This repository contains the official implementation of the paper "Enhancing E-Commerce Fulfillment Operations: Machine Learning Approaches for Order Forecasting and Cost Reduction." The paper is currently under development by Ludwig Baunach and co-author Stefan Spinler.
Please note, the code here is a subset of scripts from our private projects, and therefore the file paths are not relevant. The repository's intent is to provide a methodological overview of our paper's work.
Note: Unfortunately, we cannot share our data due to a Non-Disclosure Agreement (NDA).
Main Folder: The main folder contains all the main scripts. It serves as a good starting point to understand the code flow.
Running the Code: To use the code, start by running main_data_prep.py for data pre-processing. After that, execute main_fscript.py to perform forecasting, create ensembles, and initiate workforce optimization. Note that you will need to specify the sources you wish to run.
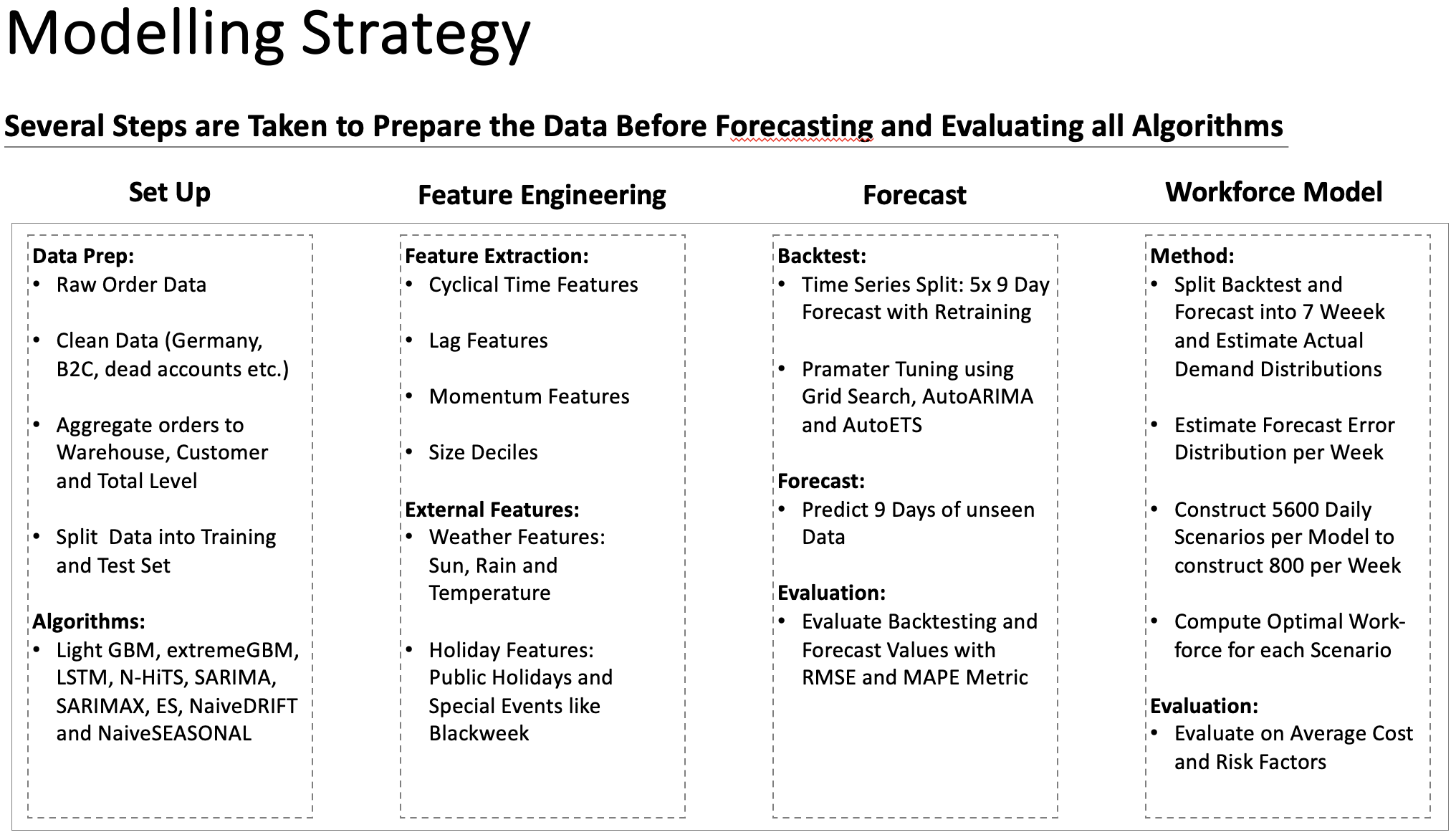
Code Structure: The repository is organized into several key folders, each serving a specific purpose: ** src**
data_prep: Contains scripts for data wrangling and preparation.forecast_models: Houses the forecasting model scripts.evaluation: Includes scripts for evaluating the forecasting models' performance.stochastic_programming: Contains a script to run our simulation single workforce models for all models and the sensitivity analysis.utils: contains custom functions used throughout the main scripts.
notebooks
Descriptives: Contains code to create an autocorrelation plot and to visualise order quantities per time frameWorkforce_Evaluation: Includes scripts to create all workforce related results
The code is currently under development. Once the paper gets accepted by a journal, we will add example data and a requirements.txt file detailing the necessary libraries and their versions.
On our dataset, the code takes approximately 30 hours to run on a machine with a 2.4 GHz Quad-Core Intel Core i5, 8GB 2133 MHz LPDDR3 RAM, Intel Iris Plus Graphics 655 1536 MB, running macOS.
How does applying novel machine learning methods affect workforce planning of warehouse operations in the e-commerce context?
To address this, our study focuses on the weekly staff sizing decision problem in warehouse operations, characterised by stochastic demand. Our methodology is tripartite, encompassing forecasting, simulation, and workforce modelling.
Firstly, we undertake an exhaustive comparison of state-of-the-art forecasting methods, comparing classical models with machine learning (ML) and deep learning (DL) approaches. These methods utilise a range of features such as lag, momentum, and time, along with weather and holiday variables across three hierarchical levels to forecast future demand. Notably, we employ five-fold time series cross-validation in addition to a test set, thereby enhancing the robustness of our findings.
Secondly, we leverage data from cross-validation and test samples to estimate seven distinct demand and forecast distributions for each of our 100 models. This is taken as input for a Monte Carlo simulation, generating 800 weekly simulations of actual and forecasted demand, thereby offering a nuanced understanding of various forecasting methods' reliability and performance.
Lastly, we introduce a multi-stage stochastic program with recourse to schedule planned workers based on forecasts and adapt with overtime and extra workers based on actual demand. This program utilises the simulated scenarios as inputs, allowing us to evaluate the operational impact of different forecasting methods in terms of labour costs and scheduling policies.