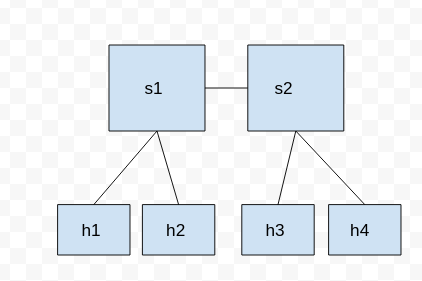
java -jar /target/floodlight.jarThis will create a simple tree topology
sudo mn --topo=tree,2 --mac --controller=remote,ip=127.0.0.1,port=6653 --switch ovsk,protocols=OpenFlow13verify it was connected by using pingall on mini net
pingall next add a link between h1 and h4 which will be invisible to the controller
py net.addLink(h1,h4)I use scapy for sniffing and forwarding. For now it forwarding all package, next step is to figure out which those are actually working so we can do injection attack
run these in mininet to open xterm for h1 and h4
xterm h1
xterm h4in xterm for h1
chmod +x relay_h1.py #make it executable
./relay_h1.py #start the scriptin xterm for h4
chmod +x relay_h4.py #make it executable
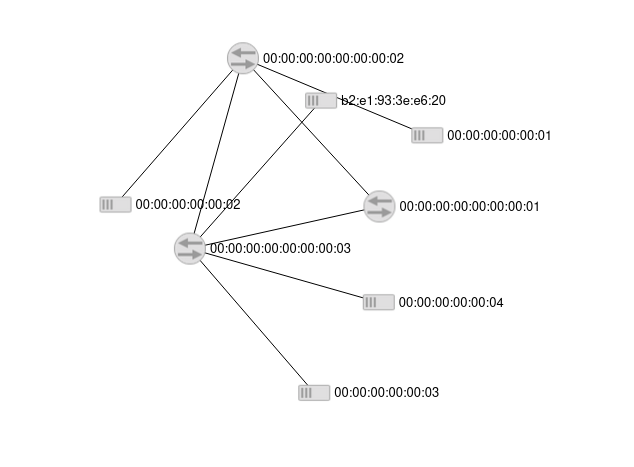
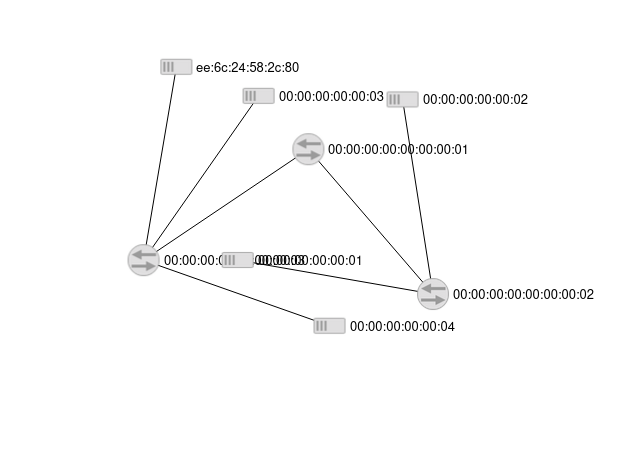
./relay_h4.py #start the scriptGive it couple second for next round of LLDP propagation, go to the GUI interface of floodlight localhost:8080/ui/index.html, you should see a fake link created between two switches
After stopping the attack the topology recoved
why there is an extra host?
The goal is to add flow rule to the switch and see how that impact the latency of LLDP packet.
- Python 3.9
- Floodlight v1.2
- mininet 2.3.1b1
- Ubuntu 22.04.1 LTS
h2 is constantly ping h4 and h4 will also change the ip address every time. In order to install new flow rule into S1 and S2
Have floodlight running first
In my environment the floodlight is running at 127.0.0.1:6653
sudo ./flow_rule_overload.pyYou can also change the frequency in the code by yourself which indicating ping/sec
There is two way you can check flow rule on each switch, you can either use this command in mininet CLI to check flow rule on s1
sh ovs-ofctl dump-flows s1This command will just return number of line, subtract by 1 is the number of flow rule on the switch
sh ovs-ofctl dump-flows s2 | wc -lFirst lets take look at sending 10 pings every sec
sudo ./flow_rule_overload.pyyou should see output
le_overload.py
[sudo] password for lamonkey:
*** Adding controller
*** Add s1
*** Add h1 and h2 to s1
*** Attach h3 h4 host to s2
*** Starting network
*** Configuring hosts
h1 h2 h3 h4
*** Starting switches
*** h2 begin install flowrule on s1 and s2
*** Starting CLI:
**** overloadingThen run
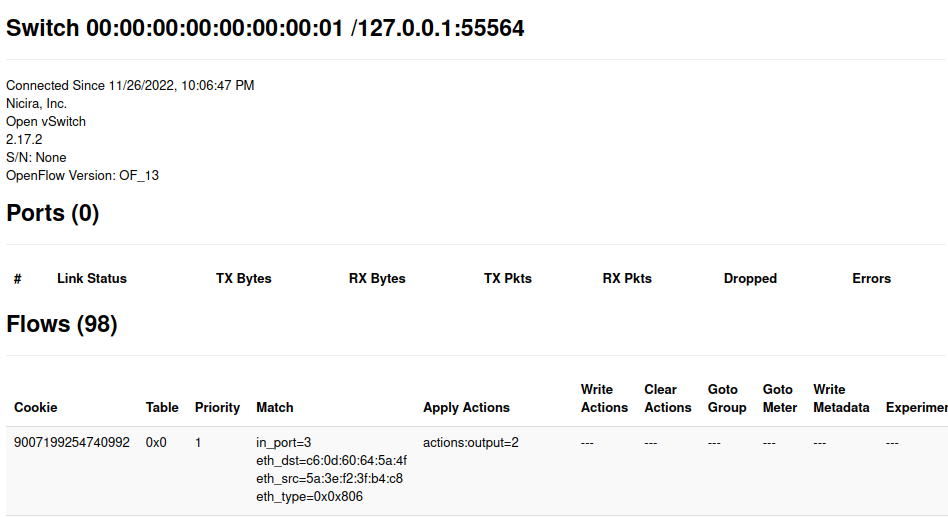
sh ovs-ofctl dump-flows s2 | wc -l98which indicate there is 97 flow rule on switch
also you can check floodlight gui for s1
Next we try 100 ping per sec
there is 650 flow rule installed this time.