RmlUi - now with added boosters taking control of the rocket, targeting your games and applications.
RmlUi is the C++ user interface package based on the HTML and CSS standards, designed as a complete solution for any project's interface needs. It is a fork of the libRocket project, introducing new features, bug fixes, and performance improvements.
RmlUi aims at being a light-weight and performant library with its own layouting engine and few dependencies. In essence, RmlUi takes your HTML/CSS-like source files and turns them into vertices, indices and draw commands, and then you bring your own renderer to draw them. And of course there is full access to the element hierarchy/DOM, event handling, and all the interactivity and customizability you would expect. All of this directly from C++, or optionally from scripting languages using plugins. The core library compiles down to fractions of the size it takes to integrate a fully fledged web browser as other libraries do in this space.
RmlUi is based around the XHTML1 and CSS2 standards while borrowing features from HTML5 and CSS3, and extends them with features suited towards real-time applications. Take a look at the conformance and enhancements sections below for details.
Documentation is located at https://mikke89.github.io/RmlUiDoc/
- Cross platform architecture: Windows, macOS, Linux, iOS, etc.
- Dynamic layout system.
- Full animation and transform support.
- Efficient application-wide styling, with a custom-built templating engine.
- Fully featured control set: buttons, sliders, drop-downs, etc.
- Runtime visual debugging suite.
- Abstracted interfaces for plugging in to any game engine.
- Decorator engine allowing custom application-specific effects that can be applied to any element.
- Generic event system that binds seamlessly into existing projects.
- Easily integrated and extensible with the Lua scripting plugin.
- The user controls their own update loop, calling into RmlUi as desired.
- The library strictly runs as a result of calls to its API, never in the background.
- Input handling and rendering is performed by the user.
- The library generates vertices, indices, and textures for the user to render how they like.
- File handling and the font engine can optionally be fully replaced by the user.
- FreeType. However, it can be fully replaced by a custom font engine.
- The standard library.
In addition, a C++14 compatible compiler is required.
RmlUi is built using CMake and your favorite compiler, see the building documentation for all the details and options. Windows binaries are also available for the latest release. Most conveniently, it is possible to fetch the library using a dependency manager such as vcpkg or Conan.
vcpkg install rmlui
That's it! See below for details on integrating RmlUi.
To build RmlUi with the included samples we can use git and CMake together with vcpkg to handle the dependency.
vcpkg install freetype
git clone https://github.com/mikke89/RmlUi.git
cd RmlUi
cmake -B Build -S . -DBUILD_SAMPLES=ON -DCMAKE_TOOLCHAIN_FILE="<path-to-vcpkg>/scripts/buildsystems/vcpkg.cmake"
cmake --build Build
Make sure to replace the path to vcpkg.
RmlUi is readily available from ConanCenter.
Here are the general steps to integrate the library into a C++ application, have a look at the documentation for details.
- Build RmlUi as above or fetch the binaries, and link it up to your application.
- Implement the abstract system interface and render interface.
- Initialize RmlUi with the interfaces, create a context, provide font files, and load a document.
- Call into the context's update and render methods in a loop, and submit input events.
- Compile and run!
Several samples demonstrate everything from basic integration to more complex use of the library, feel free to have a look for inspiration.
RmlUi aims to support the most common and familiar features from HTML and CSS, while keeping the library light and performant. We do not aim to be fully compliant with CSS or HTML, in particular when it conflicts with lightness and performance. Users are generally expected to author documents specifically for RmlUi, but any experience and skills from web design should be transferable.
RmlUi supports most of CSS2 with some CSS3 features such as
- Animations and transitions
- Transforms (with full interpolation support)
- Flexbox layout
- Media queries
- Border radius
and many of the common HTML elements including <input>, <textarea>, and <select>.
For details, see
- RCSS Property index for all supported properties and differences from CSS.
- RML Element index for all supported elements.
RmlUi adds features and enhancements over CSS and HTML where it makes sense, most notably the following.
- Data binding (model-view-controller). Synchronization between application data and user interface.
- Decorators. Full control over the styling of all elements.
- Sprite sheets. Define and use sprites with easy high DPI support.
- Templates. Making windows look consistent.
- Localization. Translate any text in the document.
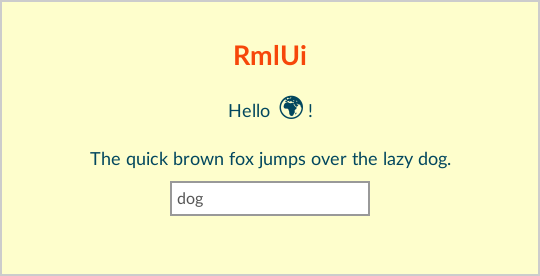
This example demonstrates a basic document with data bindings, which is loaded and displayed using the C++ code below.
hello_world.rml
<rml>
<head>
<title>Hello world</title>
<link type="text/rcss" href="rml.rcss"/>
<link type="text/rcss" href="window.rcss"/>
</head>
<body data-model="animals">
<h1>RmlUi</h1>
<p>Hello <span id="world">world</span>!</p>
<p data-if="show_text">The quick brown fox jumps over the lazy {{animal}}.</p>
<input type="text" data-value="animal"/>
</body>
</rml>The {{animal}} text and the data-if, data-value attributes represent data bindings and will synchronize with the application data.
window.rcss
body {
font-family: LatoLatin;
font-size: 18px;
color: #02475e;
background: #fefecc;
text-align: center;
padding: 2em 1em;
position: absolute;
border: 2px #ccc;
width: 500px;
height: 200px;
margin: auto;
}
h1 {
color: #f6470a;
font-size: 1.5em;
font-weight: bold;
margin-bottom: 0.7em;
}
p {
margin: 0.7em 0;
}
input.text {
background-color: #fff;
color: #555;
border: 2px #999;
padding: 5px;
tab-index: auto;
cursor: text;
box-sizing: border-box;
width: 200px;
font-size: 0.9em;
}RmlUi defines no styles internally, thus the input element is styled here, and rml.rcss is included for proper layout of common tags.
main.cpp
#include <RmlUi/Core.h>
class MyRenderInterface : public Rml::RenderInterface
{
// RmlUi sends vertices, indices and draw commands through this interface for your
// application to render how you'd like.
/* ... */
}
class MySystemInterface : public Rml::SystemInterface
{
// RmlUi requests the current time and provides various utilities through this interface.
/* ... */
}
struct ApplicationData {
bool show_text = true;
Rml::String animal = "dog";
} my_data;
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
// Initialize the window and graphics API being used, along with your game or application.
/* ... */
MyRenderInterface render_interface;
MySystemInterface system_interface;
// Install the custom interfaces.
Rml::SetRenderInterface(&render_interface);
Rml::SetSystemInterface(&system_interface);
// Now we can initialize RmlUi.
Rml::Initialise();
// Create a context to display documents within.
Rml::Context* context = Rml::CreateContext("main", Rml::Vector2i(window_width, window_height));
// Tell RmlUi to load the given fonts.
Rml::LoadFontFace("LatoLatin-Regular.ttf");
// Fonts can be registered as fallback fonts, as in this case to display emojis.
Rml::LoadFontFace("NotoEmoji-Regular.ttf", true);
// Set up data bindings to synchronize application data.
if (Rml::DataModelConstructor constructor = context->CreateDataModel("animals"))
{
constructor.Bind("show_text", &my_data.show_text);
constructor.Bind("animal", &my_data.animal);
}
// Now we are ready to load our document.
Rml::ElementDocument* document = context->LoadDocument("hello_world.rml");
document->Show();
// Replace and style some text in the loaded document.
Rml::Element* element = document->GetElementById("world");
element->SetInnerRML(reinterpret_cast<const char*>(u8"🌍"));
element->SetProperty("font-size", "1.5em");
bool exit_application = false;
while (!exit_application)
{
// We assume here that we have some way of updating and retrieving inputs internally.
if (my_input->KeyPressed(KEY_ESC))
exit_application = true;
// Submit input events such as MouseMove and key events (not shown) to the context.
if (my_input->MouseMoved())
context->ProcessMouseMove(mouse_pos.x, mouse_pos.y, 0);
// Update the context to reflect any changes resulting from input events, animations,
// modified and added elements, or changed data in data bindings.
context->Update();
// Render the user interface. All geometry and other rendering commands are now
// submitted through the render interface.
context->Render();
}
Rml::Shutdown();
return 0;
}Users can now edit the text field to change the animal. The data bindings ensure that both the document text as well as the application string my_data.animal are automatically modified accordingly.
 Game interface from the 'invader' sample
Game interface from the 'invader' sample
 Form controls from the 'demo' sample
Form controls from the 'demo' sample
 Sandbox from the 'demo' sample, try it yourself!
Sandbox from the 'demo' sample, try it yourself!

Transitions on mouse hover (entirely in RCSS)

Animated transforms (entirely in RCSS)

Vector animations with the Lottie plugin

Vector images with the SVG plugin
See the full gallery for more screenshots and videos of the library in action.
RmlUi is published under the MIT license. The library includes third-party source code and assets with their own licenses, as detailed below.
MIT License
Copyright (c) 2008-2014 CodePoint Ltd, Shift Technology Ltd, and contributors
Copyright (c) 2019-2021 The RmlUi Team, and contributors
Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:
The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in all copies or substantial portions of the Software.
THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM, OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE SOFTWARE.
See Include/RmlUi/Core/Containers/LICENSE.txt - all MIT licensed.
See Source/Debugger/LICENSE.txt - SIL Open Font License.
See
- Samples/assets/LICENSE.txt
- Samples/basic/bitmapfont/data/LICENSE.txt
- Samples/basic/lottie/data/LICENSE.txt
- Samples/basic/svg/data/LICENSE.txt