A visual and interactive front-end dependency analysis tool
Can be used in any extension project like Vue React Svelte Angular Node
English | 简体中文
- Code refactoring: By analyzing dependencies, we can better understand the structure and logic of the code, making it easier to refactor and optimize the code.
- Modular development: By analyzing dependencies, we can split the project into multiple modules, each module has clear responsibilities and dependencies, so as to achieve modular development and management.
- Code testing: By analyzing dependencies, we can more easily write and run unit tests, thereby improving the quality and reliability of the code.
- Code maintenance: By analyzing dependencies, we can more easily locate and solve problems in the code, thereby improving the maintainability and scalability of the code.
- An interactive integrated
visualdependency analysis system - Support dynamic switching of entry files
- Support
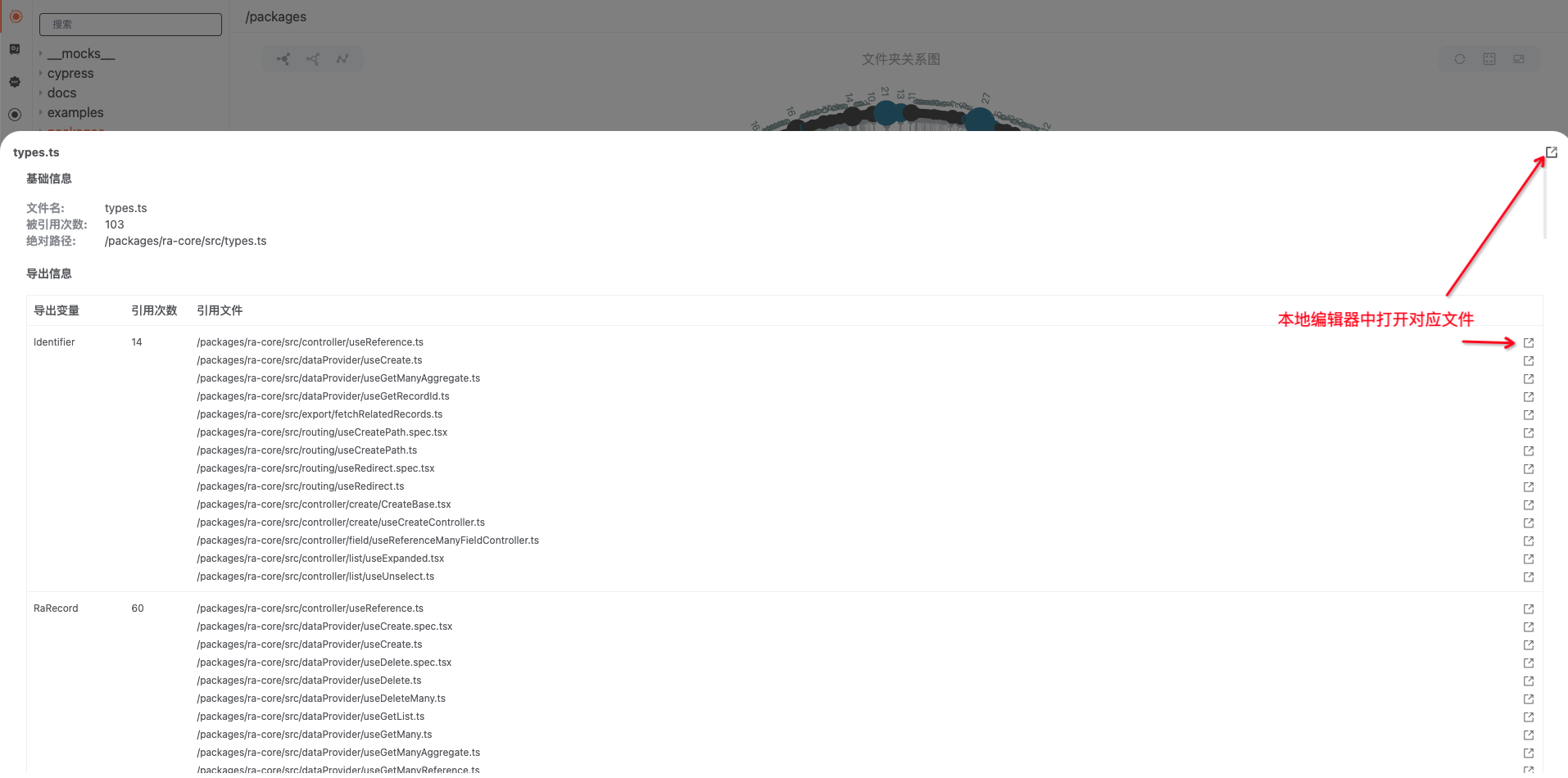
Dependency Inversion - Supports displaying the number of times a file is cited, as well as the reference address
- Support displaying the referenced information of exported variables of files
- Compatible with ES6, CommonJs
- Supported file types: JS, TS, JSX, TSX, Vue, Sass, Less, Css, html
- Support package dependency analysis
- Support unreferenced files, npm package analysis
- Local storage is
very safe, does not involve networking and uploading
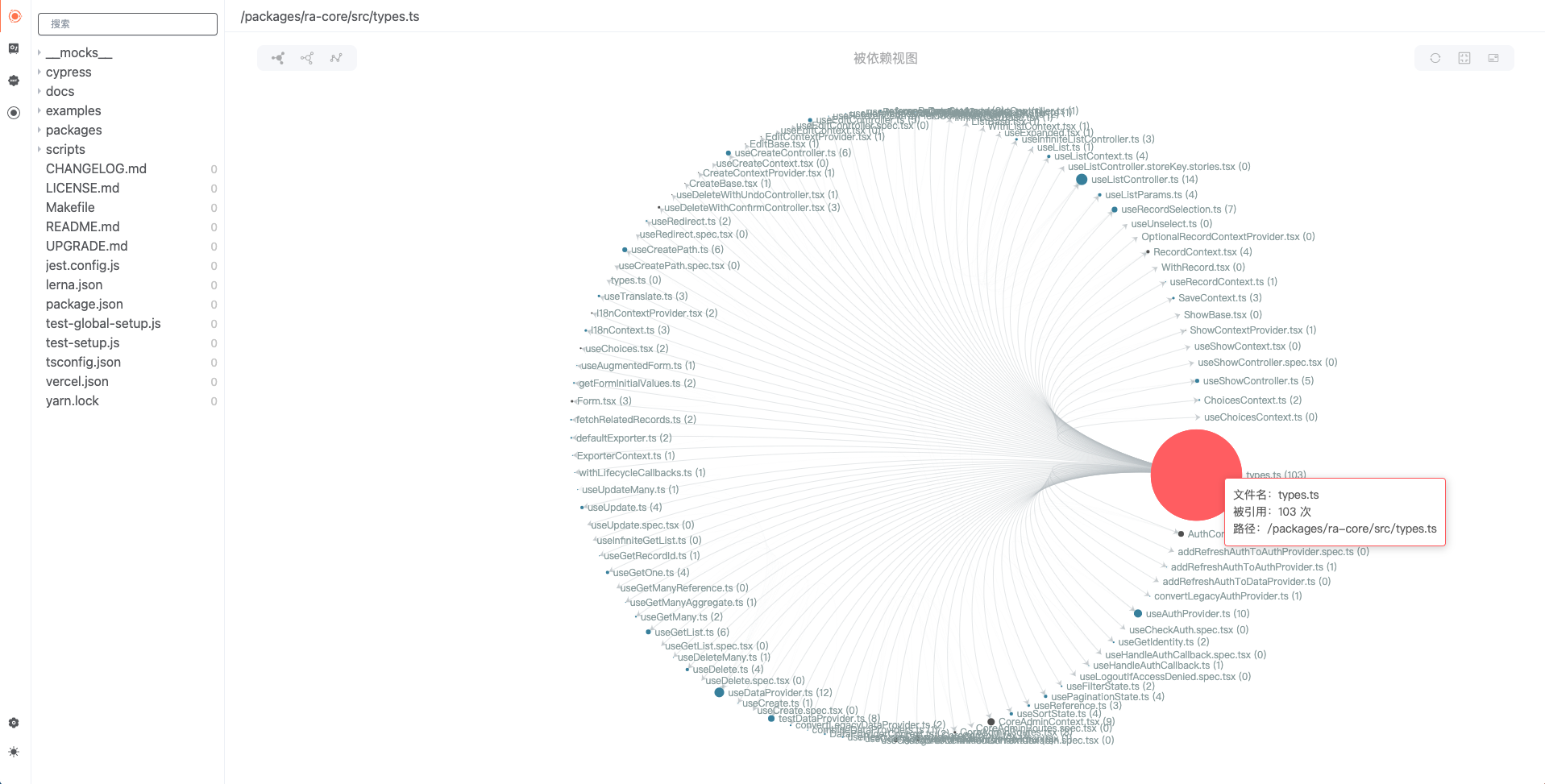
Double-click a node to enter the dependency view of the node
After double-clicking a node, click the third positive icon in the upper left corner to switch to the upstream dependency graph
Click a node in the view to pop up file dependency details
- Support VUE SETUP
- Customizable plug-ins to generate the data you want
- Built-in project hotword plug-in support
- File dependency view: support dependency view within a single folder
- Sass, Less, Css and other style file analysis (New, supported)
- Support project variable hot word map
npm install @js-analyzer/server -g
# yarn add @js-analyzer/server -g
# pnpm install @js-analyzer/server -gGo to the root directory of any project and execute js-analyzer --root ./
cd /xxx/project
js-analyzer --root ./npm install @js-analyzer/server -D
# yarn add @js-analyzer/server -D
# pnpm install @js-analyzer/server -D"scripts": {
"js-analyzer": "js-analyzer --root ./"
},2.Enter npm run js-analyzer in the console and visit http://localhost:8088/ to see it.
npm run js-analyzer
# Service started:http://localhost:8088/An analysis service can be quickly started through the above command, but the overall structure of each project is different. If you want js-analyzer to analyze better and more accurately, you need to configure some necessary information.
To specify a configuration file, you only need to modify the above startup command
"scripts": {
"js-analyzer": "js-analyzer --config ./js-analyzer.js"
},js-analyzer.js
module.exports = {
// Root directory
root: "/Users/ll/Downloads/react-admin-master",
// Directories that do not need to be analyzed
ignore: ["**/node_modules/**", "**/dist/**"],
// Priority search order when parsing files without extensions
extensions: [".js", ".ts", ".tsx", ".vue", ".json", "jsx"],
// The project's alias
alias: {
"@@/": "/",
"~~/": "/",
"@/": "/src/",
"~/": "/src/",
},
// The started server is related to the port
server: {
port: 8088,
host: "localhost",
openBrowser: true, // auto open in the browser
},
};- Project component documentation to generate shared modules
- Cyclic dependency analysis
- Module stability index analysis
The principle of this tool is to collect relevant dependency information by parsing AST. In theory, users can also collect any information they want in this process. Therefore, a plug-in method is provided to expose the life cycle of each stage and allow users to execute any logic in the life cycle function.
const myCustomPlugin = {
name: "MyCustomPlugin",
// output information
output: {
data: [],
file: "test.json",
},
// Executed when parsing script
ScriptParser({ file, content }) {
const self = this;
return {
VariableDeclarator(tPath) {
tPath.node.id && self.output.data.push(tPath.node.id.name);
},
};
},
// Executed when the script is parsed
AfterScriptParser() {},
};
module.exports = {
plugins: [myCustomPlugin],
};Custom generated data, default access address 'http://localhost:8087/data/test.json'
More interested people are very welcome to join in