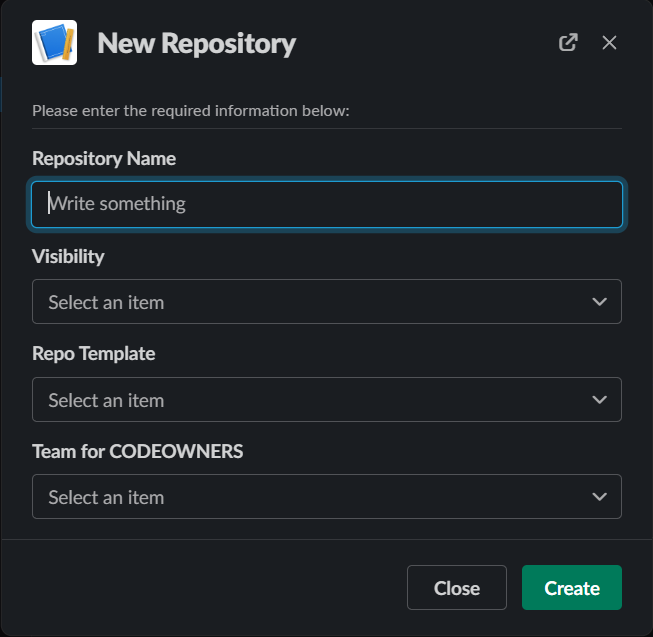
slack-gitbot is a tool for controlling the creation of github repositories through chatops
The following environmental variables must be set.
| Variable Name | Secret | Description |
|---|---|---|
| SLACK_BOT_TOKEN | True | The Slack bot token from the oauth tab of the bot configuration page in slack (xoxb-<something>) |
| SLACK_SIGNING_SECRET | True | The signing secret from the basic information page of the bot configuration page in slack |
| GITHUB_TOKEN | True | The github PAT used to create new repos |
Configuration of all other variables is done via conf.yml. This can be set at container build time or runtime by overriding the /app/conf.yml file. At a minimum you must configure the github.org value.
This project is designed to run as a container and can be run serverless. It has been tested on GCP Cloud Run specifically.
The first step to configure slack is to create a slack app:
You should modify and the app_manifest.yml to set the slack permissions, making sure to uncomment the permissions required to use azure-ad authentication if you want to use it. If you aren't a slack admin, you'll have to request for the app to be installed to your workspace.
You will need to provide a Github personal access token, preferably for a service account, with org:admin access. This PAT should be passed to slack-gitbot via the GITHUB_TOKEN environmental variable.
You will find an authentication provider for Azure AD in the auth_providers folder. It requires an Azure AD enterprise application to be configured with certificate based auth. You can enable Azure AD auth by configuring slackbot.auth to azure-ad-auth in the conf.yml file and uncommenting the azure_ad_group section in the conf.yml file.
If cert_dir is set to /secrets then the bot will look for the application certificate in /secrets/cert/cert.pem and the private key in /secrets/key/key.pem. It's designed to work this way to make working with secrets managers (like GCP Secrets) more easily.
Make a certs directory and change to it
mkdir certs && cd certsCreate a key and a cert that expires in 1 year
openssl req -x509 -nodes -newkey rsa:4096 -keyout key.pem -out cert.pem -sha256 -days 365