Koa,下一代 Node.js web 框架
由 Express 原班人马打造的 koa,致力于成为一个更小、更健壮、更富有表现力的 Web 框架。使用 koa 编写 web 应用,通过组合不同的 generator,可以免除重复繁琐的回调函数嵌套,并极大地提升常用错误处理效率。Koa 不在内核方法中绑定任何中间件,它仅仅提供了一个轻量优雅的函数库,使得编写 Web 应用变得得心应手。
Koa需要支持ES2015和async function的node v7.6.0或更高版本。
您可以使用喜欢的依赖管理工具快速安装支持的node版本:
$ nvm install 7
$ npm i koa
$ node my-koa-app.js在node 7.6版本以下,如果你想在koa里使用async functions,我们推荐babel
require('babel-core/register');
// require the rest of the app that needs to be transpiled after the hook
const app = require('./app');
你至少要使用transform-async-to-generator or transform-async-to-module-method插件,
来解析和转译async functions。例如,你可以在你的.babelrc文件里这样写:
{
"plugins": ["transform-async-to-generator"]
}你也可以在env preset里使用目标选项"node": "current"。
一个 Koa Application(以下简称 app)由一系列 generator 中间件组成。按照编码顺序在栈内依次执行,从这个角度来看,Koa app 和其他中间件系统(比如 Ruby Rack 或者 Connect/Express )没有什么太大差别,不过,从另一个层面来看,Koa 提供了一种基于底层中间件编写「语法糖」的设计思路,这让设计中间件变得更简单有趣。
在这些中间件中,有负责内容协商(content-negotation)、缓存控制(cache freshness)、反向代理(proxy support)与重定向等等功能的常用中间件(详见 中间件 章节),但如前所述, Koa 内核并不会打包这些中间件,让我们先来看看 Koa 极其简单的 Hello World 应用程序:
var koa = require('koa');
var app = new koa();
app.use(function *(){
this.body = 'Hello World';
});
app.listen(3000);如果使用Koa 2的话:
var Koa = require('koa');
var app = new Koa();
app.use(ctx => {
ctx.body = 'Hello World';
});
app.listen(3000);译者注: 与普通的 function 不同,generator functions 以 function* 声明,以这种关键词声明的函数支持 yield。generator function是ECMAScript 6定义的新的语法,想了解其基本用法,以及Koa如何利用generator function达到在保持js代码异步特性的同时无需编写大量回调函数,可以参考这篇文章。
Koa 中间件以一种非常传统的方式级联起来,你可能会非常熟悉这种写法。
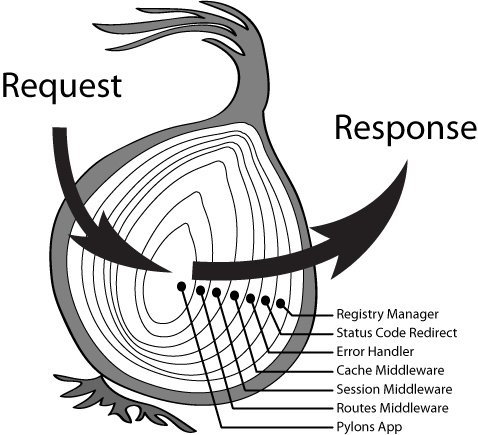
在以往的 Node 开发中,频繁使用回调不太便于展示复杂的代码逻辑,在 Koa 中,我们可以写出真正具有表现力的中间件。与 Connect 实现中间件的方法相对比,Koa 的做法不是简单的将控制权依次移交给一个又一个的中间件直到程序结束,Koa 执行代码的方式有点像回形针,用户请求通过中间件,遇到 yield next 关键字时,会被传递到下一个符合请求的路由(downstream),在 yield next 捕获不到下一个中间件时,逆序返回继续执行代码(upstream)。
下边这个例子展现了使用这一特殊方法书写的 Hello World 范例:一开始,用户的请求通过 x-response-time 中间件和 logging 中间件,这两个中间件记录了一些请求细节,然后「穿过」 response 中间件一次,最终结束请求,返回 「Hello World」。
当程序运行到 yield next 时,代码流会暂停执行这个中间件的剩余代码,转而切换到下一个被定义的中间件执行代码,这样切换控制权的方式,被称为
downstream,当没有下一个中间件执行 downstream 的时候,代码将会逆序执行。
var koa = require('koa');
var app = koa();
// x-response-time
app.use(function *(next){
// (1) 进入路由
var start = new Date;
yield next;
// (5) 再次进入 x-response-time 中间件,记录2次通过此中间件「穿越」的时间
var ms = new Date - start;
this.set('X-Response-Time', ms + 'ms');
// (6) 返回 this.body
});
// logger
app.use(function *(next){
// (2) 进入 logger 中间件
var start = new Date;
yield next;
// (4) 再次进入 logger 中间件,记录2次通过此中间件「穿越」的时间
var ms = new Date - start;
console.log('%s %s - %s', this.method, this.url, ms);
});
// response
app.use(function *(){
// (3) 进入 response 中间件,没有捕获到下一个符合条件的中间件,传递到 upstream
this.body = 'Hello World';
});
app.listen(3000);在上方的范例代码中,中间件依次被执行的顺序已经在注释中标记出来。你也可以自己尝试运行一下这个范例,并打印记录下各个环节的输出与耗时。
译者注: 「级联」这个词许多人也许在 CSS 中听说过,如果你不能理解为什么在这里使用这个词,可以将这种路由结构想象成 LESS 的继承嵌套书写方式:
.middleware1 {
// (1) do some stuff
.middleware2 {
// (2) do some other stuff
.middleware3 {
// (3) NO next yield !
// this.body = 'hello world'
}
// (4) do some other stuff later
}
// (5) do some stuff lastest and return
}
上方的伪代码中标注了中间件的执行顺序,看起来是不是有点像 ruby 执行代码块(block)时 yield 的表现了?也许这能帮助你更好的理解 koa 运作的方式。
译者注: 更加形象的图可以参考 Django Middleware
应用的配置是 app 实例的属性。目前来说,Koa 的配置项如下:
- app.name 应用名称
- app.env 执行环境,默认是
NODE_ENV或者"development"字符串 - app.proxy 决定了哪些
proxy header参数会被加到信任列表中 - app.subdomainOffset 被忽略的
.subdomains列表,详见下方 api
- koa-router
- trie-router
- route
- basic-auth
- etag
- compose
- static
- static-cache
- session
- compress
- csrf
- logger
- mount
- send
- error
用于启动一个服务的快捷方法,以下范例代码在 3000 端口启动了一个空服务:
var koa = require('koa');
var app = koa();
app.listen(3000);app.listen 是 http.createServer 的简单包装,它实际上这样运行:
var http = require('http');
var koa = require('koa');
var app = koa();
http.createServer(app.callback()).listen(3000);如果有需要,你可以在多个端口上启动一个 app,比如同时支持 HTTP 和 HTTPS:
var http = require('http');
var koa = require('koa');
var app = koa();
http.createServer(app.callback()).listen(3000);
http.createServer(app.callback()).listen(3001);返回一个可被 http.createServer() 接受的程序实例,也可以将这个返回函数挂载在一个 Connect/Express 应用中。
将给定的 function 当做中间件加载到应用中,详见 中间件 章节
设置一个签名 Cookie 的密钥。这些参数会被传递给 KeyGrip 如果你想自己生成一个实例,也可以这样:
app.keys = ['im a newer secret', 'i like turtle'];
app.keys = new KeyGrip(['im a newer secret', 'i like turtle'], 'sha256');注意,签名密钥只在配置项 signed 参数为真时才会生效:
this.cookies.set('name', 'tobi', { signed: true });除非 NODE_ENV 被配置为 "test",Koa 都将会将所有错误信息输出到 stderr,也可以自定义「错误事件」来监听 Koa app 中发生的错误,比如记录错误日志:
app.on('error', function(err){
log.error('server error', err);
});当任何 req 或者 res 中出现的错误无法被回应到客户端时,Koa 会在第二个参数传入这个错误的上下文:
app.on('error', function(err, ctx){
log.error('server error', err, ctx);
});任何错误有可能被回应到客户端,比如当没有新数据写入 socket 时,Koa 会默认返回一个 500 错误,并抛出一个 app 级别的错误到日志处理中间件中。
Koa 的上下文封装了 request 与 response 对象至一个对象中,并提供了一些帮助开发者编写业务逻辑的方法。为了方便,你可以在 ctx.request 和 ctx.response 中访问到这些方法。
每一个请求都会创建一段上下文。在控制业务逻辑的中间件中,上下文被寄存在 this 对象中:
app.use(function *(){
this; // 上下文对象
this.request; // Request 对象
this.response; // Response 对象
});为了使用方便,许多上下文属性和方法都被委托代理到他们的 ctx.request 或 ctx.response,比如访问 ctx.type 和 ctx.length 将被代理到 response 对象,ctx.path 和 ctx.method 将被代理到 request 对象。
ctx.request 对象包括以下属性和别名方法,详见 Request 章节
- ctx.header
- ctx.method
- ctx.method=
- ctx.url
- ctx.url=
- ctx.path
- ctx.path=
- ctx.query
- ctx.query=
- ctx.querystring
- ctx.querystring=
- ctx.length
- ctx.host
- ctx.fresh
- ctx.stale
- ctx.socket
- ctx.protocol
- ctx.secure
- ctx.ip
- ctx.ips
- ctx.subdomains
- ctx.is()
- ctx.accepts()
- ctx.acceptsEncodings()
- ctx.acceptsCharsets()
- ctx.acceptsLanguages()
- ctx.get()
ctx.response 对象包括以下属性和别名方法,详见 Response 章节
- ctx.body
- ctx.body=
- ctx.status
- ctx.status=
- ctx.length=
- ctx.type
- ctx.type=
- ctx.headerSent
- ctx.redirect()
- ctx.attachment()
- ctx.set()
- ctx.remove()
- ctx.lastModified=
- ctx.etag=
- ctx.req: Node.js 中的 request 对象
- ctx.res: Node.js 中的 response 对象,方法有:
- res.statusCode
- res.writeHead()
- res.write()
- res.end()
- ctx.app: app 实例
- ctx.state: 推荐的命名空间,用来保存那些通过中间件传递给视图的参数或数据。比如
this.state.user = yield User.find(id); - ctx.cookies.get(name, [options]) 对于给定的 name ,返回响应的 cookie
- options
signed[boolean]
- options
- ctx.cookies.set(name, value, [options]) 对于给定的参数,设置一个新 cookie
- options
signed[boolean]expires[date]path[string] 默认为'/'domain[string]secure[boolean]httpOnly[boolean] 默认为true
- options
- ctx.throw(msg, [status]) 抛出常规错误的辅助方法,默认 status 为 500。
以下几种写法都有效:
this.throw(403)
this.throw('name required', 400)
this.throw(400, 'name required')
this.throw('something exploded')实际上,this.throw('name required', 400) 是此代码片段的简写方法:
var err = new Error('name required');
err.status = 400;
throw err;需要注意的是,ctx.throw 创建的错误,均为用户级别错误(标记为err.expose),会被返回到客户端。
- ctx.assert(value, [msg], [status], [properties]) 用来断言的辅助方法,类似 Node 中的
assert()方法。this.assert(this.user, 401, 'User not found. Please login!');此方法由http-assert模块支持。
ctx.request 对象是对 Node 原生请求对象的抽象包装,提供了一些非常有用的方法。
详细的 Request 对象 API 如下:
返回请求头
返回请求方法
设置 req.method ,用于实现输入 methodOverride() 的中间件
返回 req 对象的 Content-Length (Number)
返回请求 url
设置请求 url,用于进行 url 重写
返回请求 pathname
设置请求 pathname,如果原有 url 存在查询字符串,则保留这些查询。
返回 url 中的查询字符串,去除了头部的 '?'
设置查询字符串,不包含 '?'
返回 url 中的查询字符串,包含了头部的 '?'
设置查询字符串,包含 '?'
返回请求主机名,不包含端口;当 app.proxy 设置为 true 时,支持 X-Forwarded-Host。
返回 req 对象的 Content-Type,不包括 charset 属性,范例代码:
var ct = this.type;
// => "image/png"返回经过解析的查询字符串,类似 Express 中的 req.query,当不存在查询字符串时,返回空对象。
当 url 包含查询字符串 "color=blue&size=small" 时,返回如下:
{
color: 'blue',
size: 'small'
}设置给定的对象为查询对象。范例代码如下:
this.query = { next: '/login' };检查客户端请求的缓存是否是最新。当缓存为最新时,可编写业务逻辑直接返回 304,范例代码如下:
this.set('ETag', '123');
// 当客户端缓存是最新时
if (this.fresh) {
this.status = 304;
return;
}
// 当客户端缓存已过期时,返回最新的数据
this.body = yield db.find('something');与 req.fresh 返回的结果正好相反
返回请求协议名,如 "https" 或者 "http";当 app.proxy 设置为 true 时,支持 X-Forwarded-Proto。
判断请求协议是否为 HTTPS 的快捷方法,等同于 this.protocol == "https"
返回请求IP;当 app.proxy 设置为 true 时,支持 X-Forwarded-For。
返回请求IP列表,仅当 app.proxy 设置为 true ,并存在 X-Forwarded-For 列表时,否则返回空数组。
返回请求对象中的子域名数组。子域名数组会自动由请求域名字符串中的 . 分割开,在没有设置自定义的 app.subdomainOffset 参数时,默认返回根域名之前的所有子域名数组。
例如,当请求域名为 "tobi.ferrets.example.com" 时候,返回 ["ferrets", "tobi"],数组顺序是子代域名在前,孙代域名在后。
此例中,如果设置了自定义的 app.subdomainOffset 为 3,将忽略三级域名,返回 ["tobi"]。
判断请求对象中 Content-Type 是否为给定 type 的快捷方法,如果不存在 request.body,将返回 undefined,如果没有符合的类型,返回 false,除此之外,返回匹配的类型字符串。
// 客户端 Content-Type: text/html; charset=utf-8
this.is('html'); // => 'html'
this.is('text/html'); // => 'text/html'
this.is('text/*', 'text/html'); // => 'text/html'
// 客户端 Content-Type 为 application/json 时:
this.is('json', 'urlencoded'); // => 'json'
this.is('application/json'); // => 'application/json'
this.is('html', 'application/*'); // => 'application/json'
this.is('html'); // => false又如,下方的代码使用 req.is(type),仅当请求类型为图片时才进行操作:
if (this.is('image/*')) {
// process
} else {
this.throw(415, 'images only!');
}判断请求对象中 Accept 是否为给定 type 的快捷方法,当匹配到符合的类型时,返回最匹配的类型,否则返回 false(此时服务器端应当返回 406 "Not Acceptable" ),传入参数可以是字符串或者数组。
// Accept: text/html
this.accepts('html');
// => "html"
// Accept: text/*, application/json
this.accepts('html');
// => "html"
this.accepts('text/html');
// => "text/html"
this.accepts('json', 'text');
// => "json"
this.accepts('application/json');
// => "application/json"
// Accept: text/*, application/json
this.accepts('image/png');
this.accepts('png');
// => undefined
// Accept: text/*;q=.5, application/json
this.accepts(['html', 'json']);
this.accepts('html', 'json');
// => "json"注意,当请求头中不包含 Accept 属性时,给定的第一个 type 将会被返回。
判断客户端是否接受给定的编码方式的快捷方法,当有传入参数时,返回最应当返回的一种编码方式。
// Accept-Encoding: gzip
this.acceptsEncodings('gzip', 'deflate');
// => "gzip"
this.acceptsEncodings(['gzip', 'deflate']);
// => "gzip"当没有传入参数时,返回客户端的请求数组:
// Accept-Encoding: gzip, deflate
this.acceptsEncodings();
// => ["gzip", "deflate"]使用方法同 req.acceptsEncodings(encodings)
使用方法同 req.acceptsEncodings(encodings)
详细的 Response 对象 API 如下:
获取返回头
获取返回状态
设置返回状态,可用状态如下:
- 100 "continue"
- 101 "switching protocols"
- 102 "processing"
- 200 "ok"
- 201 "created"
- 202 "accepted"
- 203 "non-authoritative information"
- 204 "no content"
- 205 "reset content"
- 206 "partial content"
- 207 "multi-status"
- 300 "multiple choices"
- 301 "moved permanently"
- 302 "moved temporarily"
- 303 "see other"
- 304 "not modified"
- 305 "use proxy"
- 307 "temporary redirect"
- 400 "bad request"
- 401 "unauthorized"
- 402 "payment required"
- 403 "forbidden"
- 404 "not found"
- 405 "method not allowed"
- 406 "not acceptable"
- 407 "proxy authentication required"
- 408 "request time-out"
- 409 "conflict"
- 410 "gone"
- 411 "length required"
- 412 "precondition failed"
- 413 "request entity too large"
- 414 "request-uri too large"
- 415 "unsupported media type"
- 416 "requested range not satisfiable"
- 417 "expectation failed"
- 418 "i'm a teapot"
- 422 "unprocessable entity"
- 423 "locked"
- 424 "failed dependency"
- 425 "unordered collection"
- 426 "upgrade required"
- 428 "precondition required"
- 429 "too many requests"
- 431 "request header fields too large"
- 500 "internal server error"
- 501 "not implemented"
- 502 "bad gateway"
- 503 "service unavailable"
- 504 "gateway time-out"
- 505 "http version not supported"
- 506 "variant also negotiates"
- 507 "insufficient storage"
- 509 "bandwidth limit exceeded"
- 510 "not extended"
- 511 "network authentication required"
设置返回头的 Content-Length 属性
返回返回头的 Content-Length 属性,当不存在 Content-Length 属性时,根据 res.body 推断
获取 res.body,当 res.body 为 null ,但返回状态仍为 200 时,koa 将会返回 404 页面。
设置请求返回的主要内容,可以是以下几种类型:
-
string
Content-Type 将默认设置为 text/html 或者 text/plain,默认字符集是 utf-8,Content-Length 也将一并设置
-
Buffer
Content-Type 将默认设置为 application/octet-stream,Content-Length 也将一并设置
-
Stream
Content-Type 将默认设置为 application/octet-stream
-
Object
Content-Type 将默认设置为 application/json 注意:默认的json返回会添加空格,如果你希望压缩json返回中的空格,可以这样配置:
app.jsonSpaces = 0 -
null
获取指定的返回头属性,属性名称区分大小写。
var etag = this.get('ETag');使用给定的参数设置一个返回头属性:
this.set('Cache-Control', 'no-cache');使用给定的对象一次设置多个返回头属性:
this.set({
'Etag': '1234',
'Last-Modified': date
});删除指定的返回头属性
获取返回头中的 Content-Type,不包括 "charset" 等属性。
var ct = this.type;
// => "image/png"使用字符串或者文件后缀设定返回的 Content-Type
this.type = 'text/plain; charset=utf-8';
this.type = 'image/png';
this.type = '.png';
this.type = 'png';注意:当使用文件后缀指定时,koa 会默认设置好最匹配的编码字符集,比如当设定 res.type = 'html' 时,koa 会默认使用 "utf-8" 字符集。但当明确使用 res.type = 'text/html' 指定时,koa 不会自动设定字符集。
返回一个 302 跳转到给定的 url,您也可以使用关键词 back 来跳转到该 url 的上一个页面(refer),当没有上一个页面时,默认会跳转到 '/'
this.redirect('back');
this.redirect('back', '/index.html');
this.redirect('/login');
this.redirect('http://google.com');如果你需要覆盖 302 状态码,并在跳转时返回一些文案,可以这样做:
this.status = 301;
this.redirect('/cart');
this.body = 'Redirecting to shopping cart';设置返回熟悉 Content-Disposition 为 "attachment",并告知客户端进行下载。
判断一个响应头是否已经发送到客户端,通常用来检测客户端是否收到了错误信息。
如果返回头中存在 Last-Modified 属性,则返回它。
设置返回头中的 Last-Modified 属性,可以使用时间对象或者时间字符串。
this.response.lastModified = new Date();设置返回头的 Etag 字段。koa 不提供关于 Etag 的获取方法。
this.response.etag = crypto.createHash('md5').update(this.body).digest('hex');挂载不同数量的中间件,wrk 得出 benchmarks 如下:
1 middleware
8367.03
5 middleware
8074.10
10 middleware
7526.55
15 middleware
7399.92
20 middleware
7055.33
30 middleware
6460.17
50 middleware
5671.98
100 middleware
4349.37
一般来说,我们通常要使用约50个中间件,按这个标准计算,单应用可支持 340,260 请求/分钟,即 20,415,600 请求/小时,也就是约 4.4 亿 请求/天。
发现更多第三方的 koa 中间件,或者一起来参与社区的讨论和建设吧:
- Fork this repo
- Clone your repo
- Install dependencies
- Checkout a feature branch
- Feel free to add your features
- Make sure your features are fully tested
- Open a pull request, and enjoy <3
Copyright (c) 2013 turing <o.u.turing@gmail.com>
Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:
The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in all copies or substantial portions of the Software.
THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM, OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE SOFTWARE.