This manual is for the code implementation of paper 'Hypergraph based Persistent Cohomology(HPC) for molecular
representations in drug design'
Platform: Python>=3.6
Packages needed: math, numpy>=1.18.1, scipy>=1.4.1, scikit-learn>=0.22.1
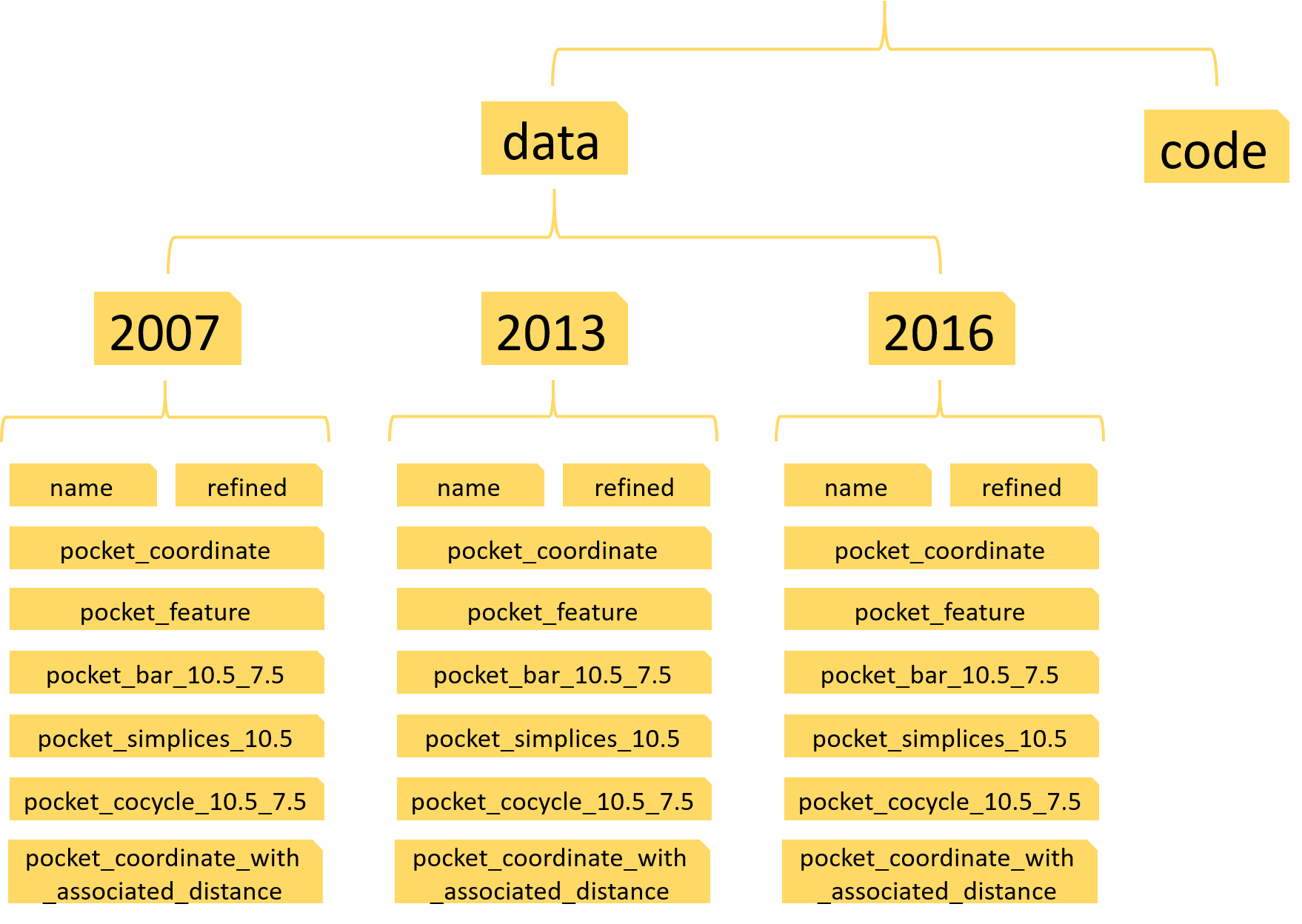
In order to make the protein-ligand binding affinity prediction, you need to download the PDBbind data from this link http://www.pdbbind.org.cn/. To ensure you can use our code easily, you need to build some folders with the following structure:
Here, three python scripts: code_for_PDBbind2007.py, code_for_PDBbind2013.py and code_for_PDBbind2016.py need to be put into the folder ’code’. There are three sub-folders in folder ’data’, which are named as 2007, 2013 and 2016. For each folder(2007 or 2013 or 2016), there are eight sub-folders and a INDEX_refined.data file. This INDEX_refined.data file helps to build the targets for the supervised learning. The parameter 10.5 and 7.5 refer to the cutoff and filtration value we used. More details about eight folders are as follows:
- name: we have put three index files in this folder, which gives specific training and testing data information.
- refined: you need to put all the refined entries into this file, 1300 entries for PDBbind-2007, 2959 entries for PDBbind-2013, 4057 entries for PDBbind-2016. Each entry corresponds a folder named the entry’s name and this folder contains the protein and ligand files.
- pocket_coordinate: this folder place the coordinate data
- pocket_feature: this folder place the feature vectors we construct
- pocket_bar_10.5_7.5: this folder places the barcode
- pocket_simplices_10.5: this folder places the associated simplicial complex of the hypergraph
- pocket_cocycle_10.5_7.5: this folder places the cohomology generators
- pocket_coordinate_with_associated_distance: this folder places the coordinate data and some adjacent distance information, which contributes to the enriched barcode generation
- We have constructed these folders with required files. You can clone our project. Then the only thing you need to do is putting all the entries into the folder ’refined’ for three databases.
Further, we have added all the data needed for PDBbind-2007, you can clone our code and run the script code_for_PDBbind2007.py to repeat our results for PDBbind2007. You can take it as an example
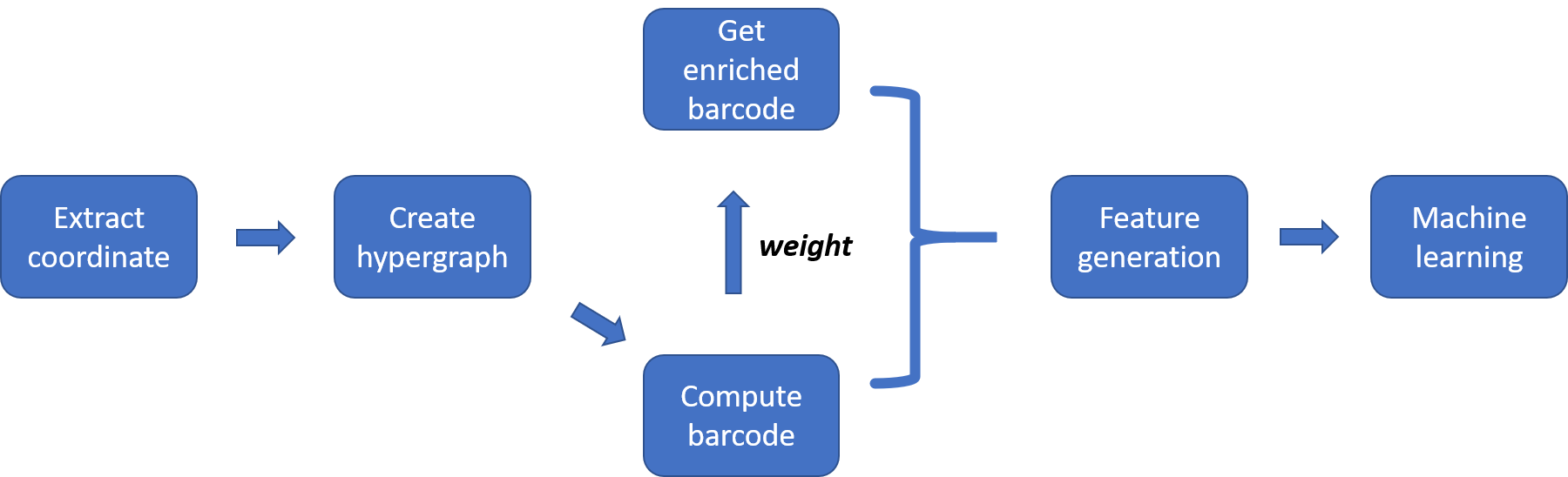
With the PDBbind data, we firstly need to extract the atom coordinates. Here, for each protein-ligand complex, totally 36 atom-combinations are formed with C, N O and S from protein and C, N, O, P, S, F, Cl, Br and I from ligand, which results in 36 hypergraphs for each protein-ligand complex. In our code, 36 pair files are created, each pair is a coordinate file and a counting file that records the number of corresponding protein and ligand atoms. Major functions are as follows:
def pocket_coordinate_data_to_file(start,end):
####################################################################################
'''
this function extract the atom coordinates for each atom-pair of protein-ligand
complex.
output is a coordinate file and a description file, the description file records
the number of atoms for protein and ligand. the coordinate file has four columns,
the former three columns are the coordinate, the last column are 1 and 2 for protein
and ligand atoms respectively.
(1) start and end are index of data you will deal with
(2) before this function, you need to prepare the PDBbind data
'''
####################################################################################After getting the coordinate data, now we can construct the hypergraph. In our paper, we have proven that it suffices to build the filtered associated simplicial complex of the filtered hypergraph because their persistent cohomology are same. So here we construct the associated simplicial complex of the hypergraph. Major functions are as follows:
def create_simplices_with_filtration(atom,cutoff,name,P_atom,L_atom,kill_time):
###########################################################################################
'''
this function creates the filtered associated simplicial complex for the hypergraph.
the dimension only up to 2. you can add higher dimensional information by adding some code.
(1) atom is the atom coordinates. the format is same with output of function
pocket_coordinate_to_file()
(2) cutoff determines the binding core region we extract, that is, we extract the ligand
atoms and the protein atoms within cutoff distance of the ligand. Here, cutoff also
determines the largest length of the edges we use to build the hypergraph, here also
the associated simplicial complex.(of course you can use many others methods to build
the complex, like you can add another parameter max_edge to control the largest length
of an edge, this is just a way)
(3) name is the data name.(for example, for PDBbind-2007, it has 1300 data, each data has
a name)
(4) P_atom and L_atom are the atom-combination, like C-C, C-N, etc.
(5) kill_time is an additional parameter, larger value will lead to longer persistence for
all the barcode. here we use 0.
(6) output is a sequence of ordered simplices, i.e. a filtered simplicial complex.
the format for each simplex is as follows:
[ index, filtration_value, dimension, vertices of the simplex ]
'''
###########################################################################################With the associated simplicial complex of the hypergraph, we can compute its persistent cohomology barcode. The coefficient we use is Z/2. Major functions are as follows:
def get_result(point_cloud,simplices_with_filtration):
###########################################################################################
'''
this function generates the persistent cohomology barcodes and generators for the
associated simplicial complex of a hypergraph.
(1) point_cloud is the coordinate data of a specific atom-combination of some data,
the format is same with the output of pocket_coordinate_data_to_file()
(2) simplicies_with_filtration is the output of function "create_simplices_with_filtration"
(3) output is the zero_barcodes, zero_generators, one_barcodes and one_generators.
you can get higher dimensional information by adding some code.
'''
###########################################################################################By adding some weight to the barcode, we can get the enriched barcode. Here, we combine the enriched barcode
generation and feature generation process. Totally, we mainly have three parts, major functions are as follows:
(1). HPC feature generation
def get_feature_of_train(start,end,cutoff,filtration,unit):
##########################################################################
'''
this function generate the training feature vectors from HPC, the method
is bin counts.
(1) cutoff and filtration are same with function "bar_and_cocycle_to_file"
(2) unit is the size of each bin
(3) before this function, function bar_and_cocycle_to_file() should be
performed to prepare the barcode
'''
##########################################################################
def get_feature_of_test(start,end,cutoff,filtration,unit):
##########################################################################
'''
this function generate the testing feature vectors from HPC, the method
is bin counts.
(1) cutoff and filtration are same with function "bar_and_cocycle_to_file"
(2) unit is the size of each bin
(3) before this function, function bar_and_cocycle_to_file() should be
performed to prepare the barcode
'''
##########################################################################(2). HWPC feature generation
def get_cocycle_feature_of_train(start,end,cutoff,filtration,unit,eta):
#######################################################################################
'''
this function generate the training feature vectors from HWPC, the method is bin counts.
(1) start and end are the indexes of the data we deal with
(2) cutoff and filtration are same with function "bar_and_cocycle_to_file"
(3) unit is the size of each bin
(4) eta is the parameter for weight
(5) before this funcition, function create_coordinate_with_associated_distance() should
be performed.
'''
#######################################################################################
def get_cocycle_feature_of_test(start,end,cutoff,filtration,unit,eta):
######################################################################################
'''
this function generate the testing feature vectors from HWPC, the method is bin counts.
(1) start and end are the indexes of the data we deal with
(2) cutoff and filtration are same with function "bar_and_cocycle_to_file"
(3) unit is the size of each bin
(4) eta is the parameter for weight
(5) before this funcition, function create_coordinate_with_associated_distance() should
be performed.
'''
######################################################################################(3). combined feature generation
def get_combined_feature(typ,cutoff,filtration,unit):
#####################################################################
'''
this function get the combined feature vectors from HWPC with
a lower eta 2.5 and another HWPC with a higher eta 10
'''
#####################################################################After getting the training and testing features, it is a routine procedure to use machine learning algorithm to make the prediction. we use gradient boosting tree to make the regression, the parameter setting are as follows:
| No. of Estimators | Learning rate | Max depth | Subsample | Min_samples_split | Loss function | Max features | Repetitions |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 40000 | 0.001 | 9 | 0.7 | 2 | Least square | SQRT | 10 |
If you have successfully build the folders, insert the PDBbind data and import the packages we mentioned. Then you can repeat our results by running these three python scripts: code_for_PDBbind2007.py, code_for_PDBbind2013.py and code_for_PDBbind2016.py.
`We have added all the needed data into the folder for PDBbind2007, so just clone our project, then you can repeat
our results for PDBbind2007 by running python script code_for_PDBbind2007.py. More specifically, you can run the
following command one by one:`
git clone https://github.com/LiuXiangMath/Hypergraph-based-Persistent-Cohomology.git
cd Hypergraph-based-Persistent-Cohomology
pip install -r requirements.txt
cd code
python code_for_PDBbind2007.py