Latest Release:
Analysis 1.127.0 | Visualization 1.128.0
Key Features • How To Use • Feedback • Further Info • About
-
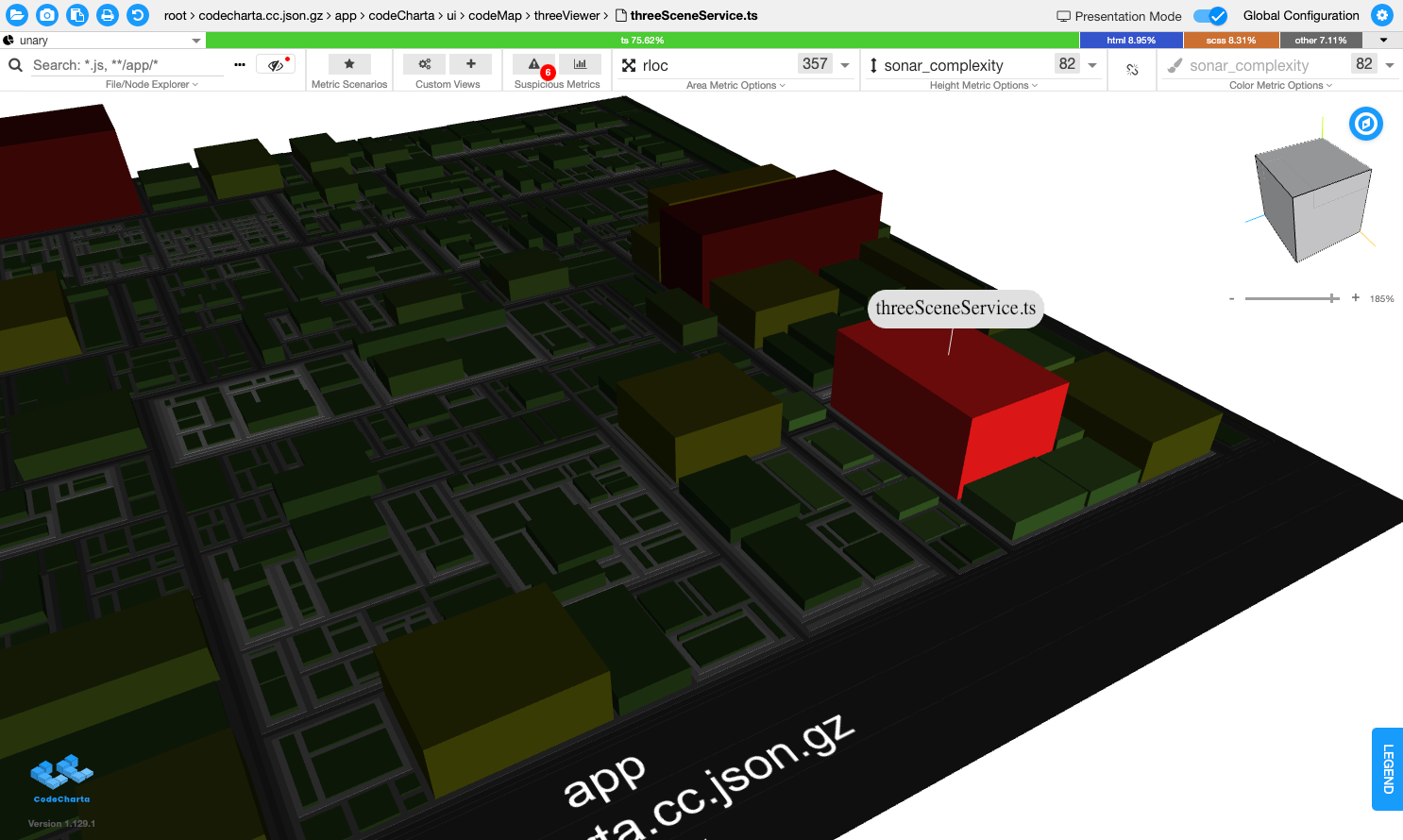
- CC visualizes code bases as 3D cities, so that you can understand it - view the Web Demo.
- It uses code metrics from
.cc.jsonfiles. - The imported files are validated using JSON Schema as defined in generatedSchema.json.
- You can change the way the file is displayed and save and later load it as a Custom View.
-
- CC Analysis is used to calculate or to import metrics from third party tools for a code base.
- It generates
.cc.jsonfiles for CC Visualization through a Command-Line-Tool. - It includes some pre-defined importers for e.g. SonarQube, SourceMonitor, Git, generic CSV data
- It also includes commands to validate and merge multiple
.cc.jsonfiles.
For using CodeCharta the following needs to be installed on your system:
- Node >= 20
- Java >= 11, <= 21
- Online: You can try the web visualization without any installation and explore the CodeCharta code (shown by default).
- Local: See here.
- Analysis is split into different parsers that generate
.cc.jsonfiles. To run these parsers you need the CodeCharta Shell.
In this example we will generate a .cc.json from JUnit4 using the Source Code Parser (that parses java projects).
# Install codecharta-analysis globally
$ npm i -g codecharta-analysis
# Clone the junit4 repository
$ git clone https://github.com/junit-team/junit4
# Parse sources with CodeCharta Shell
$ ccsh sourcecodeparser junit4 -p junit4 -o junit4.source.cc.json
# Now you can upload `junit4.source.cc.json` to CodeCharta VisualizationNote If you want to be guided through selecting the arguments. Just execute
ccshand you can run the parsers interactively with dialogs.
Have a bug, a feature request or any question? Please open a new issue. Feedback is always welcome.
Want to have even more information? Please check our documentation and news.
MIT
maibornwolff.de · GitHub @MaibornWolff