- Realtek 8723BS is not working properly. It overloads the system. Bitrate can be very valueable and unstable. Sometimes connection hanged. There is an alternative Realtek 8723BS driver. But if you want to compile it with the current kernel you will fail because there is no kernel headers with the right version compatible with the loaded kernel. Alternative driver is loading faster and works more stable. It gives no highest speed but it gives a stability.
- Alternative driver gives an ability to change channel etc.
- System looks like it was used with different versions of mcu, has a lot of strange services and misconfigurations (i.e. damaged logrotate configuration files).
- Kingroon support didn't help. They just said "You can buy a wifi signal receiver yourself to increase the signal. In this case, the effect should be better." Of course i can buy another adapter and of course another printer. But it is already has embeded wifi adapter and there is a way to make it work better so why not?
- I want to dig deep into the setting process to develop my experience.
- USB Type C cable to connect the printer to PC for serial port connection.
- Kingroon KP3SPro V2 with Cheetah V2.0 Motherboard (WARNING. NOT Cheetah V2.2 (it has some difference. THR plate connected as serial and mcu as USB dev. Moreover firmware image filename which bootloader should recognize is unknown)
- Plate in the extruder should be recognized in the printer OS as RP2040 (OpenMoko, Inc. rp2040)
- MKS EMMC Adapter V1.0 or analog (supplied included). It is possible to change system image without printer disassembling check here
- microSD card reader suitable to work with EMMC (read below)
- Virtual Machine or PC with Linux (i.e. Ubuntu/Xubuntu) and docker installed install docker in ubuntu
- Ability to solve common linux problems (missed dependencies, software and so on).
- Time and patience
First of all clone mkspi repository and build your own Armbian image. Assumed docker is already installed and you can resolve any issues caused by missing dependencies.
mkdir Kingroon && cd Kingroon && git clone https://github.com/redrathnure/armbian-mkspi &&
cd armbian-mkspi &&
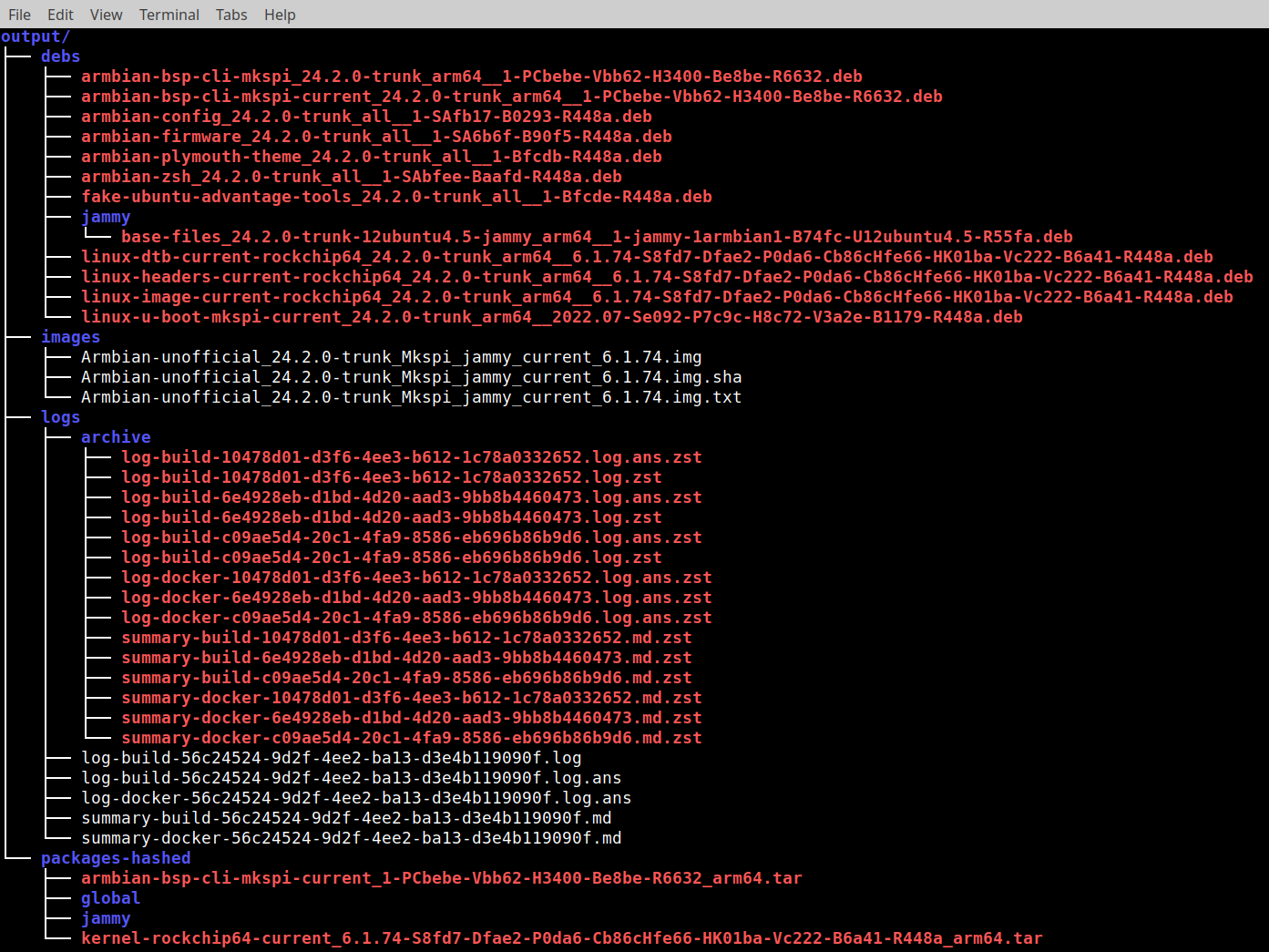
./compile.shNow you just need to have patience (it takes about an hour depending on your PC hardware). As the result of building you will get some files in an output directory as shown on a picture.
output directory tree
The required package to build Realtek 8723BS driver is located in debs directory:
linux-headers-current-rockchip64_24.2.0-trunk_arm64__6.1.74-S8fd7-Dfae2-P0da6-Cb86cHfe66-HK01ba-Vc222-B6a41-R448a.deb
The Armbian image is located in images directory:
Armbian-unofficial_24.2.0-trunk_Mkspi_jammy_current_6.1.74.img
In case you do not want to disassemble the printer or you do not have an emmc adapter you can use USB flash drive. Prepare USB flash drive:
sudo dd if=$(ls armbian-mkspi/output/images/*.img) of=/dev/sdb bs=1M status=progress && syncAnd copy armbian image somewhere to root partiotion of this flash drive to have it after booting available. Then we need to boot printer from this USB flash drive. Uboot bootloader autoboot process can be interrupted by hiting any key. But it has no bootdelay for that by default. So you need to hiting any key too fast and sometimes it works. To do that you need to start serial communication program like minicom:
minicom -b 1500000 -D /dev/ttyUSB0Baud rate should be 1500000 to see booting log corectly. Then reboot your printer and start hiting an any key as fast as you can :-) If failed reboot and try to hit faster. If success you will see an uboot prompt:
Hit any key to stop autoboot: 0
=>
=>
Change boot_targets environment variable:
setenv boot_targets "usb0 mmc1 mmc0 pxe dhcp"
By default the first booting device is mmc1. And type "boot". When it boots you should follow the provided steps (create root password, user etc). After that you can use dd to deploy armbian image to /dev/mmcblk1. Reboot and repeat the previous step.
Remove the bottom cover of your KP3SProV2 and unscrew two screws fastening the EMMC module. Put the EMMC card into microSD adapter (supplied included) and insert it into your PC. Some adapters are not working with Makerbase EMMC-microSD adapter. For example Kingston MobiLite G4 is not working.
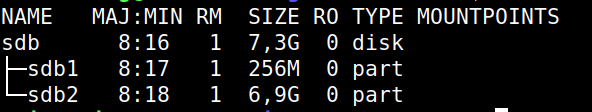
After insertion of EMMC into USB appears a new block device like /dev/sdb in lsblk output:
Create backup of your current system:
mkdir backup &&
sudo dd if=/dev/sdb of=./backup/backup.img bs=1M status=progress &&
syncThis image contains all files of your current system and it will be needed during next steps so we mount it right after dd completed.
sudo losetup --partscan --find --show ./backup/backup.imgIn Xubuntu it will mount automatically to /media/$USER/ and commands are assumed that.
Deploy an builded Armbian image to /dev/sdb
sudo dd if=$(ls armbian-mkspi/output/images/*.img) of=/dev/sdb bs=1M status=progress && syncIt will mount automatically again after dd finishes. Now we need to copy the linux-headers package and an old dtb file and old configurations to EMMC (with a new dtb wifi is not working).
linux-headers package:
sudo cp $(ls armbian-mkspi/output/debs/linux-headers*.deb) /media/$USER/armbi_root/root/old dtb file:
sudo mv /media/$USER/armbi_boot/dtb/rockchip/rk3328-roc-cc.dtb /media/$USER/armbi_boot/dtb/rockchip/rk3328-roc-cc.dtb.bck &&
sudo cp /media/$USER/BOOT/dtb/rockchip/rk3328-roc-cc.dtb /media/$USER/armbi_boot/dtb/rockchip/rk3328-roc-cc.dtbOld configurations (check GUID in path to the mounted image of an old system):
sudo cp -a /media/$USER/4148ed1f-7865-4fd6-84b0-9564c15dbeac/home/mks/printer_data /media/$USER/armbi_root/root/Now we are ready to turn back EMMC to the printer boot it and make the first login atempt. The first login we should do as root and with password 1234 (default for Armbian official image).
Ethernet adapter should work so you can connect it to your router and try to enter with root through ssh if it is not disabled. Instead you can use USB type C cable and connect the printer to your PC (usb type-c socket is located on the front panel of the printer). Then you can use something like minicom to connect to the serial console of the printer. After is everything connected you can turn printer on and start minicom.
minicom -b 115200 -D /dev/ttyUSB0If everything is go as it should be you can see something like this in a terminal window:
After some minuts hit enter few times and you can get a greeting to login. Otherwise try to turn the printer off and on. After printer is turned off wait until all LED are turned off especially LEDS on the motherboard. You can see it throught the bottom cooler holes on your table. This is important because the power supply keeps giving the energy to it during its capacitors are discharging. Login with root and password 1234 and answer all questions. It will create new user (I used mks with password makerbase as it should be from the box). You can try to connect via wireless but for me it doesn't work. So I skiped this stage. Now you can set wired connection manually and connect to the printer though ssh. I connected the printer to laptop and use it as a router for the printer.
Configure laptop as router and printer as client manually
Laptop:
#protect interface of beeing managed by network manager
nmcli device set enp43s0 managed off
#turn on NAT for printer where 192.168.2.2 is a printer ethernet interface address
#and 192.168.1.11 is the address of the laptop given by WiFi router
sudo iptables -t nat -A POSTROUTING -s 192.168.2.2 -j SNAT --to 192.168.1.11
#add address to the laptop ethernet interface
sudo ip addr add 192.168.2.1/24 dev enp43s0
#enable ip forwarding in the kernel
sudo sysctl net.ipv4.ip_forward=1 Printer:
nmcli device set eth0 managed off
#set ip address on ethernet interface
ip addr add 192.168.2.2/24 dev eth0
#set default route through the laptop
ip route add default via 192.168.2.1To have a key authorization you can run:
ssh-copy-id mks@192.168.2.2Freeze important packages:
armbian-configChoose System -> Freeze (Disable Armbian kernel packages)
Create sudoers file to have sudo without a password:
sudo bash -c 'cat <<EOF >/etc/sudoers.d/mks
mks ALL=NOPASSWD: ALL
EOF'Compile and install new driver Armbian documentation:
apt-get install -y libelf-dev &&
dpkg -i /root/linux-headers*.deb &&
git clone https://github.com/youling257/rockchip_wlan &&
cd rockchip_wlan/rtl8723bs &&
make ARCH=arm64Check if compiled module works:
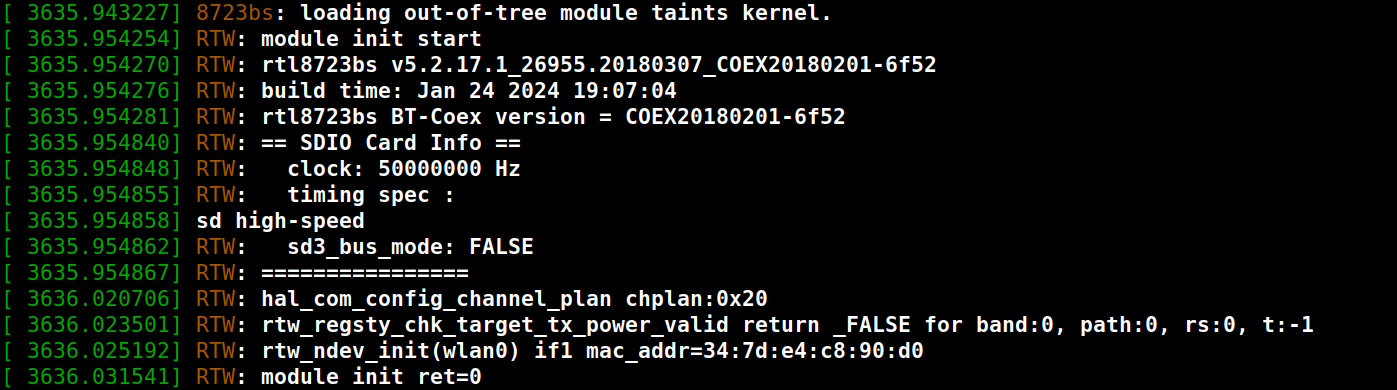
rmmod r8723bs &&
insmod 8723bs.koIf everything is ok in dmesg will be something like this:
Now you can install it at the same place where an old is located:
make -B MODDESTDIR=/lib/modules/$(uname -r)/kernel/drivers/staging/rtl8723bs/ installPut an old driver to modprobe blacklist:
sudo bash -c 'cat <<EOF >/etc/modprobe.d/blacklist-r8723bs.conf
blacklist r8723bs
EOF'Now you can reboot your printer by executing reboot command to check if the new module is loading. After reboot you can try to connect to a wireless network. Create wpa_supplicant.conf file:
sudo bash -c 'cat <<EOF >/etc/wpa_supplicant/wpa_supplicant-wlan0.conf
country=US
ctrl_interface=DIR=/var/run/wpa_supplicant GROUP=netdev
update_config=1
EOF'
Enable wpa_supplicant on wlan0 interface:
sudo systemctl enable wpa_supplicant@wlan0 &&
sudo systemctl start wpa_supplicant@wlan0Run wpa_cli and enter the following commads:
add_network
set_network 0 ssid "YOUR_SSID"
set_network 0 psk "YOUR_KEY"
set_network 0 key_mgmt WPA-PSK
set_network 0 proto WPA2
enable_network 0
save_config
quit
Enable DHCP on wlan0 interface
sudo bash -c 'cat <<EOF >/etc/network/interfaces.d/wlan0
auto wlan0
iface wlan0 inet dhcp
EOF'
Restart networking:
sudo systemctl restart networkingWork under mks user. Clone and use kiauh as described Here:
git clone https://github.com/th33xitus/kiauh.git &&
./kiauh/kiauh.shSelect software to install.
Klipper: 1->1->1->1
Moonraker: 2
Fluidd: 4
After installation completed we need to compile new klipper firmware and binary read here and here. I tried to use a new binary with an old firmware but it is not completely compatible and throws an error.
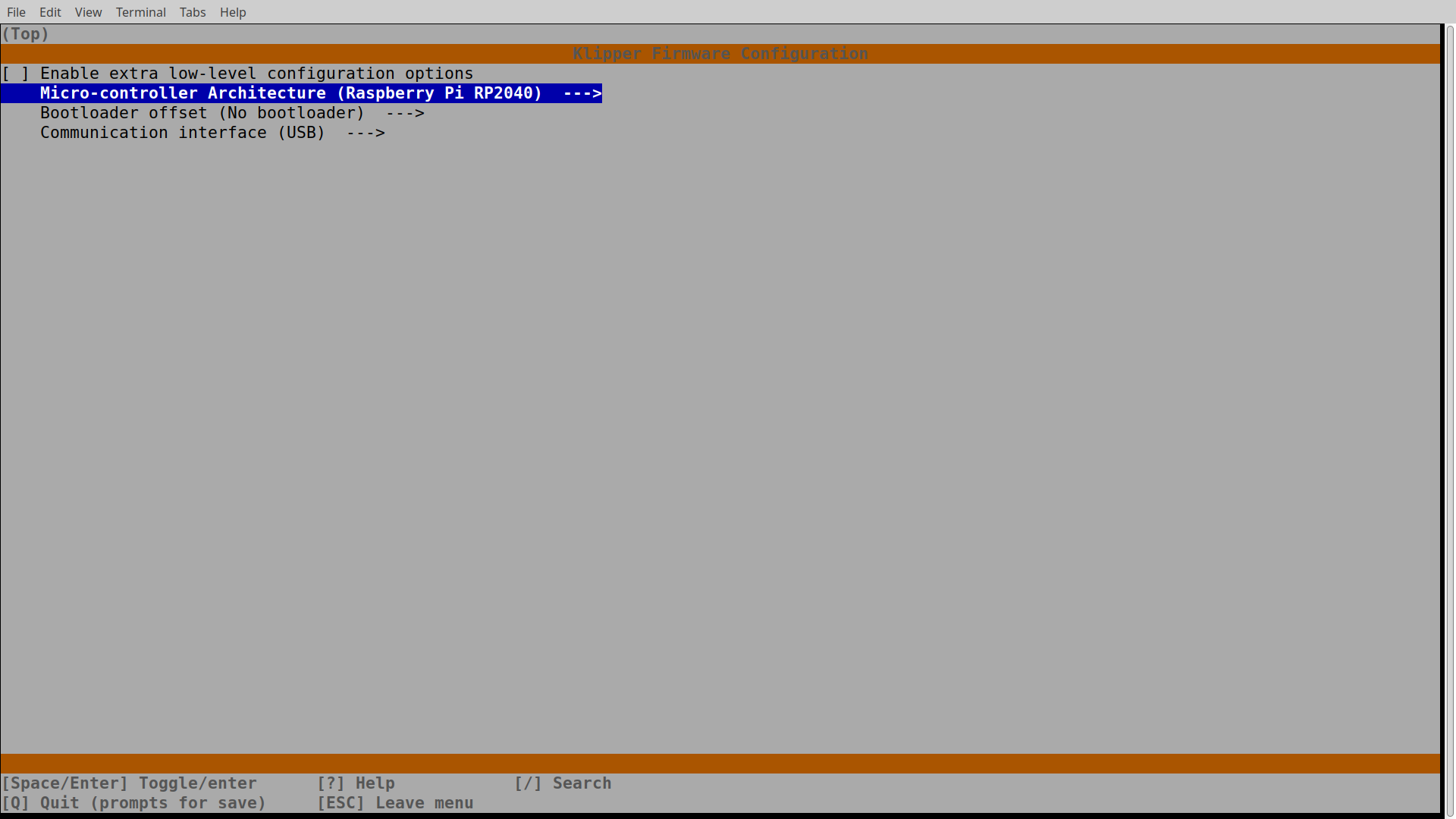
All described is suitable for Raspberry Pi RP2040. You can check if it is exists with command lsusb. It should be something like this:
Bus 001 Device 002: ID 1d50:614e OpenMoko, Inc. **rp2040**
Run:
cd /home/mks/klipper &&
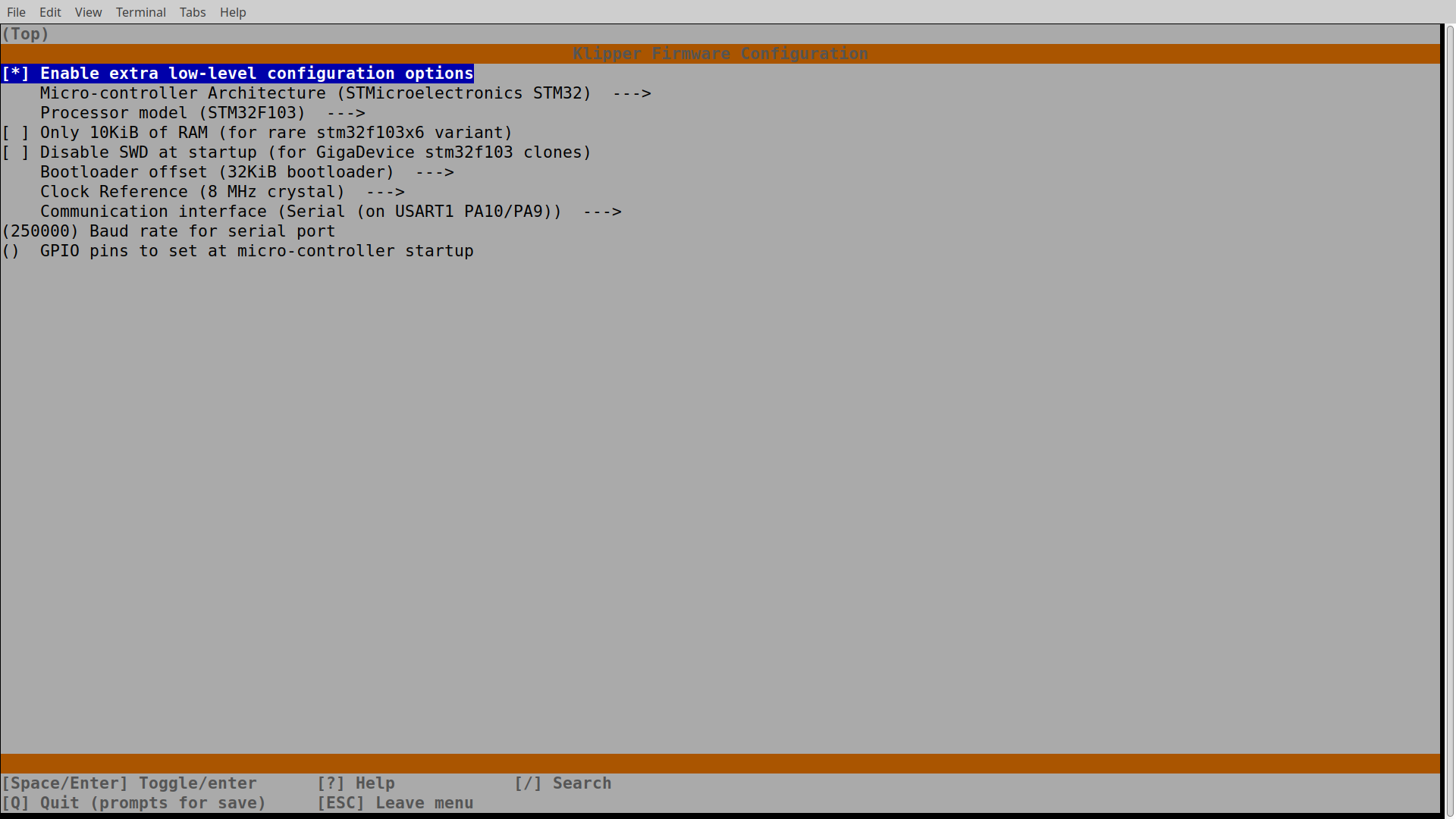
make menuconfigCheck if your MCU is available by path /dev/serial/by-id/. Otherwise try to turn your printer off and on. Instead of powering your printer off you can press RESET button under the cooler cover. Flash MCU with compiled firmware:
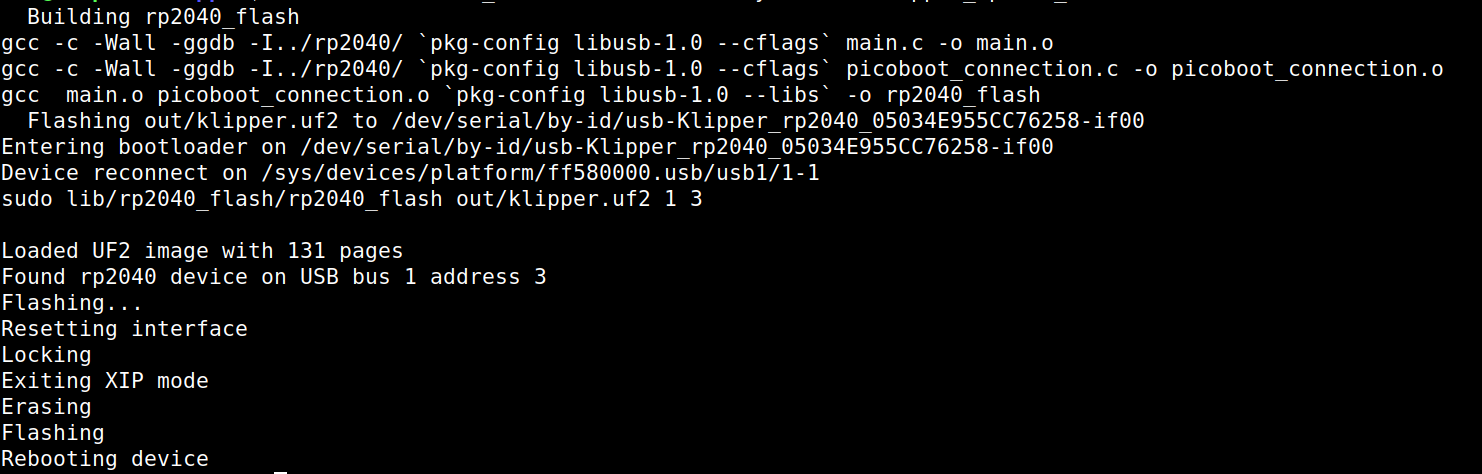
make flash FLASH_DEVICE=/dev/serial/by-id/usb-Klipper_rp2040_05034E955CC76258-if00
make menuconfigmakeDon't want to use external external SD card reader or copying files manually?
FatFS module included in klipper repository has no long file names support enabled (why so?) We need to enable it.
Edit file:
mcedit /home/mks/klipper/lib/fatfs/ffconf.h
Set:
#define FF_USE_LFN 0
to:
#define FF_USE_LFN 1
Edit file:
mcedit /home/mks/klipper/scripts/spi_flash/fatfs_lib.py
Set:
char name[13];
to:
char name[255];
Add board defenition:
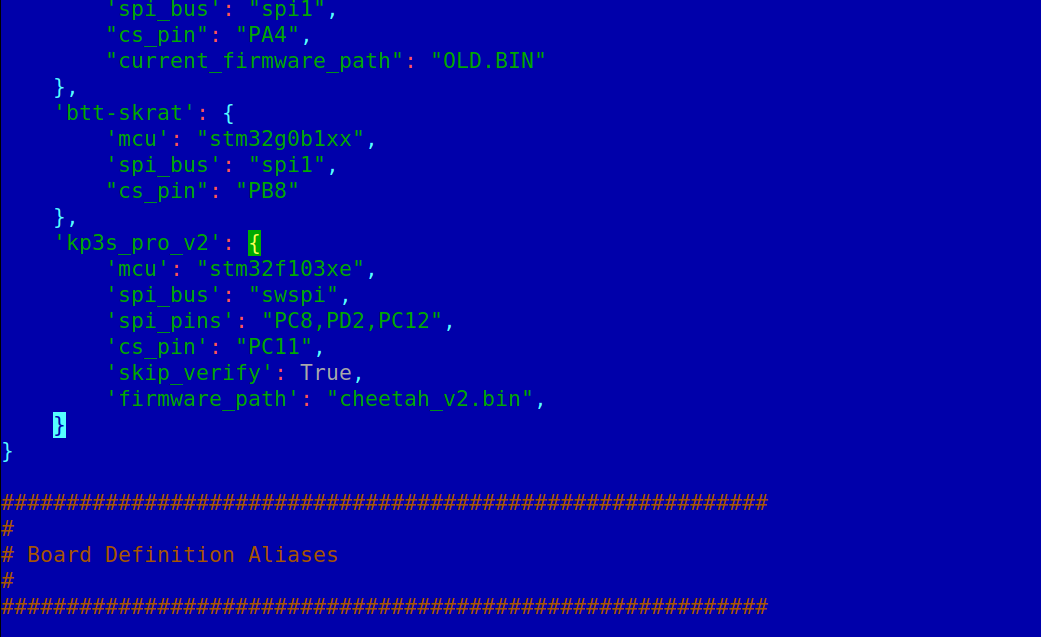
mcedit /home/mks/klipper/scripts/spi_flash/board_defs.py
Add the following lines to BOARD_DEFS dictionary:
'kp3s_pro_v2': {
'mcu': "stm32f103xe",
'spi_bus': "swspi",
'spi_pins': "PC8,PD2,PC12",
'cs_pin': "PC11",
'skip_verify': True,
'firmware_path': "cheetah_v2.bin"
}
SD card should be in printer SD card slot at this moment. Now run the following command:
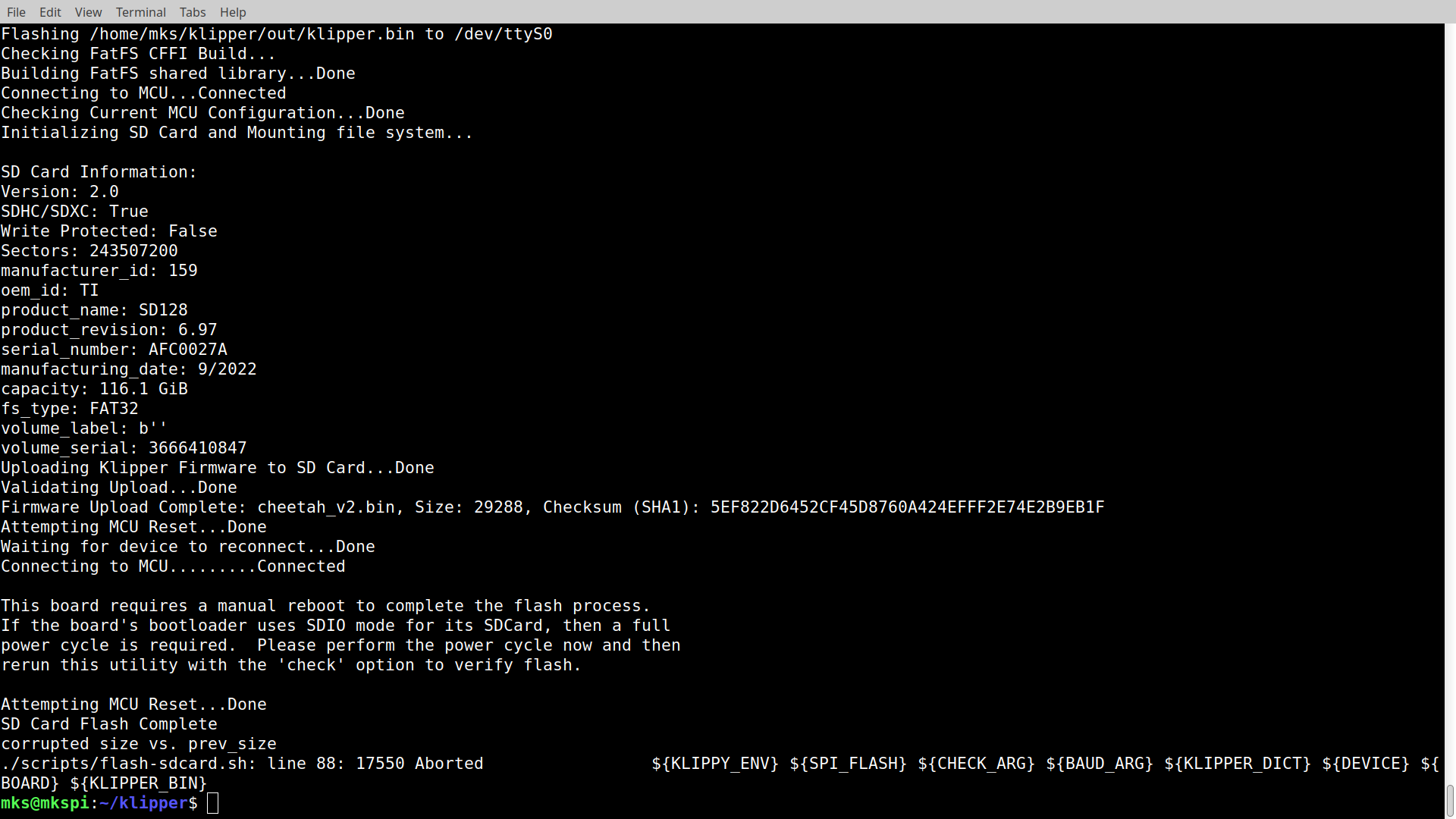
./scripts/flash-sdcard.sh /dev/ttyS0 kp3s_pro_v2Beeper will make the sound.
Result:
Ignore this error. Now just need to turn printer off and on with poweroff command. After establishing ssh connection run the following command from the klipper directory:
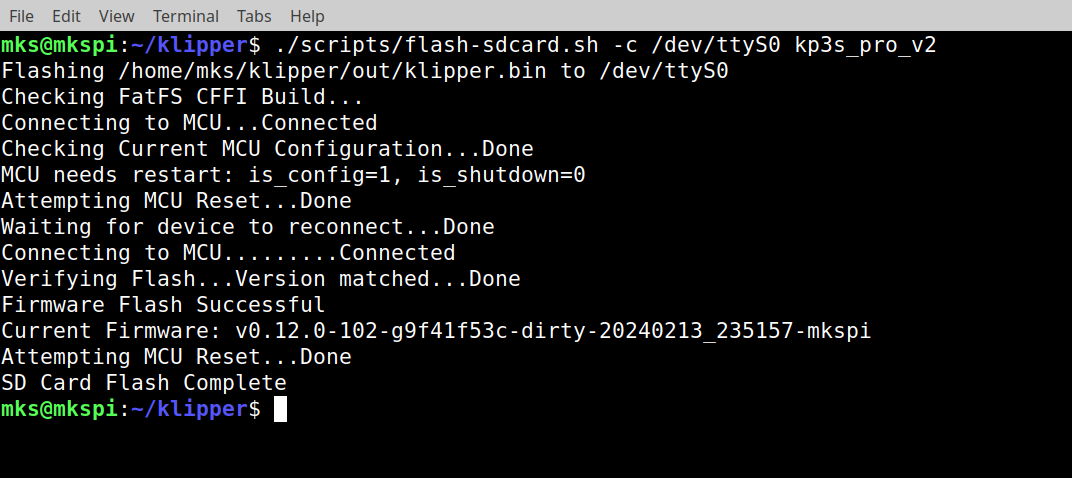
./scripts/flash-sdcard.sh -c /dev/ttyS0 kp3s_pro_v2It will compare flashed firmware with its image on the host system. If everything is ok then result will be:
After building copy klipper.bin file to SD card with name cheetah_v2.bin (filename is important). Put SD card into printer card slot turn it off and on.
How to get an actual firmware file name
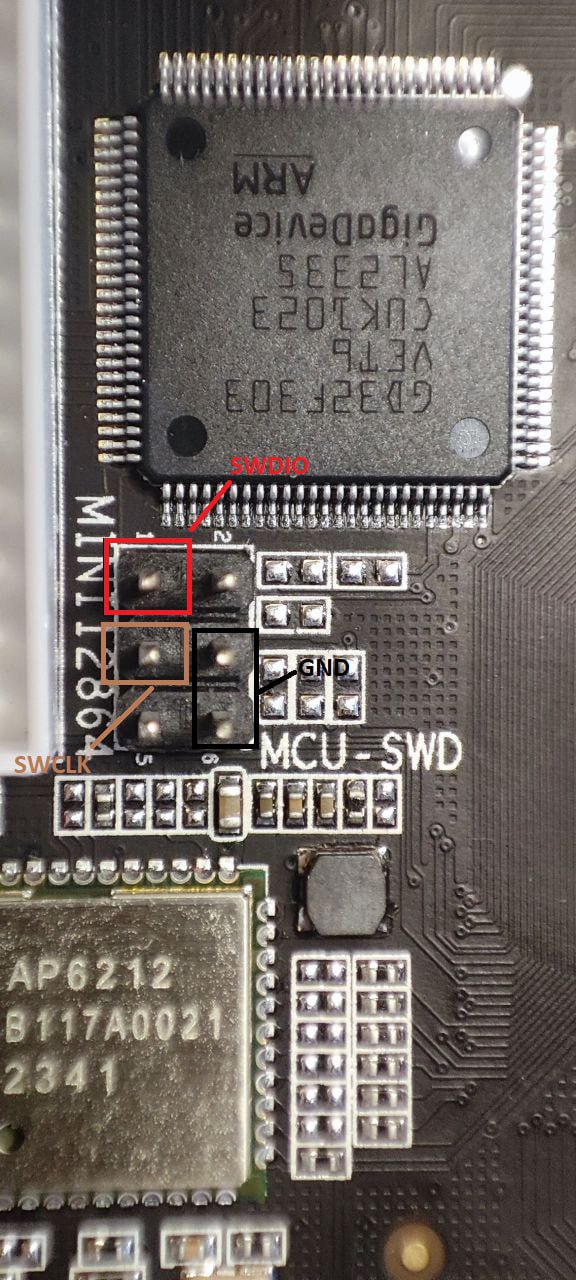
If you have st-link programmer you can use it to dump bootloader and determine firmware file name with strings utility. St-link can be connected to the pins shown on the picture.Check if the device in /dev/serial/by-id is available. In my case it was not. So turn the printer off and on.
Now copy an old configuration files from the image mounted on the host machine:
scp /media/$USER/4148ed1f-7865-4fd6-84b0-9564c15dbeac/home/mks/printer_data/config/MKS_THR.cfg \
mks@192.168.1.15:/home/mks/printer_data/config/ &&
scp /media/$USER/4148ed1f-7865-4fd6-84b0-9564c15dbeac/home/mks/printer_data/config/moonraker.conf \
mks@192.168.1.15:/home/mks/printer_data/config/ &&
scp /media/$USER/4148ed1f-7865-4fd6-84b0-9564c15dbeac/home/mks/printer_data/config/printer.cfg \
mks@192.168.1.15:/home/mks/printer_data/config/I suggest you replace env files for systemd from this repository becuase service logs are located inside the printer_data directory but it is better to put them to RAM drive mounted to /var/log. So copy them to the printer and replace in ~/printer_data/systemd directory.
Now we need to make some changes in systemd files.
Run:
sudo EDITOR=mcedit systemctl edit klipper.serviceAnd put the following content right in the place for them (read file content):
[Service]
LogsDirectory=klipper
RuntimeDirectory=klipper
Save changes by hiting F2 and exit.
Do the same for moonraker:
sudo EDITOR=mcedit systemctl edit moonraker.service[Service]
LogsDirectory=moonraker
Now stop all services, remove logs from printer_data directory and start them again.
sudo systemctl stop moonraker.service klipper.service &&
rm -rf ~/printer_data/logs/{klip*,moon*} &&
sudo systemctl start moonraker.service klipper.serviceCheck logs in /var/log for them for errors. I didn't copy an old fluidd configuration and macroses but you can do that.
It was annoying that the encoder works in reverse. When it is rotating CW it decreases values but it should increase. All we need to do to fix that is to sweep its pins in printer.cfg. You can do it through fluidd interface in the Configuration tab.
#encoder_pins:^PE13,^PE14
encoder_pins:^PE14,^PE13
After updating firmware of THR kingroon menu will dissapear. You can turn it back by comparing menu.cfg file from the image with the new one. But don't edit it. You can put chages inside your printer.cfg file. Except one function. Kingroon added IP determination as a python code.
Recalibrate mesh and that is all. Now you can uninstall linux-headers to free some space. But it is good to have this package at hand in the target system. Before you turn the bottom cover back recommend you to make a backup image of your system as described in the beginning. Thanks for reading.