GotoSSH is committed to helping you improve work efficiency.
There are some pics, they will show you to what this shell can do.
Normal login with no subsequent operation:
Login the jump server first, and then jump to the online server:
Login the server and view the log:
Login the jump server and then login the online sever to view the log:
Copy file from the remote server:
Copy file from the online server:
List all the servers:
List all the custum commands and common commands the server supported:
CentOS :
$ sudo yum install -y expectUbuntu :
$ sudo apt-get install tcl tk expectMac :
$ brew install expect$ brew install gnu-sed --with-default-names
$ export PATH="$(brew --prefix coreutils)/libexec/gnubin:/usr/local/bin:$PATH"
$ export MANPATH="/usr/local/opt/coreutils/libexec/gnuman:$MANPATH"$ git clone https://github.com/MFrank2016/GotoSSH.git
$ cd GotoSSH
$ chmod a+x gotossh
$ sudo cp gotossh /usr/local/bin/If you have installed the older version, you need to remove it in /usr/local/bin/.
$ vim ~/.gotossh_config
JumpServer||111.231.59.85||root||password||22||0
JumpServer2||111.231.59.85||root||password||22||0
OnlineServer||118.24.163.31||root||password||22||1
[Server-JumpServer]
distributor-log=tail -f -n 500 /var/log/[service-name]/[service-name].log
cd=cd /var/log/[service-name]/
cd1=cd [P1][P2]
[Server-Attribute-JumpServer]
service-name=test-service
[Server-OnlineServer]
[Server-Attribute-OnlineServer]
service-name=online-service
[scp]
log1=~/testfile2
log2=/var/log/omp-distribution-facade-service/omp-distribution-facade-service.log
log3=~/testlog.log
log4=/var/log/test-service/test-service.log
log5=/logs/openapi/service/omp-distributor-service.log
bill-log=/var/log/omp-bill-service/omp-bill-service.log
[settings]
version=3.0
[common-command]
log=tail -f -n 500 /var/log/[service-name]/[service-name].log
error-log=tail -f -n 500 /var/log/[service-name]/[service-name]-error.log
The config file consists of four parts.
The first part is the server base info:
link_name||ip||username||password||port||rely_server_no||service_name
For example:
JumpServer||111.231.59.85||root||password||22||0||test-service
The rely_server_no column means this server relies another server, so this shell script will login that server first.(the rely_server_no starts form 1, so 0 means this server doesn’t rely any other server)
The second part is custom commands and custom attributes, you could set any command here for each server.
[Server-link_name]
command=xxxxxx
[Server-Attribute-link_name]
attribute=xxx
Server-link_name means it's set for the server who has the link-name of link_name.
command is the name of your command, that could be any name you like, and the actual command is behind the equals sign.
The part of Server-Attribute-link_name is setted for custom command and common command, when you use custom attribute in command like this /var/log/[service-name]/[service-name].log, this script will find this attribute in the node of Server-Attribute-link_name.
For example:
[Server-JumpServer]
distributor-log=tail -f -n 500 /var/log/[service-name]/[service-name].log
cd=cd /var/log/[service-name]/
cd1=cd [P1][P2]
[Server-Attribute-JumpServer]
service-name=test-service
As you can see, there are two special attibutes:[P1] [P2] that means the params you send to this script.
So you could use it by this way:
gotossh 1 cd1 /var /log
The final command will be : cd /var/log.
And it will login the first server and excute this command cd /var/log.
Notice that, if your command needs a password, like 'scp root@xxxx:xxx xxx', you should add the pwd after the command.
For example:
[Server1]
command=scp root@111.231.59.85:/var/log/test-service/test-service.log ./test-server.log|testpassword2
The next part is the support of scp command:
[scp]
log1=~/testfile2
log2=/var/log/omp-distribution-facade-service/omp-distribution-facade-service.log
log3=~/testlog.log
log4=/var/log/test-service/test-service.log
log5=/logs/openapi/service/omp-distributor-service.log
bill-log=/var/log/omp-bill-service/omp-bill-service.log
log1 and log2 are the name you set, and the actual path of the file in server is behind the equals sign.
You could use it like this:
gotossh 1 scp log1
It will copy the remote file on the first server to your local computer.
gotossh 3 scp log2
It will login the first server, and copy that file from the third server, and then copy that file to your local computer.
And you can also use it like this:
gotossh 3 scp /var/log/online-service/online-service.log
This script will find the log name of /var/log/online-service/online-service.log in the scp node, if it cann't find the log name, the script will treat it as the file path.
The last part of the config file is settings and common command, in settings node, there is only the version info now. Maybe we could change many other things ,like color etc, here.
common command is a global setting for all servers, you can treat it as template command, there will appear in all servers's COMMAND LIST. And you could use custom attribute here.
For example:
[settings]
version=3.0
[common-command]
log=tail -f -n 500 /var/log/[service-name]/[service-name].log
error-log=tail -f -n 500 /var/log/[service-name]/[service-name]-error.log
$ gotossh
#############################################################################
# [GOTO SSH] #
# #
# #
# [1] JumpServer #
# [2] JumpServer2 #
# [3] OnlineServer #
# #
#############################################################################
Server Number:1
#############################################################################
# [COMMAND LIST] #
# #
# [1] no-subsequent-operation #
# [2] distributor-log #
# [3] cd #
# [4] cd1 #
# [5] log #
# [6] error-log #
# #
# #
#############################################################################
Command Number:1
You could select the server you want to login in the first step. And then you will see all the
$ gotossh 1
#############################################################################
# [COMMAND LIST] #
# #
# [1] no-subsequent-operation #
# [2] distributor-log #
# [3] cd #
# [4] cd1 #
# [5] log #
# [6] error-log #
# #
# #
#############################################################################
Command Number:1gotossh 2gotossh 1 log
gotossh 2 log
gotossh 2 cd
gotossh 1 scp log3
gotossh 3 scp /var/log/online-service/online-service.log
GotoSSH 是一个一键登录 SSH 的脚本,可直接从跳板机登录到线上服务器,致力于帮助你提高工作效率。
这里有一些动态图,可以帮助你快速了解这个脚本能够做什么。
普通的一键登录到服务器:
先登录跳板机,然后自动跳转到线上服务器:
登录服务并查看日志:
登录跳板机,然后跳转线上服务器并查看指定日志:
从服务器复制文件到本地:
从线上服务器复制文件到跳板机,然后再复制到本地:
列举所有服务器:
列举服务器支持的所有命令:
CentOS :
$ sudo yum install -y expectUbuntu :
$ sudo apt-get install tcl tk expectMac :
$ brew install expect$ git clone https://github.com/MFrank2016/GotoSSH.git
$ cd GotoSSH
$ chmod a+x gotossh
$ sudo cp gotossh /usr/local/bin/如果你已经安装过旧的版本,你需要先在 /usr/local/bin/目录下删除gotossh。如果是mac,记得要安装一下上面的依赖。
$ vim ~/.gotossh_config
JumpServer||111.231.59.85||root||password||22||0
JumpServer2||111.231.59.85||root||password||22||0
OnlineServer||118.24.163.31||root||password||22||1
[Server-JumpServer]
distributor-log=tail -f -n 500 /var/log/[service-name]/[service-name].log
cd=cd /var/log/[service-name]/
cd1=cd [P1][P2]
[Server-Attribute-JumpServer]
service-name=test-service
[Server-OnlineServer]
[Server-Attribute-OnlineServer]
service-name=online-service
[scp]
log1=~/testfile2
log2=/var/log/omp-distribution-facade-service/omp-distribution-facade-service.log
log3=~/testlog.log
log4=/var/log/test-service/test-service.log
log5=/logs/openapi/service/omp-distributor-service.log
bill-log=/var/log/omp-bill-service/omp-bill-service.log
[settings]
version=3.0
[common-command]
log=tail -f -n 500 /var/log/[service-name]/[service-name].log
error-log=tail -f -n 500 /var/log/[service-name]/[service-name]-error.log
配置文件由四部分组成:
第一部分是服务器的基本信息:
link_name||ip||username||password||port||rely_server_no||service_name
举个栗子:
JumpServer||111.231.59.85||root||password||22||0||test-service
rely_server_no代表的是这台服务器是否依赖其他服务器,如果设置为0,代表它不依赖其他服务器,直接登录,如果设置为大于0的值,则会先登录那台服务器,然后再跳转到这台服务器。
第二部分是服务器自定义命令和自定义属性,你可以在这里为各个服务器设置任何自定义命令。
[Server-link_name]
command=xxxxxx
[Server-Attribute-link_name]
attribute=xxx
Server-link_name 代表这个节点是为哪台服务器设置的,link_name代表前面配置中服务器的链接名称.
command 是命令的名称,可以是任何值,但不能有空格,最好简短一点。当然,强烈建议,不要把类如rm -rf 等危险操作放到这里。
Server-Attribute-link_name 部分是设置自定义属性,这些属性可以在自定义命令以及全局公用命令中进行替换。
例如,你可以像这样设置一个自定义属性:
[Server-Attribute-JumpServer]
service-name=test-service
然后在自定义命令中使用它:
[Server-JumpServer]
distributor-log=tail -f -n 500 /var/log/[service-name]/[service-name].log
cd=cd /var/log/[service-name]/
cd1=cd [P1][P2]
脚本将会自定将[service-name]替换成自定义属性中设置的值test-service,所以distributor-log命令的最终执行版本就是:/var/log/test-service/test-service.log。
举个栗子:
[Server-JumpServer]
distributor-log=tail -f -n 500 /var/log/[service-name]/[service-name].log
cd=cd /var/log/[service-name]/
cd1=cd [P1][P2]
[Server-Attribute-JumpServer]
service-name=test-service
注意,这里还有两个特殊的值[P1][P2],代表你传入脚本的参数,
所以你可以这样使用:
gotossh 1 cd1 /var /log
脚本最终将会先登录第一台服务器然后执行这条命令 : cd /var/log.
注意,如果你执行的命令需要进行登录,比如:scp root@xxxx:xxx xxx 那么你应该将密码也加到命令后面。
举个栗子:
[Server-JumpServer]
command=scp root@111.231.59.85:/var/log/test-service/test-service.log ./test-server.log|testpassword2
配置文件的下一部分是对scp命令的支持:
[scp]
log1=~/testfile2
log2=/var/log/omp-distribution-facade-service/omp-distribution-facade-service.log
log3=~/testlog.log
log4=/var/log/test-service/test-service.log
log5=/logs/openapi/service/omp-distributor-service.log
bill-log=/var/log/omp-bill-service/omp-bill-service.log
log1 和 log2 是为文件路径设置的别名。
经过上述设置后,你可以这样使用它:
gotossh 1 scp log1
脚本将会将第一台服务器上路径为~/testfile2的文件复制到本地。
gotossh 3 scp log2
这条命令中,脚本将会先登录第一台服务器,然后将路径为/var/log/omp-distribution-facade-service/omp-distribution-facade-service.log的文件复制到第一台服务器,接着再把该文件复制到本地。
你还可以这样使用:
gotossh 3 scp /var/log/online-service/online-service.log
这里不同的是,我们直接使用了我们想要复制的文件路径,而不是使用它的别名。
配置的最后一部分是“settings 和 公用命令”,在“settings”节点中,目前仅有version一个属性,用来表明当前的版本号,以后后续升级配置文件时使用,后续会增加更多自定义的内容,比如颜色等等。
common command 是为所有服务器的全局配置,可以把它当做命令模板,它会显示在所有服务器的命令列表中,你可以在其中使用自定义属性。
举个栗子:
[settings]
version=3.0
[common-command]
log=tail -f -n 500 /var/log/[service-name]/[service-name].log
error-log=tail -f -n 500 /var/log/[service-name]/[service-name]-error.log
$ gotossh
#############################################################################
# [GOTO SSH] #
# #
# #
# [1] JumpServer #
# [2] JumpServer2 #
# [3] OnlineServer #
# #
#############################################################################
Server Number:1
#############################################################################
# [COMMAND LIST] #
# #
# [1] no-subsequent-operation #
# [2] distributor-log #
# [3] cd #
# [4] cd1 #
# [5] log #
# [6] error-log #
# #
# #
#############################################################################
Command Number:1
在第一步选择你想要登录的服务器,然后你将会看到该服务器所支持的所有命令。
$ gotossh 1
#############################################################################
# [COMMAND LIST] #
# #
# [1] no-subsequent-operation #
# [2] distributor-log #
# [3] cd #
# [4] cd1 #
# [5] log #
# [6] error-log #
# #
# #
#############################################################################
Command Number:1gotossh 2gotossh 1 log
gotossh 2 log
gotossh 2 cd
gotossh 1 scp log3
gotossh 3 scp /var/log/online-service/online-service.log
在测试环境使用barge发布项目时,每次都会获得一个浮动IP,每次需要使用新IP略显麻烦,因此将该部分也接入了GotoSSH来简化操作。
使用barge的服务器配置如下:
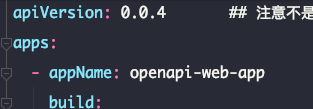
link_name||barge-project-name||root||password||22||0这里是 project-name 要与服务 barge 中的项目名称一致。
即图中的 appName 对应的值。
对应的 password 也需要改为该服务的 password。
其余配置跟其他服务一样,使用[Server-link_name]来配置其自定义命令,使用[Server-Attribute-link_name]来配置其自定义属性,详情可参见上面配置说明。
注意,使用该特性时,会在当前路径下生成barge.yaml文件,如果当前已经有barge.yaml文件,则会覆盖当前文件,所以请不要在项目路径下使用该特性。