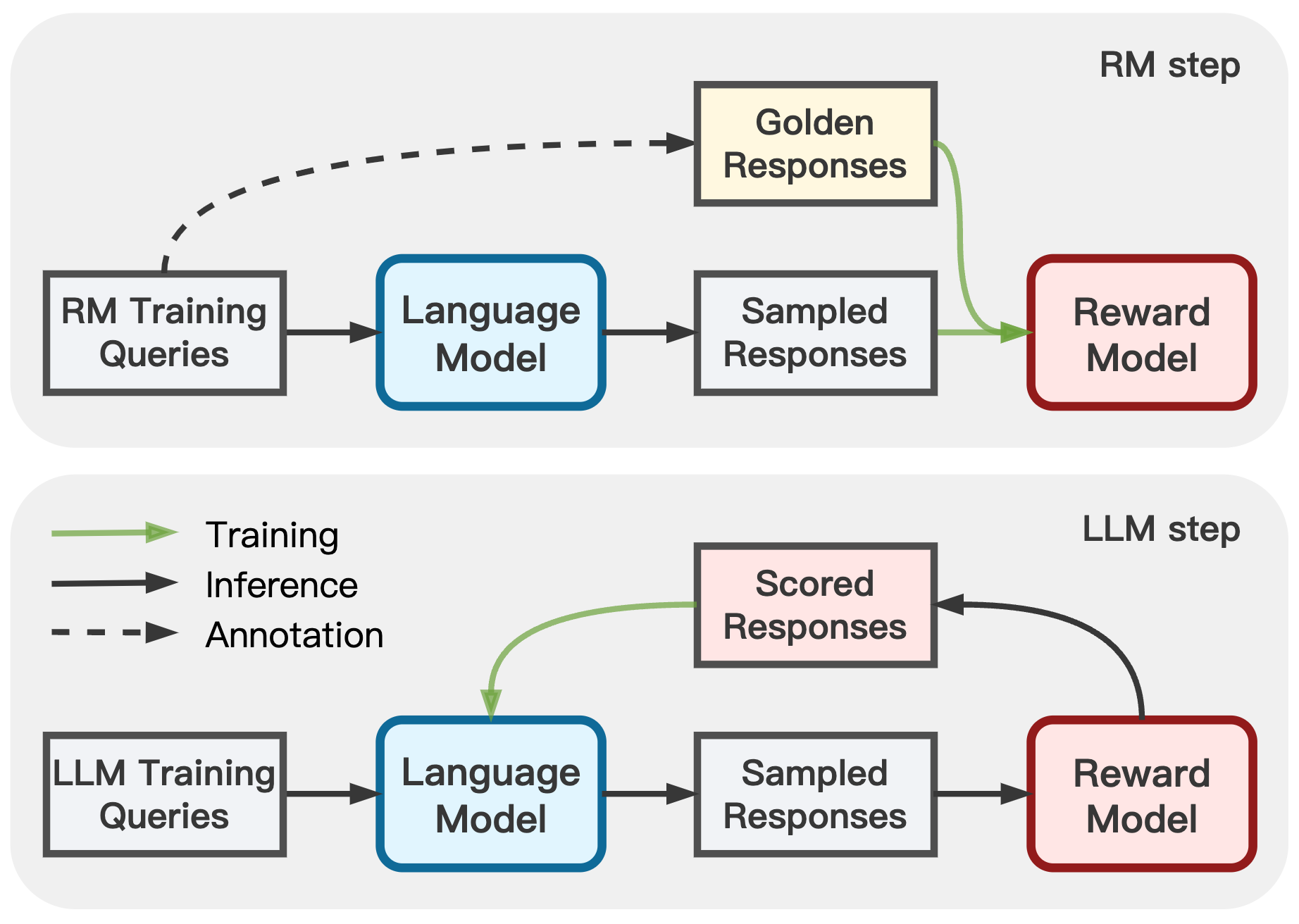
This repo contains the implementation of the ACL 2024 paper:
In Adversarial Preference Optimization (APO), we let the reward model (RM) and LLM agent play a min-max game, through which both models can be further enhanced without additional preference annotation.
For an overview, the repo contains:
- Split Helpful&Harmless (HH) dataset
- GPT-4 responses as golden annotation on HH-RM training set
- The base RM, testing RM, and APO RM training & scoring pipelines
- The LLM response generation pipeline
We use Python3.8 with the dependencies listed in requirements.txt. To build the appropriate environment, use the following command:
pip3 install -r requirements.txt
To separately update RM and LLM, we split the cleaned Helpful&Harmless (HH) dataset into an RM training set and a LLM training set.
| Data Type | HH-RM Train Set | HH-LLM Train Set | HH Test Set |
|---|---|---|---|
| Preference Pairs | RM training set | RM validation set (sampled 10K pairs) | RM testing set |
| Golden Answers | APO positive responses | ||
| LLM Samples | APO negative responses (alpaca_rm_samples) |
LLM alignment samples (alpaca_llm_samples) |
LLM testing Queries |
On both HH-RM and HH-LLM training sets, we infer four LLM responses for each query as alpaca_rm_samples and alpaca_llm_samples. alpaca_rm_samples is combined with the golden responses on the HH-RM set as APO RM training pairs. alpaca_llm_samples is further scored by RMs and used for LLM alignment. To obtain LLM responses by yourself, run the command:
bash tools/llm_response_gen.shWe build our RM on the pretrained LLaMA-7B (decapoda-research/llama-7b-hf). To train the base RM for rejection sampling, use the following command:
REPO_DIR=<path_to_this_repo>
DATA_DIR=${REPO_DIR}/data/hh-split
TRAIN_DATA_LIST="${DATA_DIR}/rm_data/hh_split_rm.train.json"
TEST_DATA_LIST="${DATA_DIR}/eval_data/hh_cleaned_origin.test.json\
${DATA_DIR}/eval_data/hh_split_llm.valid.json"
NUM_GPUS=8
BATCH_SIZE=64
MICRO_BATCH_SIZE=1
LEARNING_RATE=1e-6
GRADIENT_ACCUMULATION_STEP=$((BATCH_SIZE / NUM_GPUS / MICRO_BATCH_SIZE))
torchrun --nproc_per_node=${NUM_GPUS} --master_port=6000 ${REPO_DIR}/train.py \
--task_type hh_split \
--do_train True \
--eval_at_start False \
--model_type reward \
--model_name_or_path "decapoda-research/llama-7b-hf" \
--data_type "comparison_pair" \
--train_data_path ${TRAIN_DATA_LIST} \
--eval_data_path ${TEST_DATA_LIST} \
--rm_calibration True \
--data_suffix rm_base \
--add_sep_token True \
--remove_unused_columns false \
--output_dir <path_to_save_your_RM_checkpoint> \
--num_train_epochs 1 \
--per_device_train_batch_size ${MICRO_BATCH_SIZE} \
--per_device_eval_batch_size ${MICRO_BATCH_SIZE} \
--gradient_accumulation_steps ${GRADIENT_ACCUMULATION_STEP} \
--evaluation_strategy steps \
--padding_side right \
--truncation_side left \
--pooling_type last \
--max_length 512 \
--save_strategy steps \
--learning_rate ${LEARNING_RATE} \
--warmup_steps 100 \
--deepspeed configs/default_offload_opt_param.json \
--tf32 false --fp16 falseWe also trained a testing RM to automatically evaluate the LLM response quality on the testing queries. To train the testing RM, change TRAIN_DATA_LIST=${DATA_DIR}/hh_cleaned_origin.train.json in the above command to learn with all the HH training comparisons.
The RM training data files (values in TRAIN_DATA_LIST) are lists of dictionaries, where each dictionary is an RM training item (--data_type="comparison_pair") including the following keys:
text: a list of query-response text, split by a special token<sep>.scores: a list of float numbers, representing the preference scores of the corresponding query-response text.query_id: a unique ID to the RM training item.
To train the APO RM, first merge LLM samples and golden annotations into APO comparison pairs:
REPO_DIR=<path_to_this_repo>
DATA_DIR="${REPO_DIR}/data/hh-split"
python3 ${REPO_DIR}/tools/apo_data_converter.py \
--golden_data_path ${DATA_DIR}/rm_data/hh_split_rm.golden.json \
--sample_data_path ${DATA_DIR}/rm_data/hh_split_rm_alpaca_v0.sample.json \
--output_dir ${DATA_DIR}/apo_data \
--apo_data_name "rm_apo_data_v0"
Then use the following command to conduct APO RM finetuning:
REPO_DIR=<path_to_this_repo>
DATA_DIR=${REPO_DIR}/data/hh-split
TRAIN_DATA_LIST="${DATA_DIR}/rm_data/hh_split_rm.train.json \
${DATA_DIR}/apo_data/rm_apo_data_v0_text_scores.json"
NUM_APO_SAMPLES=4
TEST_DATA_LIST="${DATA_DIR}/eval_data/hh_cleaned_origin.test.json \
${DATA_DIR}/eval_data/hh_split_llm.valid.json"
NUM_GPUS=8
BATCH_SIZE=64
MICRO_BATCH_SIZE=1
LEARNING_RATE=1e-6
APO_COEFF=0.1
GRADIENT_ACCUMULATION_STEP=$((BATCH_SIZE / NUM_GPUS / MICRO_BATCH_SIZE))
torchrun --nproc_per_node=${NUM_GPUS} --master_port=6000 ${REPO_DIR}/train.py \
--task_type apo \
--do_train True \
--eval_at_start False \
--model_type reward \
--model_name_or_path "decapoda-research/llama-7b-hf" \
--data_type "comparison_pair" \
--train_data_path ${TRAIN_DATA_LIST} \
--eval_data_path ${TEST_DATA_LIST} \
--rm_calibration True \
--data_suffix rm_apo_v1 \
--add_sep_token True \
--remove_unused_columns false \
--output_dir <path_to_save_your_APO_RM_checkpoint> \
--num_train_epochs 1 \
--apo_loss_coeff ${APO_COEFF} \
--apo_sample_num ${NUM_APO_SAMPLES} \
--per_device_train_batch_size ${MICRO_BATCH_SIZE} \
--per_device_eval_batch_size ${MICRO_BATCH_SIZE} \
--gradient_accumulation_steps ${GRADIENT_ACCUMULATION_STEP} \
--evaluation_strategy steps \
--padding_side right \
--truncation_side left \
--pooling_type last \
--max_length 512 \
--save_strategy steps \
--save_total_limit 10 \
--learning_rate ${LEARNING_RATE} \
--warmup_steps 100 \
--deepspeed configs/default_offload_opt_param.json \
--tf32 false --fp16 false
After finishing the RM training, we can use the following command to scoring new LLM samples:
REPO_DIR=<path_to_this_repo>
DATA_DIR=${REPO_DIR}/data/hh-split/llm_data
DATA_PATH="${DATA_DIR}/hh_split_llm_alpaca_v0.sample.json"
MODEL_PATH=<path_to_your_RM_checkpoint>
MODEL_NAME="base_rm" # or "apo_rm"
NUM_GPUS=8
MICRO_BATCH_SIZE=16
torchrun --nproc_per_node=${NUM_GPUS} --master_port=6000 ${REPO_DIR}/train.py \
--task_type inference \
--do_train False \
--eval_at_start True \
--model_type reward \
--model_name_or_path ${MODEL_PATH} \
--data_type "reject_sample" \
--eval_data_path ${DATA_PATH} \
--rm_calibration False \
--data_suffix ${MODEL_NAME} \
--add_sep_token True \
--remove_unused_columns false \
--output_dir <path_to_save_your_inference_results> \
--per_device_eval_batch_size ${MICRO_BATCH_SIZE} \
--evaluation_strategy steps \
--padding_side right \
--truncation_side left \
--pooling_type last \
--max_length 512 \
--deepspeed configs/default_offload_opt_param.json \
--tf32 false --fp16 false
# rejection sampling
SCORE_PATH=${DATA_PATH}_pred_${MODEL_NAME}_results.json
OUTPUT_FILE_NAME=${DATA_PATH}_rjs_${MODEL_NAME}.json
python3 ${REPO_DIR}/tools/rejection_sampling.py \
--data_path ${DATA_DIR} \
--score_path ${SCORE_PATH} \
--output_dir ${DATA_DIR} \
--rm_scorer ${MODEL_NAME} \
--output_file_name ${OUTPUT_FILE_NAME}
# remove tmp inference files
rm ${DATA_DIR}/*rank*.jsonlAfter inference process, we obtain a RM scoring file ${DATA_PATH}_rjs_${MODEL_NAME}.json. Then we can update the Alpaca model with the training pipeline here.
@inproceedings{cheng2024adversarial,
title={Adversarial Preference Optimization: Enhancing Your Alignment via RM-LLM Game},
author={Cheng, Pengyu and Yang, Yifan and Li, Jian and Dai, Yong and Hu, Tianhao and Cao, Peixin and Du, Nan and Li, Xiaolong},
booktitle={Findings of the Association for Computational Linguistics},
year={2024}
}