This repo has tools and deployment configs for a performance testing environment to be able to run performance tests of a 3scale API Management solution, focussing on the traffic intensive parts of the solution (the API Gateway and the Service Management API).
We have open sourced it to enable partners, customers and support engineers to run their own performance tests on "self-managed" (i.e. Not SaaS) installations of the 3scale API Management solution.
By running performance test with the same tools, scripts, traffic patterns and measurements as we at 3scale do, we hope it will help produce results that can be more easily compared with the results we achieve in our regular in-house performance testing and that we can run internally.
The goal is to help to resolve doubts or issues related to scalability or performance more quickly and easily - allowing you to achieve the high levels of low-latency performance we strive for and ensure in our own internal testing.
Generated using github-markdown-toc
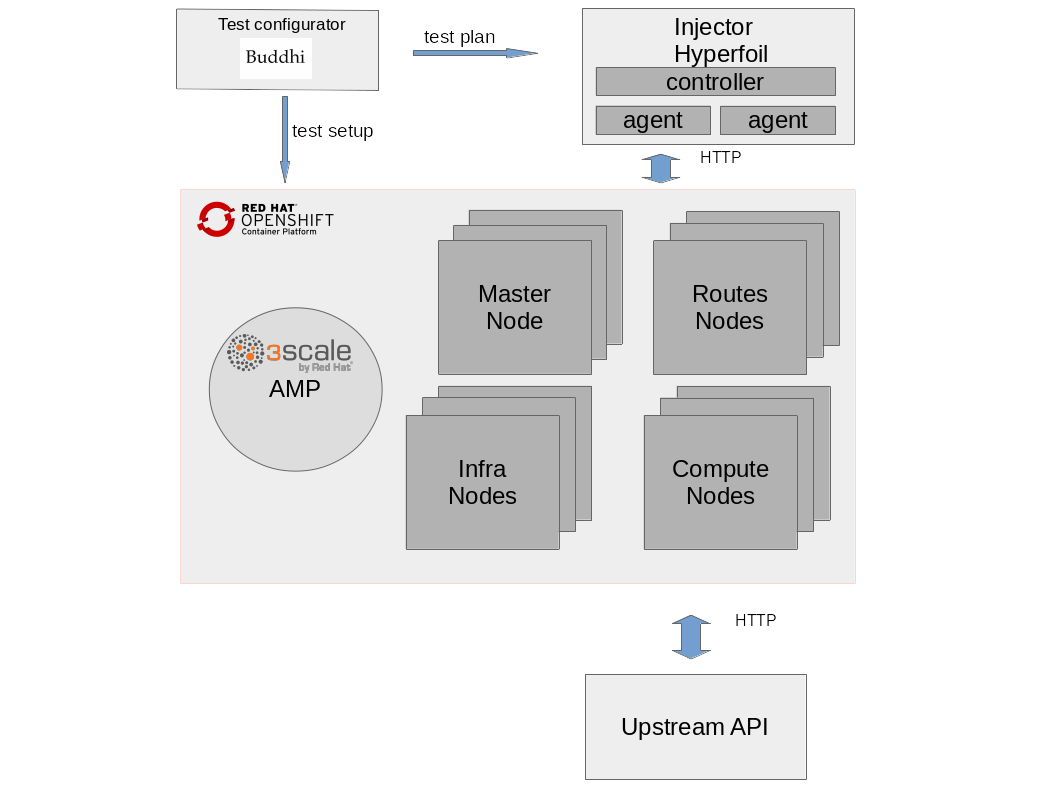
High level overview is quite simple. Main components are represented in the diagram below.
- Injector: Source of HTTP/HTTPS traffic requests
- Openshift Container Platform with 3scale installed
- Upstream API: Also named as backend API, this is the final API service as an HTTP traffic endpoint. Optionally, for testing purposes, deploy Upstream API.
- Test Configurator (Buddhi): 3scale setup and traffic generation tool
There are two ways of running your tests and the injector has to be configured accordingly.
-
Test your own 3scale services: The injector will be custom configured to use your 3scale products (a.k.a. services).
-
Setup traffic profiles: Configure your performance tests to use synthetically generated traffic based on traffic models.
Requirements:
Control node:
- ansible >= 2.9.14
- python >= 3.0
- Install ansible requirements
cd deployment
ansible-galaxy install -r requirements.yaml
Managed node host:
- Docker >= 1.12
- python >= 2.7
- docker-py >= 1.7.0
Make sure that the injector host’s hardware resources is not the performance tests bottleneck. Enough cpu, memory and network resources should be available.
** HTTP/HTTPS **
By default, the injector will generate HTTPS traffic on the port number 443. You can change this setting editing injector_hyperfoil_target_protocol and injector_hyperfoil_target_port parameters.
File: group_vars/all.yml
injector_hyperfoil_target_protocol: https
injector_hyperfoil_target_port: 443
Steps:
1. Provide hyperfoil controller host IP address or DNS name and at least one hyperfoil agent host IP address or DNS name. For example:
File: hosts
[hyperfoil_controller]
controllerhost.example.com ansible_host=controllerhost.example.com ansible_role=root
[hyperfoil_agent]
agenthost.example.com ansible_host=agenthost.example.com ansible_role=root
Note 01: make sure defined ansible user has ssh login access to the host without password.
Note 02: make sure hyperfoil controller host has ssh login access to the agent host without password.
More than one hyperfoil agent can be configured. Useful when the injector becomes a bottleneck. For example to configure two agents:
File: hosts
[hyperfoil_controller]
controllerhost.example.com ansible_host=controllerhost.example.com ansible_role=root
[hyperfoil_agent]
agenthost01.example.com ansible_host=agenthost01.example.com ansible_role=root
agenthost02.example.com ansible_host=agenthost02.example.com ansible_role=root
2. Configure the following settings in roles/user-traffic-reader/defaults/main.yml file:
threescale_portal_endpoint: 3scale portal endpointthreescale_services: Select the 3scale services you want to use for the tests. Leave it empty to use them all.
File: roles/user-traffic-reader/defaults/main.yml
# URI that includes your password and portal endpoint in the following format: <schema>://<password>@<admin-portal-domain>.
# The <password> can be either the provider key or an access token for the 3scale Account Management API.
# <admin-portal-domain> is the URL used to log into the admin portal.
# Example: https://access-token@account-admin.3scale.net
threescale_portal_endpoint: <THREESCALE_PORTAL_ENDPOINT>
# Comma separated list of services (Id's or system names)
# If empty, all available services will be used
threescale_services: ""
3. Execute the playbook injector.yml to deploy injector.
Avoid ssh issues when running anisble playbooks
$ cat ~/.ansible.cfg
[ssh_connection]
ssh_args = -o ServerAliveInterval=30
pipelining = TrueStart the playbook
cd deployment/
ansible-playbook -i hosts injector.ymlSkip these steps if testing your own 3scale services. This steps will setup 3scale services for performance testing.
Steps:
1. Provide hyperfoil controller host IP address or DNS name and at least one hyperfoil agent host IP address or DNS name. For example:
File: hosts
[hyperfoil_controller]
controllerhost.example.com ansible_host=controllerhost.example.com ansible_role=root
[hyperfoil_agent]
agenthost.example.com ansible_host=agenthost.example.com ansible_role=root
Note 01: make sure defined ansible user has ssh login access to the host without password. Note 02: make sure hyperfoil controller host has ssh login access to the agent host without password.
More than one hyperfoil agent can be configured. Useful when the injector becomes a bottleneck. For example to configure two agents:
File: hosts
[hyperfoil_controller]
controllerhost.example.com ansible_host=controllerhost.example.com ansible_role=root
[hyperfoil_agent]
agenthost01.example.com ansible_host=agenthost01.example.com ansible_role=root
agenthost02.example.com ansible_host=agenthost02.example.com ansible_role=root
2. Configure the following settings in roles/profiled-traffic-generator/defaults/main.yml file:
threescale_portal_endpoint: 3scale portal endpointtraffic_profile: Currently available profiles:simple, backend, medium, standardprivate_base_url: Private Base URL used for the tests. Make sure your private application behaves like an echo api service.public_base_url: Optionally, configure thePublic Base URLused for the tests for self managed apicast environments. Otherwise, leave it empty.
File: roles/traffic-configurator/defaults/main.yml
# URI that includes your password and portal endpoint in the following format: <schema>://<password>@<admin-portal-domain>.
# The <password> can be either the provider key or an access token for the 3scale Account Management API.
# <admin-portal-domain> is the URL used to log into the admin portal.
# Example: https://access-token@account-admin.3scale.net
threescale_portal_endpoint: <THREESCALE_PORTAL_ENDPOINT>
# Used traffic for performance testing is not real traffic.
# It is synthetically generated traffic based on traffic models.
# Information about available traffic profiles (or test plans) can be found here:
# https://github.com/3scale/perftest-toolkit/blob/master/buddhi/README.md#profiles
# Currently available profiles: [ simple | backend | medium | standard ]
traffic_profile: <TRAFFIC_PROFILE>
# Private Base URL
# Make sure your private application behaves like an echo api service
# example: https://echo-api.3scale.net:443
private_base_url: <PRIVATE_BASE_URL>
# Public Base URL
# Public address of your API gateway in the production environment.
# Optional. When it is left empty, public base url will be the hosted gateway url
# example: https://gw.example.com:443
public_base_url: <PUBLIC_BASE_URL>
3. Execute the playbook profiled-injector.yml to deploy injector.
Avoid ssh issues when running anisble playbooks
$ cat ~/.ansible.cfg
[ssh_connection]
ssh_args = -o ServerAliveInterval=30
pipelining = TrueStart the playbook
ansible-playbook -i hosts profiled-injector.yml
1. Configure testing settings:
File: run.yml
USERS_PER_SEC: Requests per second
DURATION_SEC: Duration of the performance test in seconds
SHARED_CONNECTIONS: Number of connections open per target HOST
2. Run tests
ansible-playbook -i hosts -i benchmarks/3scale.csv run.yml3. View Report
The test results of the last execution are automatically stored in deployment/benchmarks/index-.html. The html file can be directly opened with your favorite web browser.
Some performance test are looking for peak and sustained traffic maximum performance. Sustained traffic is defined as traffic load where Job Queue size is always at low levels, or even empty. For sustained traffic performance benchmark, Job Queue must be monitorized.
This is a small guideline to monitor Job Queue size:
- Get backend redis pod
$ oc get pods | grep redis
backend-redis-2-nkrkk 1/1 Running 0 14d- Get Job Queue size
$ oc rsh backend-redis-2-nkrkk /bin/sh -i -c 'redis-cli -n 1 llen resque:queue:priority'
(integer) 0Sometimes, even though all deployment commands run successfully, performance traffic may be broken. This might be due to a misconfiguration in any stage of the deployment process. When performance HTTP traffic response codes are not as expected, i.e. 200 OK, there are few checks that can be very handy to find out configuration mistakes.
First, scale down apicast-production service to just one pod.
Monitor pod's logs for traffic accesslog.
oc logs -f apicast-production-X-podIdRun tests and check for logs.
Check response codes on accesslog.
If accesslog shows could not find service for host error, then the configured virtual hosts do not match traffic Host header. For example:
2018/06/05 13:32:41 [warn] 25#25: *883 [lua] errors.lua:43: get_upstream(): could not find service for host: 9ccd143c-dbe4-471c-9bce-41df7dde8d99.benchmark.perftest.3sca.net, client: 10.130.4.1, server: _, request: "GET /855aaf5c-a199-4145-a3ab-ea9402cc35db/some-request?user_key=32313d20d99780a5 HTTP/1.1", host: "9ccd143c-dbe4-471c-9bce-41df7dde8d99.benchmark.perftest.3sca.net"
Another issue might be when response codes are 404 Not Found.Then proxy-rules do not match traffic path.
In anyone of the previous cases, it seems that apicast gateway does not have latest configuration. Pods restart is required or wait until process fetches new configuration based on APICAST_CONFIGURATION_CACHE apicast configuration parameter.
Restart is easily done downscaling to 0 and then scaling back to desired number of pods.
$ oc scale dc apicast-production --replicas=0
$ oc scale dc apicast-production --replicas=2First, scale down backend-listener service to just one pod.
Monitor pod's logs for traffic accesslog.
oc logs -f backend-listener-X-podIdRun tests and check for logs.
If no logs are shown, check gateway troubleshooting section
If logs are shown, check response codes on accesslog. Other than 200 OK means
- redis is down,
- redis address is misconfigured in backend-listener
- redis does not have required data to authenticate requests
When backend-listener accesslog shows requests are being answered with 200 OK response codes, the last usual suspect is upstream or upstream configuration.
Check upstream uri is correctly configured in your 3scale configuration