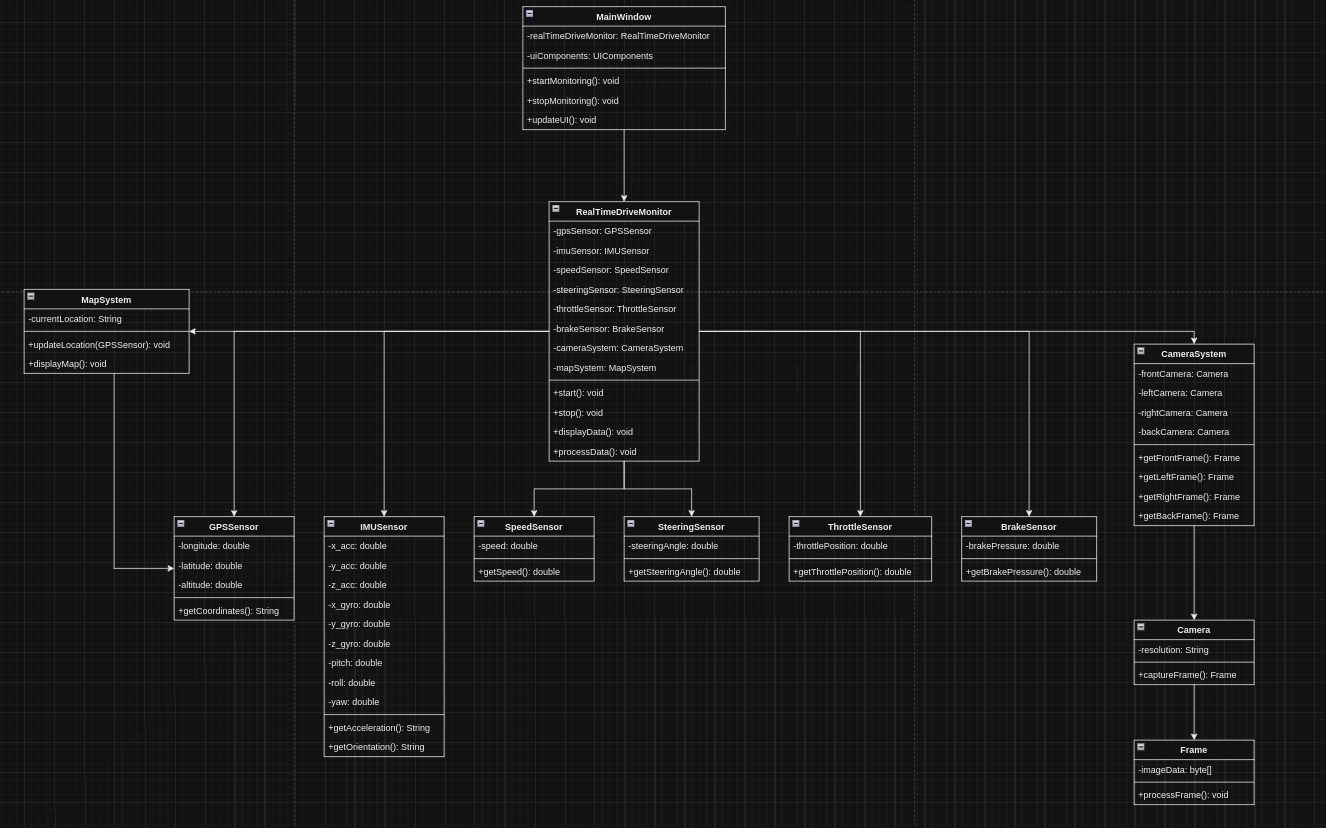
RealTimeDriveMonitor is a real-time monitoring system that provides a visual interface for displaying live camera feeds (front, left, right, back) from a vehicle along with sensor data such as GPS, IMU, speed, steering, throttle, and brake. The system integrates with Google Maps to show the vehicle's current location and ensures synchronized data display with camera frames.
The RealTimeDriveMonitor system integrates various vehicle sensors to provide real-time data along with visual camera feeds. The key sensors include:
- Real-Time Camera Feeds: Displays live video from four vehicle-mounted cameras (front, left, right, back), enabling comprehensive monitoring of the vehicle's surroundings.
- Synchronized Sensor Data: Displays relevant sensor data (speed, steering, GPS, etc.) alongside the camera feeds, all synchronized to the current timestamp of the video frames.
- Map Integration: Integrates Google Maps to display the vehicle's real-time location based on GPS data.
- Data Prioritization: Starts reading and displaying frames from the first available front camera frame, ensuring consistency in the visual feed.
- User-Friendly Interface: A clean and organized UI to easily monitor the vehicle’s environment and sensor data in real-time.
- Each camera captures video frames showing the surrounding environment of the car from different perspectives.
- The system will show synchronized frames from all four cameras on the screen.
- The video frames must be timestamped to ensure synchronization across all camera feeds.
- Data: Longitude, Latitude, Altitude: The GPS provides geographical coordinates (longitude and latitude) and altitude data. This data is used to determine the car's exact position on the Earth's surface.
- Google Maps Integration: The position data will be used to show the car's current location on a map. The map can be updated in real-time using Google Maps or any other mapping service API.
The Inertial Measurement Unit provides the vehicle's current movement status to all requesting devices. IMU data helps track the car's movement and orientation in space. This data is crucial for understanding the vehicle's dynamics, especially during turns or rough terrains.
- Accelerometer (x, y, z): Measures the car's acceleration in three dimensions.
- Gyroscope (x, y, z): Measures the car's angular velocity or rotation in three dimensions.
- Magnetometer (x, y, z): Measures the magnetic field, which helps determine the car's orientation relative to Earth's magnetic field.
- Orientation (pitch, roll, yaw): These values represent the orientation of the vehicle in three-dimensional space
Pitch: Rotation around the x-axis (e.g., nose up or down).Roll: Rotation around the y-axis (e.g., tilting side to side).Yaw: Rotation around the z-axis (e.g., turning left or right).
- Orientation (pitch, roll, yaw): These values represent the orientation of the vehicle in three-dimensional space
- Speed: The current speed of the vehicle, typically provided by the car's onboard systems.
- Steering Angle: The angle at which the steering wheel is turned, which helps understand the car's direction.
- Throttle Position: Indicates the degree to which the accelerator pedal is pressed, reflecting how much power the driver is requesting from the engine.
- Brake Pressure: Measures the pressure applied to the brake pedal, indicating the braking force being applied.
The speed sensor measures the vehicle’s current speed, providing real-time feedback to the system and the driver. Speed data is critical for monitoring compliance with speed limits, controlling cruise control systems, and assisting in various safety features like automatic braking.
The steering angle sensor measures the angle of the steering wheel, indicating the direction the vehicle is moving or about to move. Its data used in lane-keeping assist, stability control systems, and automated driving features to ensure the vehicle follows the intended path.
This sensor monitors the position of the throttle (the pedal that controls acceleration), indicating how much power the driver is demanding from the engine. Its data used for controlling engine power, cruise control systems, and optimizing fuel efficiency.
The brake sensor detects when and how hard the brake pedal is pressed, providing real-time information on braking actions. Its data essential for safety systems like ABS (Anti-lock Braking System), collision avoidance systems, and for general vehicle control during deceleration.
The RealTimeDriveMonitor system employs a central clock mechanism to ensure all sensor data and camera feeds are synchronized accurately in real-time. This is critical to presenting a cohesive view of the vehicle's environment and status at any given moment.
- Clock-Based Data Coordination: The system starts monitoring from the first available front camera frame, and all sensor data (GPS, IMU, Speed, etc.) is aligned with the clock time. This approach ensures that all displayed information across the UI (including sensor data and camera feeds) is in sync.
- Tick Interval: The system processes data based on a fixed tick interval, ensuring that sensor readings and camera frames are updated at regular intervals, creating a smooth and consistent real-time experience.
To handle the large volume of data being processed in real-time, an efficient buffer management system has been implemented:
- Max Buffer Size: Ensures that the buffer does not overflow by removing the oldest data when the buffer reaches its maximum size.
- Data Cleanup: Automatically clears data that is no longer needed after processing to optimize memory usage.
- Factory Pattern: A factory pattern has been applied for sensor data creation, simplifying the creation of sensor data objects and making the code more maintainable.
- Modularization: The code has been refactored to improve modularity, making it easier to manage and extend the system with new features.
- Clock System: The clock system is used for precise synchronization of sensor and camera data, ensuring all data is aligned based on the current timestamp.