This repository is an unofficial implementation of "Street Gaussians: Modeling Dynamic Urban Scenes with Gaussian Splatting", building on top of the Nerfstudio framework.
Our goal in reproducing and open-sourcing this work is to provide a basic reference for the self-driving community and to inspire more work. Any creative ideas are welcome to be discussed with us! Feel free to contact with us by email: contact@lightwheel.ai
Waymo:
depth-1906.mp4
rgb-1906.mp4
object_rgb-1906.mp4
background_rgb-1906.mp4
Waymo:
| Sequence | frame | Paper | This repo | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PSNR | SSIM | PSNR | SSIM | ||
| 10448102132863604198 | [0,85] | 33.50 | 0.945 | 33.12 | 0.942 |
| 2094681306939952000 | [20,115] | 36.70 | 0.955 | 35.72 | 0.960 |
| 8398516118967750070 | [0,160] | 36.74 | 0.948 | 38.29 | 0.965 |
Training time is about 0.5 hours per sequence on 1 RTX4090.
The quickstart will help you get started with the street-gaussians model on a Waymo sequence.
Our installation steps largely follow Nerfstudio, with some added dataset-specific dependencies. You must have an NVIDIA video card with CUDA installed on the system. This library has been tested with version 11.8 of CUDA. You can find more information about installing CUDA here.
conda create --name street-gaussians-ns -y python=3.8
conda activate street-gaussians-ns
pip install --upgrade pipInstall PyTorch with CUDA (this repo has been tested with CUDA 11.8) and tiny-cuda-nn.
cuda-toolkit is required for building tiny-cuda-nn.
For CUDA 11.8:
pip install torch==2.1.2+cu118 torchvision==0.16.2+cu118 --extra-index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cu118
conda install -c "nvidia/label/cuda-11.8.0" cuda-toolkit
pip install ninja git+https://github.com/NVlabs/tiny-cuda-nn/#subdirectory=bindings/torchInstall nerfstudio.
pip install nerfstudio==1.0.0We refer to Nerfstudio for more installation support.
Clone and Install street-gaussians-ns. We use cube map to represent sky.
git clone https://github.com/LightwheelAI/street-gaussians-ns.git --recursive
cd street-gaussians-ns
pip install -e .
pip install dependencies/nvdiffrast/For segments generating, which is necessary to model sky, Mask2Former is required.
cd dependencies/detectron2
pip install -e .
cd dependencies/Mask2Former
pip install -r requirements.txt
cd mask2former/modeling/pixel_decoder/ops
sh make.shAfter installing Mask2Former, we need to download the pretrained model and place it at dependencies/mask2former/models
We refer to Detectron2 and Mask2Former for more installation support.
The following will train a street-gaussians-ns model, our recommended model for real world AD scenes.
Begin by downloading dataset from Waymo and unzip it, we use waymo perception_v1.4.0 to test our model.
Use the script to extract it to our data structure.
python scripts/python/extract_waymo.py --waymo_root path/to/your/waymo_root --out_root path/to/your/out_root
After this step you will get our dataset format as follow:
clip root
|-- images
| |-- ${cam0 name}
| | |-- t0.jpg/png
| | |-- t1.jpg/png
| | |-- ...
| |
| |-- ${cam1 name}
| |-- ...
|
|-- lidars
| |-- ${lidar0 name}
| | |-- t0.pcd
| | |-- t1.pcd
| | |-- ...
| |
| |-- ${lidar1 name}
| |-- ...
|
|-- transform.json
|-- annotation.json
Then you can follow the data_process.sh to finish data processing.
If you can't run segs_generate.py successfully, please try to copy it under dependencies/Mask2Former and run it again.
If you want only test the model or have problem in data preprocessing, we offer our preprocessed dataset!
| Sequence |
|---|
| 10588771936253546636 |
| 10448102132863604198 |
| 2094681306939952000 |
| 8398516118967750070 |
Training models is done conveniently by scripts.
# Train model
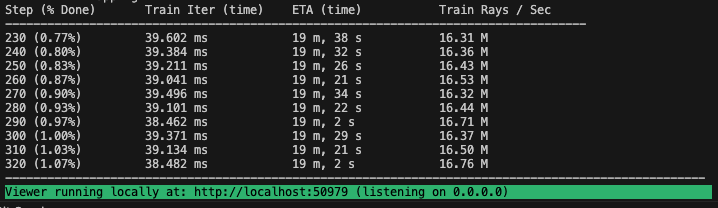
bash scripts/shells/train.sh path/to/your/dataset cuda_idIf everything works, you should see training progress like the following:
Evaluating and rendering models is done conveniently by scripts.
# Eval model
bash scripts/shells/eval.sh path/to/your/output/config.yaml cuda_id
# Render model
bash scripts/shells/render.sh path/to/your/output/config.yaml cuda_idIf you want to render a novel view video, following steps could be helpful.
- Create a json file with following format(or use our
nvs_template.jsoninscripts). - Specify the json file using
--vehicle-configofsgn-render. - Get a novel view video!
[
{
"camera": "FRONT",
"image_path_patten": ".*/FRONT/.*",
"transform": [
[
1.0,
0.0,
0.0,
0.0
],
[
0.0,
1.0,
0.0,
0.0
],
[
0.0,
0.0,
1.0,
0.0
],
[
0.0,
0.0,
0.0,
1.0
]
]
},
]
Your can use the following script to export nerfstudio model to a ply file as 3DGS.
# Export model
bash scripts/shells/export.sh path/to/your/output/config.yamlEach model contains many parameters that can be changed, too many to list here.
There are three ways to modify the configuration:
- modify the Config class' parameter in the model file
- modify the method_config.py file
- modify parameters in the command, i.e. train.sh file
There are four different methods to track training progress, using the viewer, tensorboard, Weights and Biases, and Comet. You can specify which visualizer to use by appending --vis {viewer, tensorboard, wandb, comet viewer+wandb, viewer+tensorboard, viewer+comet} to the training command. Simultaneously utilizing the viewer alongside wandb or tensorboard may cause stuttering issues during evaluation steps.
For more usage or information, please see https://github.com/nerfstudio-project/nerfstudio.
- Release main part code
- Release data processing part code
- Release preprocessed dataset

- Collaboration friendly studio for NeRFs
If you find this code useful, please be so kind to cite
@inproceedings{yan2024street,
title={Street Gaussians for Modeling Dynamic Urban Scenes},
author={Yunzhi Yan and Haotong Lin and Chenxu Zhou and Weijie Wang and Haiyang Sun and Kun Zhan and Xianpeng Lang and Xiaowei Zhou and Sida Peng},
booktitle={ECCV},
year={2024}
}