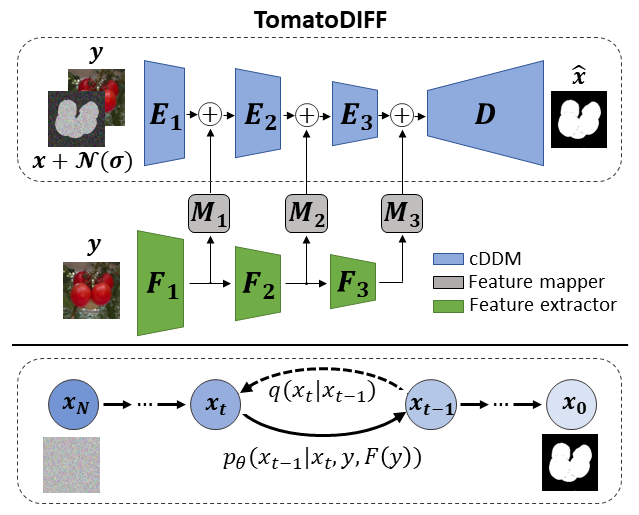
Official implementation of the paper "TomatoDIFF: On–plant Tomato Segmentation with Denoising Diffusion Models" 1. TomatoDIFF is a diffusion-based model developed for semantic segmentation of on-plant tomatoes.
For more information please refer to the paper available here.
The model is implemented using PyTorch. The full list of used libraries can be found in requirements.txt.
pip install -r requirements.txt
Our dataset Tomatopia is available for download here.
The datasets you are using for training or testing TomatoDIFF should be placed in the directory called data. Datasets should have the following directory structure:
Dataset_name
├── train
│ ├── images
│ │ └── train_img_1.png
│ │ └── train_img_2.png
│ │ └── ...
│ ├── masks
│ ├── features_1
│ ├── features_2
│ ├── features_3
├── test
│ ├── images
│ │ └── test_img_1.png
│ │ └── test_img_2.png
│ │ └── ...
│ ├── masks
│ │ └── ...
│ ├── features_1
│ │ └── ...
│ ├── features_2
│ │ └── ...
│ ├── features_3
│ │ └── ...
If you find this code useful, use our dataset Tomatopia or you want to refer to the paper, please cite using the following BibTeX:
@INPROCEEDINGS{ivanovska2023TomatoDIFF,
author={Ivanovska, Marija and Perš, Janez and Štruc, Vitomir},
booktitle={2023 18th International Conference on Machine Vision and Applications (MVA)},
title={TomatoDIFF: On–plant Tomato Segmentation with Denoising Diffusion Models},
year={2023}}
This code is based on k-diffusion.
Footnotes
-
M. Ivanovska, J. Perš, V. Štruc, TomatoDIFF: On–plant Tomato Segmentation with Denoising Diffusion Models, International Conference on Machine Vision Applications (MVA), 2023 ↩