A simple benchmarking package including visualization facilities.
The goal of this package is to provide a simple way to compare the performance of different approaches for different inputs and to visualize the result.


Using pip:
python -m pip install simple_benchmark
Or installing the most recent version directly from git:
python -m pip install git+https://github.com/MSeifert04/simple_benchmark.git
To utilize the all features of the library (for example visualization) you need to install the optional dependencies:
Or install them automatically using:
python -m pip install simple_benchmark[optional]
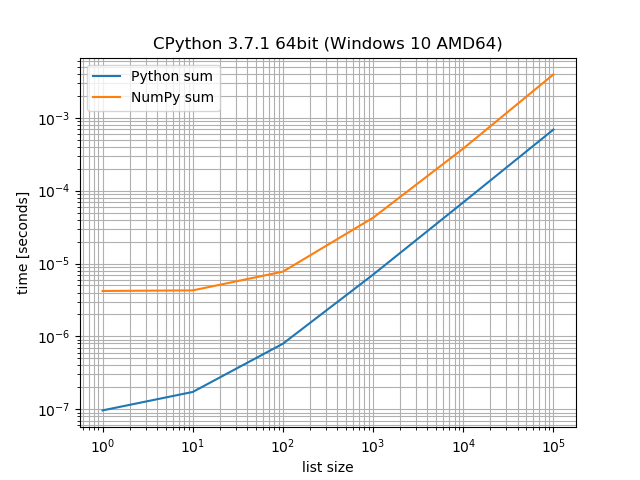
Suppose you want to compare how NumPys sum and Pythons sum perform on lists of different sizes:
>>> from simple_benchmark import benchmark
>>> import numpy as np
>>> funcs = [sum, np.sum]
>>> arguments = {i: [1]*i for i in [1, 10, 100, 1000, 10000, 100000]}
>>> argument_name = 'list size'
>>> aliases = {sum: 'Python sum', np.sum: 'NumPy sum'}
>>> b = benchmark(funcs, arguments, argument_name, function_aliases=aliases)
The result can be visualized with pandas (needs to be installed):
>>> b
Python sum NumPy sum
1 9.640884e-08 0.000004
10 1.726930e-07 0.000004
100 7.935484e-07 0.000008
1000 7.040000e-06 0.000042
10000 6.910000e-05 0.000378
100000 6.899000e-04 0.003941
Or with matplotlib (has to be installed too):
>>> b.plot()
To save the plotted benchmark as PNG file:
>>> import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
>>> plt.savefig('sum_example.png')
Warning
The command line interface is highly experimental. It's very likely to change its API.
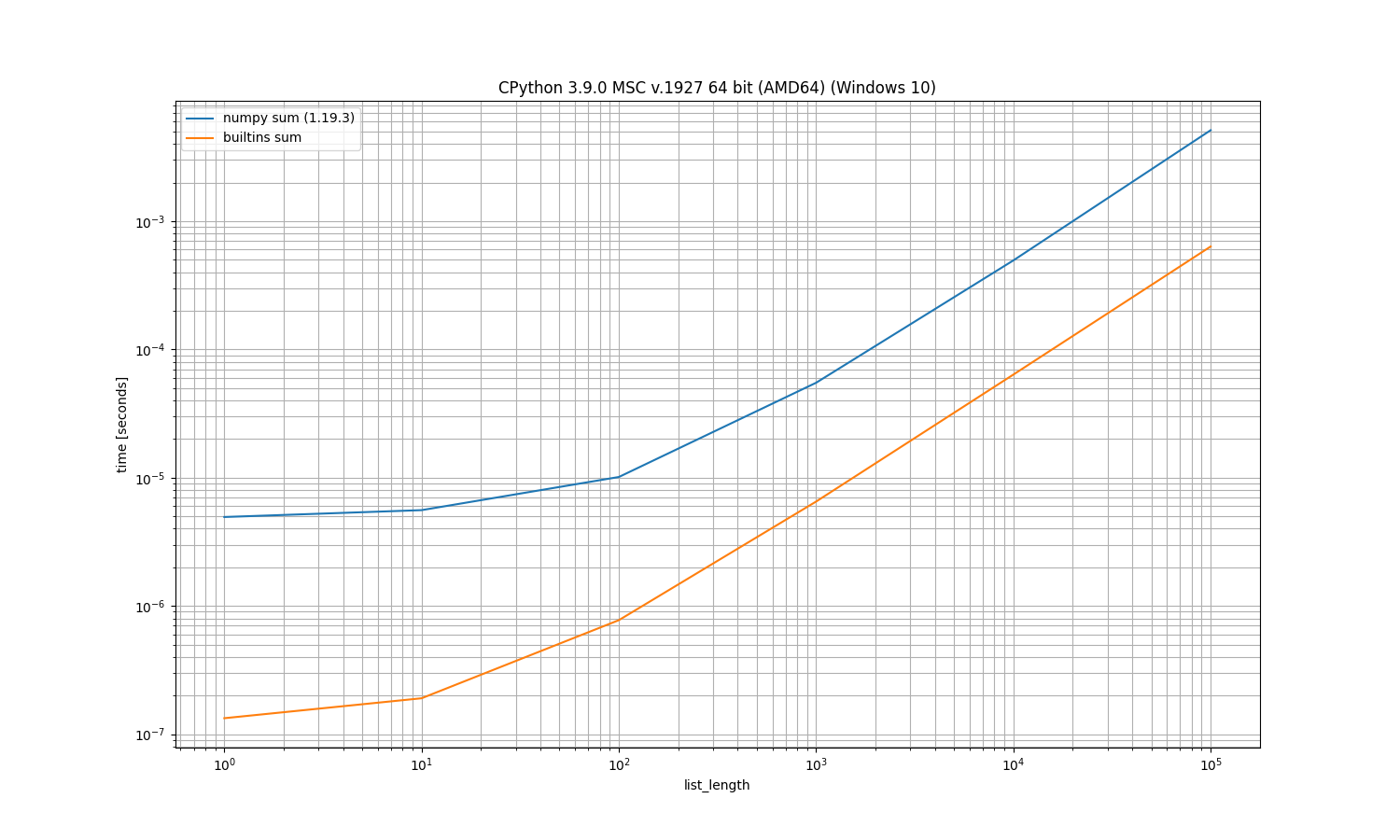
It's an experiment to run it as command-line tool, especially useful if you want to run it on multiple files and don't want the boilerplate.
File sum.py:
import numpy as np
def bench_sum(l, func=sum): # <-- function name needs to start with "bench_"
return func(l)
def bench_numpy_sum(l, func=np.sum): # <-- using func parameter with the actual function helps
return np.sum(l)
def args_list_length(): # <-- function providing the argument starts with "args_"
for i in [1, 10, 100, 1000, 10000, 100000]:
yield i, [1] * i
Then run:
$ python -m simple_benchmark sum.py sum.png
With a similar result:
- perfplot by Nico Schlömer.