(c) 2021 Matthew Blanchard, Fredrick R. Brennan & MFEK Authors
A set of utilities for stroking paths in font glyphs written in Rust.
This program is part of the MFEK project.
Notice 2 February 2022: MFEKstroke v1.0 is released! The CLI API should be considered stable.
MFEKstroke takes UFO .glif files and applies path stroking algorithms to them.
Five stroking algorithms are provided:
- PAP (Pattern-Along-Path)
- VWS (Variable Width Stroking)
- CWS (Constant Width Stroking)
- DASH (Dashes and dots along paths)
- Nib (requires FontForge be installed, uses
libfontforge.(so|dll))
This makes MFEKstroke more complete in this department than Glyphsapp, FontForge or Runebender.
MFEKstroke is a Rust project. The best way to get the Rust toolchain is via rustup.
A Makefile is provided for your convenience.
The build command is:
makeWhich runs cargo build.
You can provide the environment variables FONTFORGE and DEBUG to make. Without DEBUG, the binary goes in target/release; otherwise target/debug.
FONTFORGE will compile the nib stroking mode; it will only work if libfontforge.so (.dll on Windows) is locatable by cargo.
DEBUG=y FONTFORGE=y makeYou can pass RUSTFLAGS to either cargo or make to help them find libfontforge, where /opt/lib is the location of your libfontforge.so file:
RUSTFLAGS='-L /opt/lib' FONTFORGE=y makeIf you get an error like:
$ MFEKstroke
MFEKstroke: error while loading shared libraries: libfontforge.so.4: cannot open shared object file: No such file or directory
You can remedy that by running as:
$ LD_LIBRARY_PATH=/opt/lib MFEKstroke NIB -h
MFEKstroke-NIB 0.1.0
…
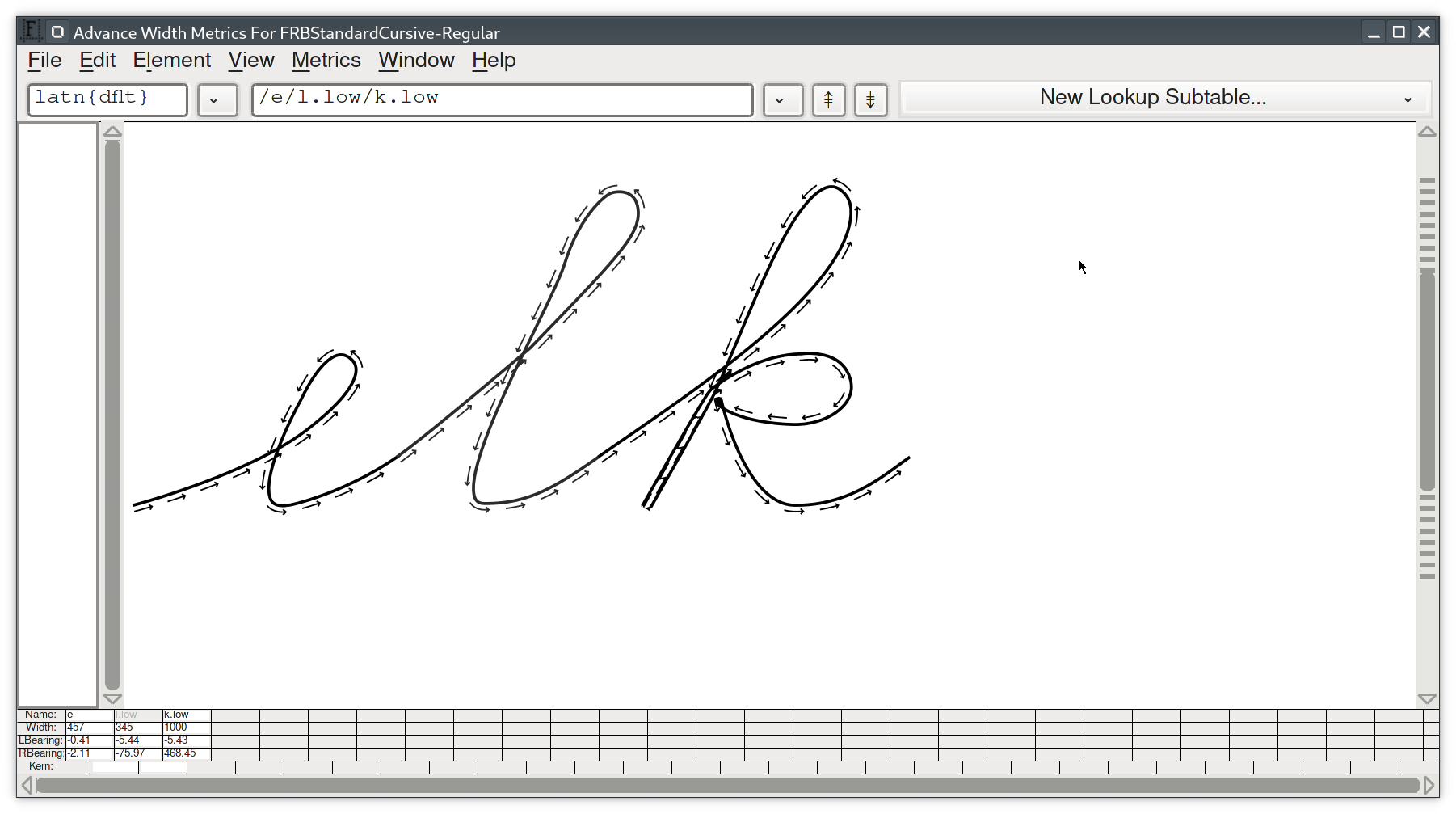
This was generated with the following command:
cargo run -- --pattern simple.glif --path Q_.glif --out arrow.glif --sx 0.3 --sy 0.1 --stretch true --subdivide 2 --mode repeated
cargo run -- --out Untitled2.ufo/glyphs/k.low.glif --path FRBStandardCursive-Regular.ufo/glyphs/k.low.glif --pattern arrow.ufo/glyphs/arrow.glif -m repeated --sx 0.1 --sy 0.1 -s 3 --simplify true --stretch true
MFEKstroke-PAP 0.2.1
Matthew Blanchard <matthewrblanchard@gmail.com>; Fredrick R. Brennan <copypasteⒶkittens.ph>; MFEK
Authors
Maps a pattern glyph along a path glyph.
USAGE:
MFEKstroke PAP [OPTIONS] --path <path>
OPTIONS:
-p, --pattern <pattern>
The path to the input pattern file. You may also provide either --dot-pattern or --dash-
pattern to use built-in patterns.
-=, --dash-pattern
Use a simple dash pattern
-w, --warp
Warp the pattern to fit the path.
-., --dot-pattern
Use a simple dot pattern
-P, --path <path>
The path to the input path file.
-o, --output <output>
The path where the output will be saved. If omitted, or `-`, stdout.
-c, --contour <contour>
<isize> if this is a positive number we stroke only that specific contour in the outline
by index. [default: -1]
-m, --mode <mode>
Repeat mode. [default: single] [possible values: single, repeated]
-s, --subdivide <subdivide>
<usize> how many times to subdivide the patterns at their midpoint. [default: 0]
-°, --subdivide-angle <subdivide_angle>
<f64> how many degrees of change in direction to subdivide the patterns at. [default: 0]
-X, --sx <sx>
<f64> how much we scale our input pattern on the x-axis. [default: 1]
-Y, --sy <sy>
<f64> how much we scale our input pattern on the y-axis. [default: 1]
-|, --split-at-discontinuity
Handle discontinuities by splitting the path.
-n, --noffset <normal-offset>
<f64> how much to offset the pattern along the normal of the path. [default: 0]
-t, --toffset <tangent-offset>
<f64> how much to offset the pattern along the tangent of the path. [default: 0]
-W, --spacing <spacing>
<f64> how much padding to trail each copy with. [default: 0]
-!, --stretch <stretch>
<stretch> false if not given, true if given, spacing mode if value of spacing given
[possible values: spacing]
-S, --simplify
<boolean> if we should run the result through Skia's (buggy) simplify routine.
-O, --remove-overlapping
Remove patterns that would overlap.
-Z, --erase-overlapping
Erase the area underneath patterns that would overlap.
-z, --erase-overlapping-stroke <erase_overlapping_stroke_width>
<float> how much we should expand the pattern when erasing overlapping patterns.
-%, --erase-overlapping-area-percent <erase_overlapping_area_percent>
<float> how much we should expand the pattern when erasing overlapping patterns.
-Q, --one-pass
<boolean> whether we should not reflow the path after culling during overdraw (faster
but worse).
-C, --no-center-pattern
<boolean> supply if you wish to center the pattern
-r, --reverse
<boolean> true will reverse the path.
-R, --reverse-culling
<boolean> true will reverse the order we check for overlaps during overlap culling.
-h, --help
Print help information
-V, --version
Print version information
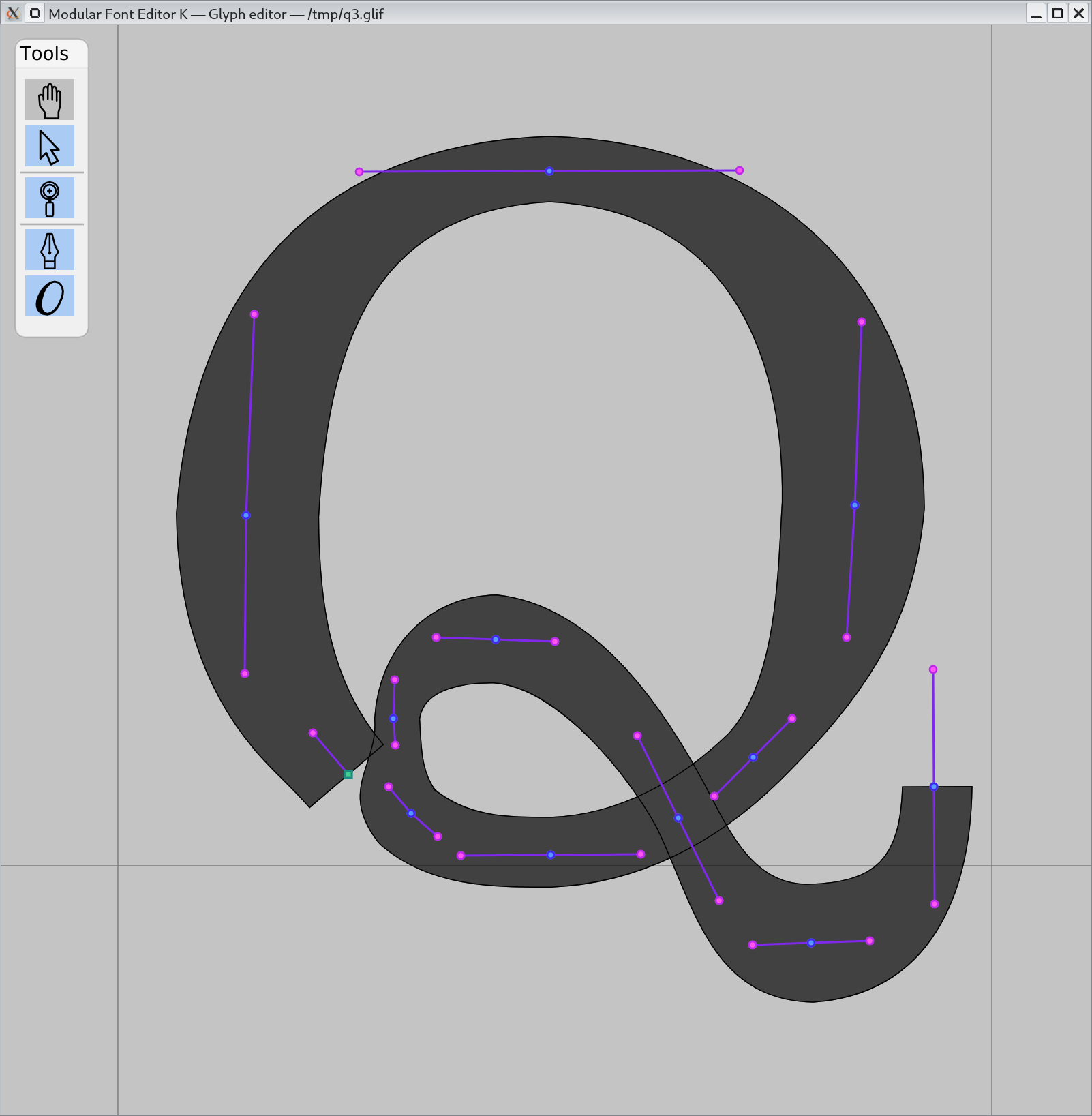
(Note: In VWS mode, it is expected that you are using MFEKglif to generate the input files. Therefore, not many helpful command line options are provided. If you wish to use VWS programatically, play with MFEKglif's VWS tool, get some output, and study it; then generate conformant XML.)
MFEKstroke-VWS 0.1
Matthew Blanchard <matthewrblanchard@gmail.com>
Takes a .glif file and strokes it with variable width.
USAGE:
MFEKstroke VWS -i <input> -o <output>
FLAGS:
-h, --help Prints help information
-V, --version Prints version information
OPTIONS:
-i <input> The path to the input file.
-o <output> The path where the output will be saved.
MFEKstroke-CWS 0.1
Fredrick R. Brennan <copypasteⒶkittens⊙ph>; Matthew Blanchard <matthewrblanchard@gmail.com>
Takes a .glif file and strokes it at a constant width.
USAGE:
MFEKstroke CWS [FLAGS] [OPTIONS] --input <input> --output <output> --width <width>
FLAGS:
-I, --remove-internal Remove internal contour
-E, --remove-external Remove external contour
-S, --segmentwise Join all segments with caps (stroke all Bézier segments one by one)
-h, --help Prints help information
-V, --version Prints version information
OPTIONS:
-i, --input <input> The path to the input file.
-o, --output <output> The path where the output will be saved.
-s, --startcap <startcap> Either the constant strings "circle", "round" or "square", or a .glif file. [default:
circle]
-e, --endcap <endcap> Either the constant strings "circle", "round" or "square", or a .glif file. [default:
circle]
-j, --jointype <jointype> How to join discontinuous splines [default: round] [possible values: round, circle,
miter, bevel]
-w, --width <width> <f64> Constant stroke width.
-l, --left <left> <f64> Constant stroke width (left).
-r, --right <right> <f64> Constant stroke width (right).
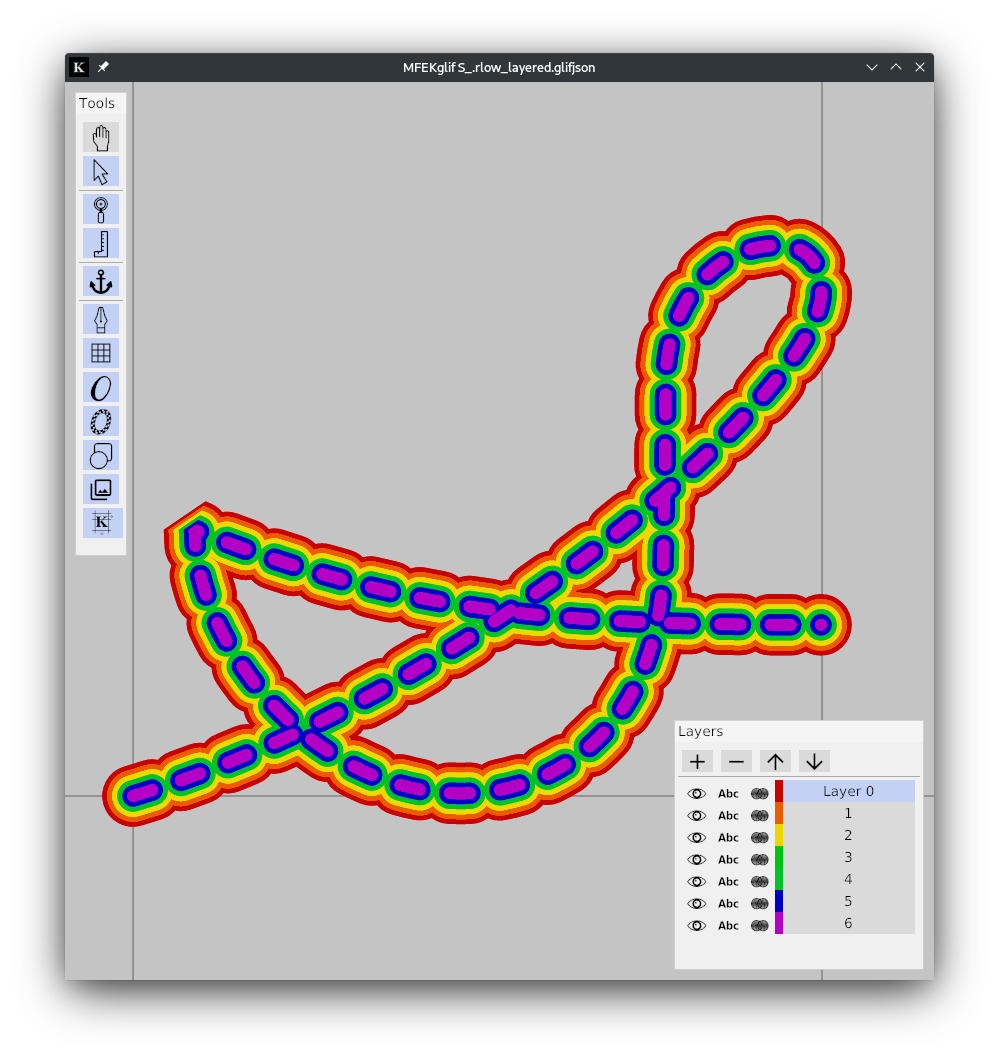
MFEKstroke-DASH 0.1.0
Fredrick R. Brennan <copypasteⒶkittens.ph>; MFEK Authors; Skia/kurbo.rs authors
Applies a dash to a glyph.
USAGE:
MFEKstroke DASH [OPTIONS] --input <input> --output <output>
OPTIONS:
-i, --input <input> The path to the input glif file.
-o, --output <output> The path to the output glif file.
-d, --dash-description <dash>... Dash description [default: 30 30]
-c, --cull Attempt to cull earlier dashes when later dashes cover them
-w, --width <width> Stroke width (to leave an open contour, use 0) [default: 30]
-W, --cull-width <cull-width> Cull width [default: 40]
-a, --min-area <area> Paths with either a height or width below this number are
culled. Do not set if unsure.
-l, --write-last Write last path
-j, --join <join-type> How to join discontinuous splines [default: round] [possible
values: round, miter, bevel]
-J, --cap <cap-type> How to cap splines [default: round] [possible values: round,
butt, square]
-h, --help Print help information
-V, --version Print version information
MFEKstroke-NIB 0.1.0
Fredrick R. Brennan <copypasteⒶkittens⊙ph>; Skef Iterum (FontForge)
Takes a nib and a path, both in .glif format, and emulates a pen, with the chosen nib, stroking the path.
Important note: FontForge is used for this, so it may be more unstable than other modes as FontForge is implemented in C
and not memory safe. To prevent bugs, we turn off simplification and overlap removal. Use MFEK for that.
USAGE:
MFEKstroke NIB --input <input> --nib <nib> --output <output>
FLAGS:
-h, --help Prints help information
-V, --version Prints version information
OPTIONS:
-n, --nib <nib> The path to the nib file. FontForge is quite strict about these. The .glif must contain
a single closed spline, running clockwise, which represents a convex shape.
-i, --input <input> The path to the input path file.
-o, --output <output> The path where the output .glif will be saved.
-a, --accuracy <accuracy> <f64> Accuracy target [default: 0.25]
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at:
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
The biggest TODO's right now:
- tests;
- documentation/demos/user stories;
- descriptions of how the algorithms work.