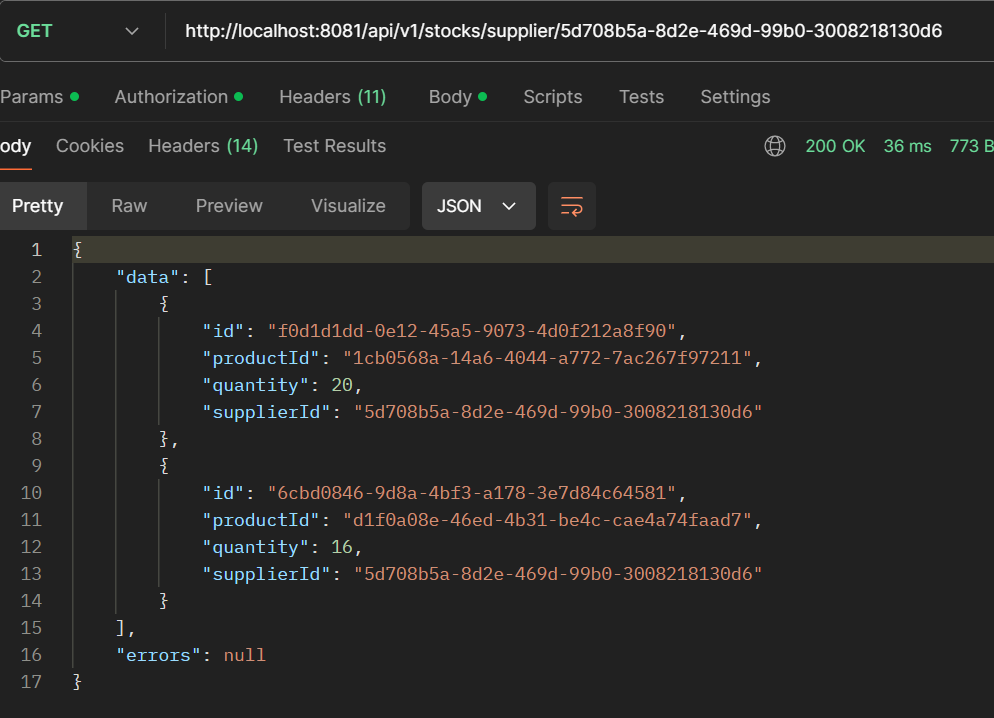
- GET /api/v1/stocks/supplier/{supplierId}: Get stocks by supplierId.
- Orders
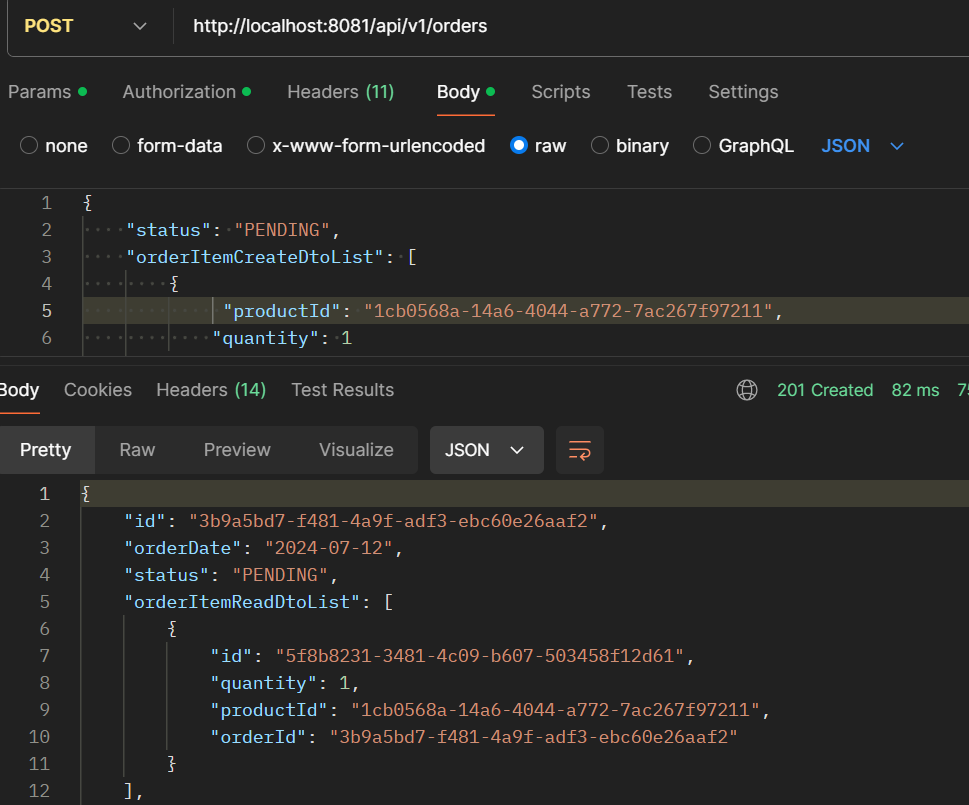
- POST /api/v1/orders: Create a new order.
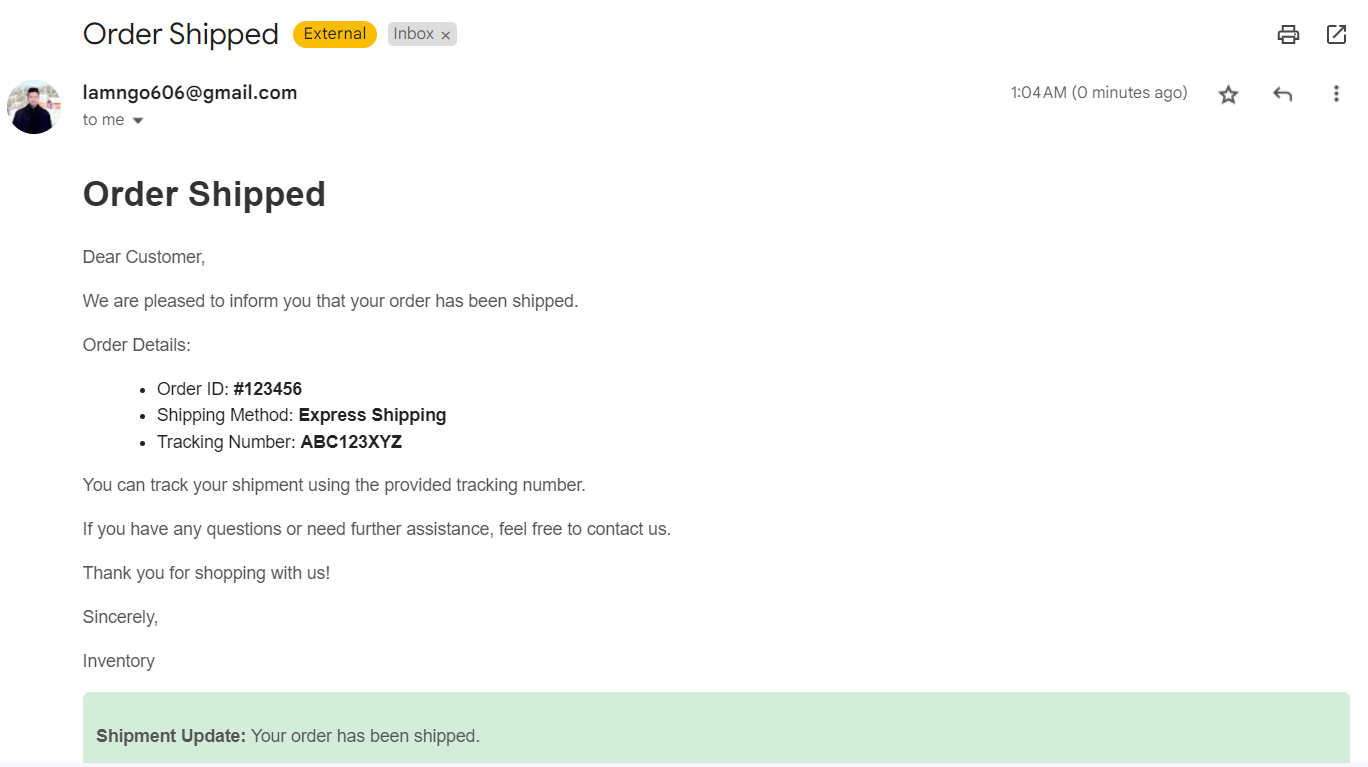
- PUT /api/v1/orders/{id}/status: Update order status.

- GET /api/v1/orders: Get all orders.
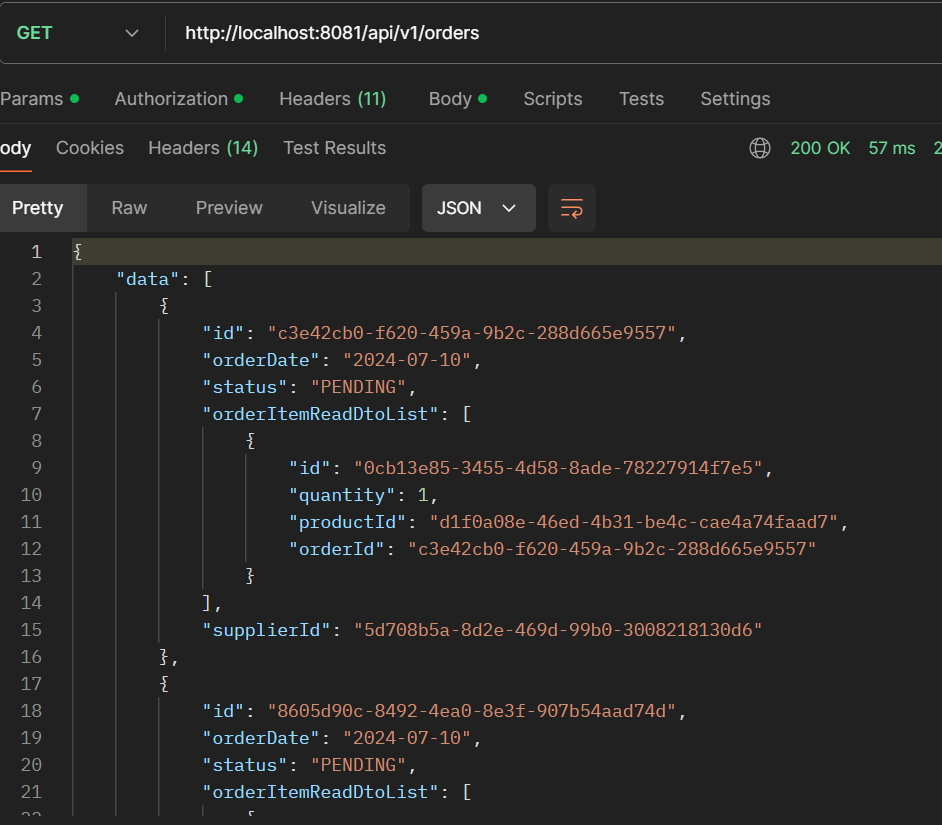
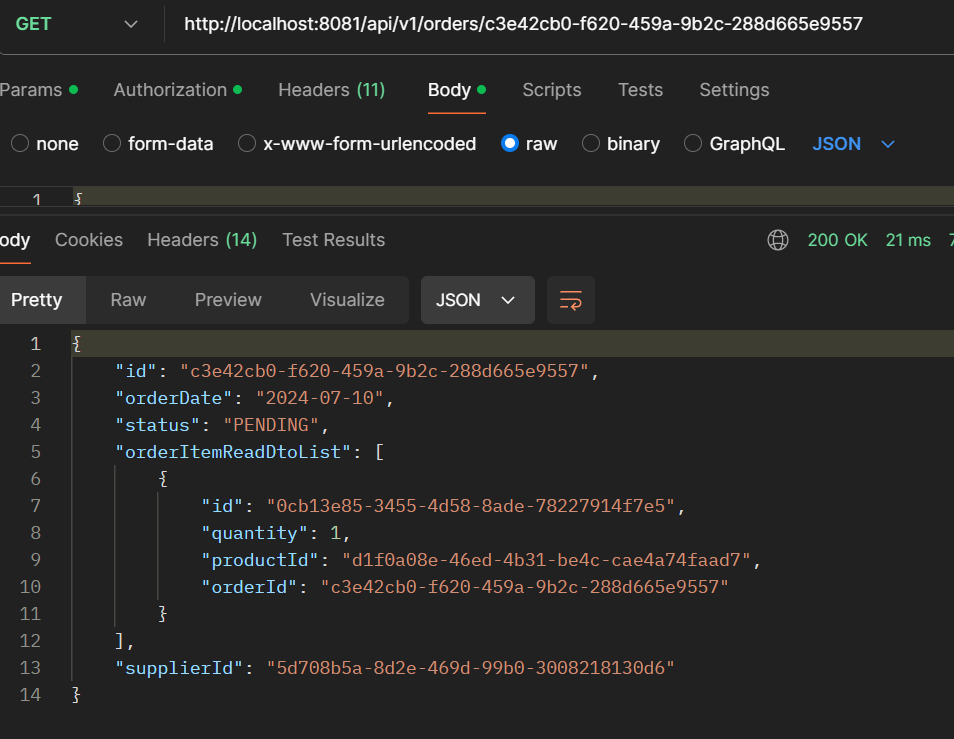
- GET /api/v1/orders/{id}: Get a single order.
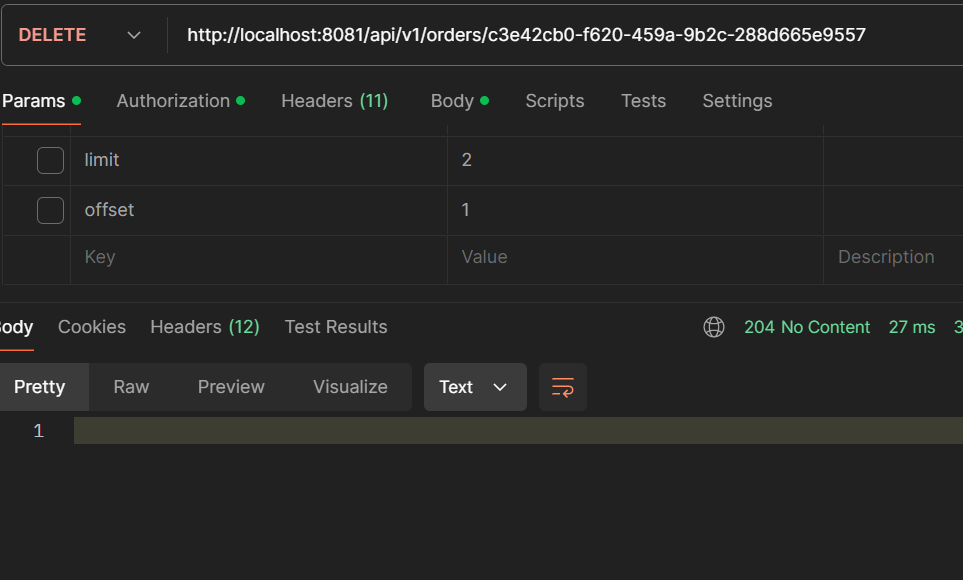
- DELETE /api/v1/orders/{id}: Delete an order.
- Reports
- This project uses PostgresSql as the database for storing data.
- Since this project was aiming at managing inventory without users, I only created Api key and set Role ADMIN for the routes to access to the endpoint.
- Make sure that I have Api key header and Api key value when you try to access to the endpoints.