LlamaIndex is a popular open-source framework for building RAG solutions, thanks to its abstractions of data connectors, indexes and processing engines. You will find a Jupyter notebook in this repo, which utilises LlamaIndex and Azure OpenAI models (GPT-4 and Embedding) to answer queries with pre-indexed local content.
Note: content file used in this demo was borrowed from Microsoft's Azure OpenAI + Azure AI Search open-source solution
To build this demo, I used the latest version of LlamaIndex (v0.10.19 at the time of writing). To upgrade your llama-index Python package, please use the following pip command:
pip install --upgrade llama-index
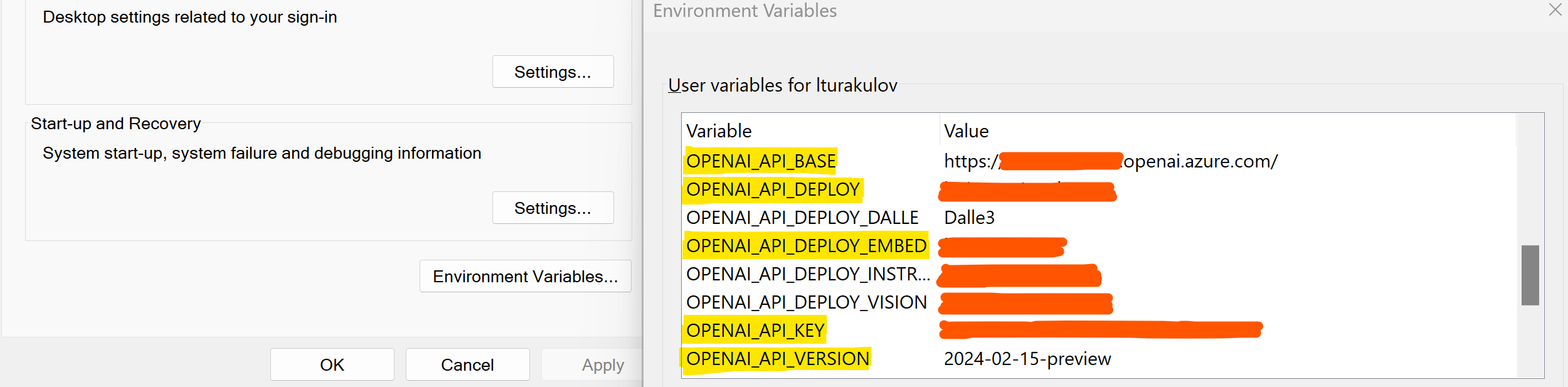
- To use Azure OpenAI backend, assign the API endpoint name, key and version, along with the Azure OpenAI deployment names of GPT and Embedding models to OPENAI_API_BASE, OPENAI_API_KEY, OPENAI_API_VERSION, OPENAI_API_DEPLOY (for GPT) and OPENAI_API_DEPLOY_EMBED (for Embedding) environment variables respectively.
- Install the required Python packages, by using the pip command and the provided requirements.txt file.
pip install -r requirements.txt
- Instantiate AzureOpenAI class with details of your GPT model (I'm using GPT-4 Turbo deployment).
llm = AzureOpenAI(
model = "gpt-4",
deployment_name = AOAI_DEPLOYMENT1,
api_key = AOAI_API_KEY,
azure_endpoint = AOAI_API_BASE,
api_version = AOAI_API_VERSION,
)- Instantiate AzureOpenAIEmbedding class with details of your Embedding model (I'm using text-embedding-ada-002 deployment).
Note: Assumptions are that both of your models are deployed in the same Azure OpenAI resource. If it's not the case, please adjust the values for Azure OpenAI endpoint and its API key accordingly.
embed_model = AzureOpenAIEmbedding(
model = "text-embedding-ada-002",
deployment_name = AOAI_DEPLOYMENT2,
api_key = AOAI_API_KEY,
azure_endpoint = AOAI_API_BASE,
api_version = AOAI_API_VERSION,
)- Next step is to set the Azure OpenAI deployments as default LLM and Embedding models in LlamaIndex's configuration settings.
Settings.llm = llm
Settings.embed_model = embed_model- We can now use the SimpleDirectoryReader class to create Document objects from all files in a given directory. In our case, the data directory contains single markdown file with description of a fictitious company, Contoso Electronics.
documents = SimpleDirectoryReader(input_dir="data").load_data()- VectorStoreIndex class can help us to chunk our Document objects, generate vector embeddings and index them in a vector store.
index = VectorStoreIndex.from_documents(documents)- We can use our vector store as a query engine to retrieve required content and feed it to the GPT-4 Turbo model for reasoning, e.g. to describe vacation perks available at Contoso.
query_engine = index.as_query_engine()
answer = query_engine.query("What are the vacation perks at Contoso Electronics?")- If successful, you should get an output similar to this one:
Query: What are the vacation perks at Contoso Electronics?
-----------------
Answer: At Contoso Electronics, the vacation perks are structured into three tiers:
1. Standard Tier: Employees receive 2 weeks of vacation with a health and wellness stipend.
2. Senior Tier: Employees receive 4 weeks of vacation along with travel vouchers for a dream destination.
3. Executive Tier: Employees are granted 6 weeks of vacation and a luxury resort getaway with family.