Brain tumors are abnormal growths of tissue in the brain that can be either benign (non-cancerous) or malignant (cancerous). Early detection of brain tumors is crucial for effective medical intervention and treatment. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is a widely used medical imaging technique that provides detailed structural images of the brain.
Developed a machine learning solution utilizing VGG-16 architecture for precise identification and localization of brain tumors in MRI images. Brain Tumor Detection with VGG-16 is an advanced machine learning project designed for accurate identification and localization of brain tumors in MRI images. This project showcases a comprehensive solution, including data preprocessing, CNN model architecture, performance evaluation, and potential future work.
The dataset used in this project is sourced from Kaggle and consists of MRI images for brain tumor detection. The dataset provides a diverse set of images, making it suitable for training and evaluating the machine learning model.
- Dataset Name: Brain MRI Images for Brain Tumor Detection
- Description: This Kaggle dataset contains MRI images of the brain, labeled for tumor detection. The images cover various conditions and scenarios, enabling robust model training and evaluation.
Please ensure compliance with Kaggle's terms of use and licensing for the specific dataset.
To implement this project, we leverage various libraries in Python:
- TensorFlow for building and training deep learning models.
- NumPy for efficient numerical operations.
- OpenCV for image processing tasks.
- Matplotlib for data visualization.
- Scikit-learn for evaluating model performance.
In the preprocessing stage, the dataset is prepared for model training and evaluation. Key steps include:
-
Data Splitting:
- The available data is divided into three sets:
- Training Set: Used to train the machine learning model. (80% of the data)
- Validation Set: Utilized for fine-tuning hyperparameters and model evaluation. (20% of the data)
- Test Set: Reserved for final model evaluation. (5 Images per class)
- The available data is divided into three sets:
-
Image Resizing and Preprocessing:
- Each image is resized to meet the input requirements of the VGG-16 architecture.
- VGG-16 preprocessing techniques are applied to enhance compatibility with the chosen model.
These preprocessing steps ensure a well-organized dataset for effective training, tuning, and evaluation.
The Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) model is built using the VGG-16 architecture. VGG-16 is a powerful pre-trained model that can be fine-tuned for specific tasks. The model is customized with additional layers for our brain tumor detection task.
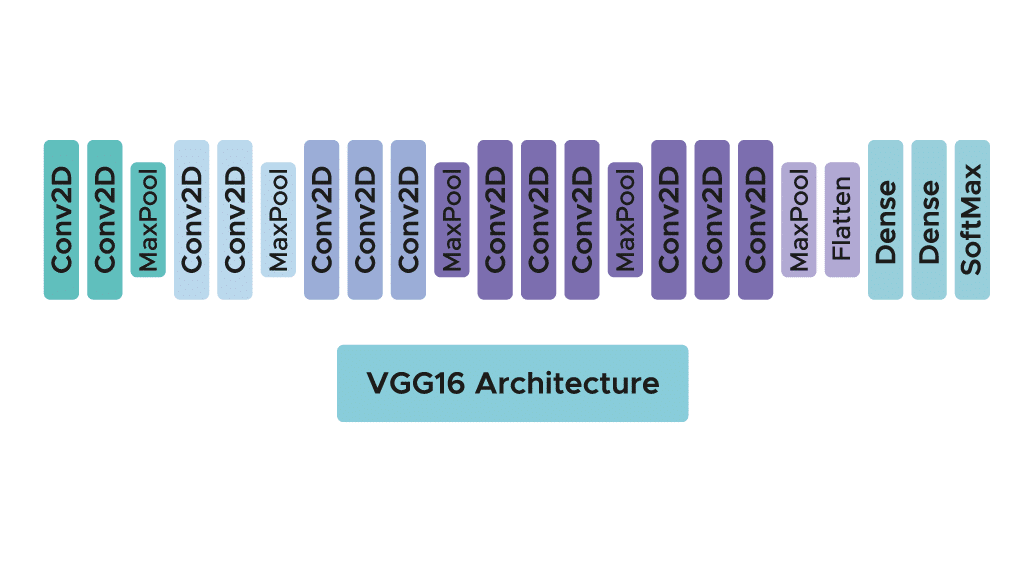
Performance evaluation is crucial to understand how well the model is performing. Key metrics such as accuracy and confusion matrix are calculated on both the validation and test sets. These metrics provide insights into the model's ability to correctly identify brain tumors.
As with any machine learning project, there are opportunities for further improvement and exploration. In the future, we may consider:
Experimenting with different CNN architectures to find the most suitable one. Fine-tuning hyperparameters for better model performance. Exploring transfer learning with larger datasets for increased accuracy.