- Maria Aurora Bertasini*
- Marco Cioci*
- Francesco Rosnati*
- Luca Tramacere*
*Master's candidate in High Performance Computing Engineering at Politecnico di Milano
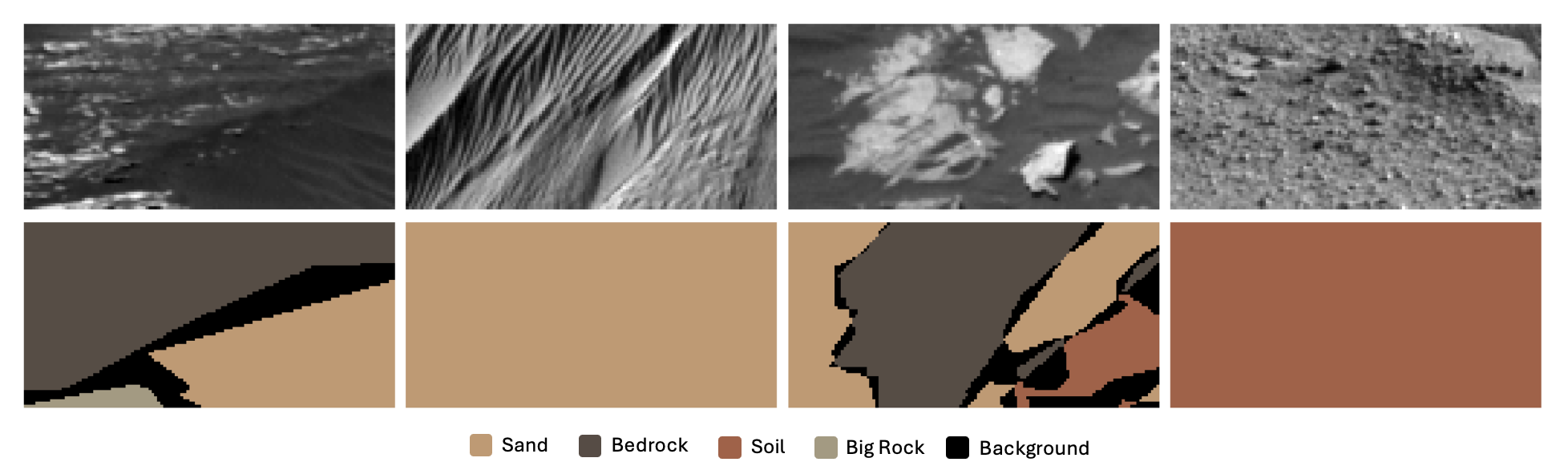
This project focuses on semantic segmentation of 64x128 grayscale Mars terrain images, assigning each pixel to one of five terrain classes. Paired masks provide pixel-wise labels. The goal is to build a model for accurate classification, evaluated by mean intersection over union (mIoU) excluding the background class (label 0).
This template serves as a comprehensive tool for testing and running various models. To use it, create a model.py file and import it in the model section.
The most notable models we tested are stored in the models folder, while the best version is executed in FinalModel.ipynb.
# Model name
model_name = 'template'from datetime import datetime
# Generate timestamp
timestamp = datetime.now().strftime("%y%m%d_%H%M%S")
# Unified filename for both the final model and checkpoint
model_filename = f"model_{model_name}_{timestamp}.keras"COLAB = True
if COLAB:
print("COLAB")
from google.colab import drive
drive.mount("/gdrive")
%cd /gdrive/My Drive
else:
print("NO COLAB")# General imports
import os
import random
from datetime import datetime
# Numerical and data manipulation
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
# TensorFlow and Keras
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow import keras as tfk
from tensorflow.keras import layers as tfkl
from tensorflow.keras.callbacks import EarlyStopping, ModelCheckpoint
# Mixed precision setup
from tensorflow.keras import mixed_precision
mixed_precision.set_global_policy('mixed_float16')
# GPU configuration
physical_devices = tf.config.list_physical_devices('GPU')
for device in physical_devices:
tf.config.experimental.set_memory_growth(device, True)
# Sklearn for train-test splitting
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
# OpenCV for image processing
import cv2
# tqdm for progress visualization
from tqdm import tqdm
# Matplotlib for visualization
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib import cm
from matplotlib import colors
%matplotlib inline
# Set seeds for reproducibility
np.random.seed(42)
tf.random.set_seed(42)
# Print environment details
print()
print(f"TensorFlow version: {tf.__version__}")
print(f"Keras version: {tfk.__version__}")
print(f"GPU devices: {len(tf.config.list_physical_devices('GPU'))}")A cleaning process was applied to the training data to address the presence of outliers. Specifically, images with objectively incorrect masks were identified and removed, while for images with uncertain mask quality, most were retained to preserve diversity and encourage generalization.
The final dataset used for training was saved as clean_dataset.npz.
# --------------- #
# Load the dataset
# --------------- #
data_name = 'clean_dataset.npz'
file_path = f"data/{data_name}"
data = np.load(file_path)
training_set = data["training_set"]
X_train = np.stack(training_set[:, 0], axis=0) # Images
y_train = np.stack(training_set[:, 1], axis=0) # Masks
X_test = data["test_set"] # Test Images
# Preprocess images and masks
if X_train.ndim == 3:
X_train = X_train[..., np.newaxis]
if X_test.ndim == 3:
X_test = X_test[..., np.newaxis]
X_train = X_train / 255.0
X_test = X_test / 255.0
if y_train.ndim == 3:
y_train = y_train[..., np.newaxis]
original_count = X_train.shape[0]
print(f"Number of images the {data_name} dataset: {original_count}")
# Define label mapping
label_mapping = {
0: 'Background',
1: 'Soil',
2: 'Bedrock',
3: 'Sand',
4: 'Big Rock'
}
category_map = {key: key for key in label_mapping.keys()}# Split data into training and validation sets
X_train_final, X_val, y_train_final, y_val = train_test_split(
X_train, y_train, test_size=0.2, random_state=42
)
# Print shapes of the datasets
print("Shape of X_train_final:", X_train_final.shape)
print("Shape of X_val:", X_val.shape)
print("Shape of y_train_final:", y_train_final.shape)
print("Shape of y_val:", y_val.shape)All the augmentation techniques we experimented with are detailed in the Augmentations.ipynb notebook.
In this template, we propose the augmentation strategy that was ultimately selected. To use it, import all the necessary functions from AugmentationsUtils.py.
The apply_augmentations function applies the selected augmentations to the training set while retaining the original images. Additionally, it plots example outputs to visualize the effects of the augmentations.
from AugmentationsUtils import *
# Augment the training set and plot images for the specified index
augmented_X_train, augmented_y_train = apply_augmentations(
X_train_final,
y_train_final,
num_augmented= 3, # Number of augmented versions per original image
plot_index= 0 # Index of the image to plot
)Please import your model from the models folder. This folder contains some of our best models, including the final model (nome.py).
The final model (final_dual_branch.py) is also imported and executed in the FinalModel.ipynb notebook.
from models.you_name_model import *
# Instantiate the model
input_shape = augmented_X_train.shape[1:] # Use the shape of the input images
num_classes = 5 # As per dataset details
model = get_model(input_shape=input_shape, num_classes=num_classes, dropout_rate=0, l2_reg=1e-4)# -------------------------------------- #
# Metric #
# -------------------------------------- #
class MeanIntersectionOverUnion(tf.keras.metrics.MeanIoU):
def __init__(self, num_classes, labels_to_exclude=None, name="mean_iou", dtype=None):
super(MeanIntersectionOverUnion, self).__init__(num_classes=num_classes, name=name, dtype=dtype)
if labels_to_exclude is None:
labels_to_exclude = [0] # Default to excluding label 0
self.labels_to_exclude = labels_to_exclude
def update_state(self, y_true, y_pred, sample_weight=None):
# Convert predictions to class labels
y_pred = tf.math.argmax(y_pred, axis=-1)
# Flatten the tensors
y_true = tf.reshape(y_true, [-1])
y_pred = tf.reshape(y_pred, [-1])
# Apply mask to exclude specified labels
mask = tf.reduce_all([tf.not_equal(y_true, label) for label in self.labels_to_exclude], axis=0)
y_true = tf.boolean_mask(y_true, mask)
y_pred = tf.boolean_mask(y_pred, mask)
# Update the state
return super().update_state(y_true, y_pred, sample_weight)
# -------------------------------------- #
# Loss Functions #
# -------------------------------------- #
def mean_iou_loss(num_classes, labels_to_exclude=None, epsilon=1e-6):
"""
Mean IoU Loss Function.
Args:
num_classes: Number of classes in the segmentation task.
labels_to_exclude: List of labels to exclude when calculating IoU.
Returns:
A function that calculates the Mean IoU loss.
"""
def loss(y_true, y_pred):
# Convert predictions to class probabilities
y_pred = tf.nn.softmax(y_pred, axis=-1)
# Convert true labels to one-hot encoding
y_true_one_hot = tf.one_hot(tf.cast(tf.squeeze(y_true, axis=-1), tf.int32), num_classes)
# Flatten the tensors
y_true_flat = tf.reshape(y_true_one_hot, [-1, num_classes])
y_pred_flat = tf.reshape(y_pred, [-1, num_classes])
# Compute intersection and union
intersection = tf.reduce_sum(y_true_flat * y_pred_flat, axis=0)
union = tf.reduce_sum(y_true_flat + y_pred_flat, axis=0) - intersection
# Mask out excluded labels
if labels_to_exclude is not None:
for label in labels_to_exclude:
intersection = tf.tensor_scatter_nd_update(
intersection,
[[label]],
[0.0]
)
union = tf.tensor_scatter_nd_update(
union,
[[label]],
[0.0]
)
# Compute IoU for each class and average over classes
iou = (intersection + epsilon) / (union + epsilon)
mean_iou = tf.reduce_mean(iou)
# Invert to use as loss (lower IoU means higher loss)
return 1.0 - mean_iou
return loss
def focal_loss_ignore_class_0(alpha=0.25, gamma=2.0, num_classes=None):
"""
Focal Loss Function that ignores class 0, with fixed alpha for all other classes.
Args:
alpha: Weighting factor for positive classes to address class imbalance.
gamma: Focusing parameter to down-weight easy examples.
num_classes: Number of classes in the segmentation task.
Returns:
A function that calculates the Focal Loss, ignoring class 0.
"""
def loss(y_true, y_pred):
# Convert predictions to class probabilities (softmax output)
y_pred = tf.nn.softmax(y_pred, axis=-1)
# Convert true labels to one-hot encoding
y_true_one_hot = tf.one_hot(tf.cast(tf.squeeze(y_true, axis=-1), tf.int32), num_classes)
# Ignore class 0 in the loss calculation
y_true_no_bg = y_true_one_hot[..., 1:] # Remove the first class (class 0)
y_pred_no_bg = y_pred[..., 1:] # Remove the first class (class 0)
# Compute the focal loss
cross_entropy = -y_true_no_bg * tf.math.log(y_pred_no_bg + 1e-8) # Cross entropy with stability
# Apply a fixed alpha for all classes and calculate the focal loss
weight = alpha * tf.math.pow(1 - y_pred_no_bg, gamma) # Focusing weight
focal_loss = weight * cross_entropy
# Average over all pixels and classes (across the batch and spatial dimensions)
return tf.reduce_mean(tf.reduce_sum(focal_loss, axis=-1))
return loss
# -------------------------------------- #
# Tools #
# -------------------------------------- #
def apply_category_mapping(label):
"""
Apply category mapping to labels.
"""
keys_tensor = tf.constant(list(category_map.keys()), dtype=tf.int32)
vals_tensor = tf.constant(list(category_map.values()), dtype=tf.int32)
# Create the lookup table
table = tf.lookup.StaticHashTable(
tf.lookup.KeyValueTensorInitializer(keys_tensor, vals_tensor),
default_value=0
)
# Ensure the label is a Tensor
label = tf.convert_to_tensor(label, dtype=tf.int32)
return table.lookup(label)
def create_segmentation_colormap(num_classes):
"""
Create a linear colormap using a predefined palette.
Uses 'viridis' as default because it is perceptually uniform
and works well for colorblindness.
"""
return plt.cm.viridis(np.linspace(0, 1, num_classes))
def apply_colormap(label, colormap=None):
"""
Apply the colormap to a label.
"""
# Ensure label is 2D
label = np.squeeze(label)
if colormap is None:
num_classes = len(np.unique(label))
colormap = create_segmentation_colormap(num_classes)
# Apply the colormap
colored = colormap[label.astype(int)]
return colored
class VizCallback(tf.keras.callbacks.Callback):
def __init__(self, images, labels, frequency=5):
"""
Initialize the visualization callback.
Args:
images: A batch of validation images (numpy array or tensor).
labels: Corresponding ground truth labels (numpy array or tensor).
frequency: Frequency (in epochs) to display visualizations.
"""
super().__init__()
self.images = images
self.labels = labels
self.frequency = frequency
def on_epoch_end(self, epoch, logs=None):
if epoch % self.frequency == 0: # Visualize only every "frequency" epochs
batch_size = len(self.images)
predictions = self.model.predict(self.images, verbose=0)
y_preds = tf.math.argmax(predictions, axis=-1).numpy()
# Define label mapping and custom colors
label_mapping = {
0: 'Background',
1: 'Soil',
2: 'Bedrock',
3: 'Sand',
4: 'Big Rock'
}
colors = [
'#000000', # 0: Background
'#A95F44', # 1: Soil
'#584C44', # 2: Bedrock
'#C5986F', # 3: Sand
'#A69980' # 4: Big Rock
]
cmap = ListedColormap(colors)
# Create legend patches
patches = [mpatches.Patch(color=colors[i], label=label_mapping[i]) for i in label_mapping]
for i in range(batch_size):
image = self.images[i]
label = self.labels[i]
label = apply_category_mapping(label)
y_pred = y_preds[i]
plt.figure(figsize=(18, 6))
# Input image
plt.subplot(1, 3, 1)
plt.title(f'Input Image (Sample {i})')
if image.shape[-1] == 1:
plt.imshow(image.squeeze(), cmap='gray')
else:
plt.imshow(image)
plt.axis('off')
# Ground truth mask
plt.subplot(1, 3, 2)
plt.title('Ground Truth Mask')
plt.imshow(label.numpy().squeeze(), cmap=cmap, vmin=0, vmax=len(label_mapping) - 1)
plt.axis('off')
# Predicted mask
plt.subplot(1, 3, 3)
plt.title('Predicted Mask')
plt.imshow(y_pred.squeeze(), cmap=cmap, vmin=0, vmax=len(label_mapping) - 1)
plt.axis('off')
# Add legend
plt.legend(handles=patches, bbox_to_anchor=(1.05, 1), loc='upper left', borderaxespad=0.)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()Please substiutite your parameters
# OPTIMIZER
optimizer = tf.keras.optimizers.AdamW(
learning_rate=1e-3, # Starting learning rate
weight_decay=1e-4 # Regularization strength
)
# METRIC
metric_main = 'sparse_categorical_accuracy'
# LOSS FUNCTION
loss_fn = focal_loss_ignore_class_0(alpha=0.25, gamma=2.0)
# Compile the model
model.compile(
optimizer=optimizer,
loss=loss_fn,
metrics=[metric_main, MeanIntersectionOverUnion(num_classes=5, labels_to_exclude=[0])]
)# Early stopping and learning rate scheduler
early_stopping = tf.keras.callbacks.EarlyStopping(
monitor='val_mean_iou', # Metric to monitor
patience=10, # Number of epochs with no improvement after which training will be stopped
restore_best_weights=True # Restore the best model found
)
lr_scheduler = tf.keras.callbacks.ReduceLROnPlateau(
monitor='val_mean_iou', # Metric to monitor
factor=0.5, # Factor by which the learning rate will be reduced
patience=5, # Number of epochs with no improvement after which learning rate will be reduced
verbose=1, # Verbosity mode
min_lr=1e-6 # Lower bound on the learning rate
)
# Add ModelCheckpoint callback to save the best model based on validation loss
model_checkpoint = tf.keras.callbacks.ModelCheckpoint(
filepath=model_filename, # Use the unified filename
monitor='val_mean_iou', # Monitor validation metrics
save_best_only=True, # Save only the best model
mode='max', # Mode to maximize the monitored quantity
verbose=1
)batch_size = 16
epochs = 1000
seed = 42
viz_callback = VizCallback(X_val[:2], y_val[:2]) # Visualize first 2 validation images
# Choose which callbacks to activate
callbacks = [early_stopping, lr_scheduler, viz_callback, model_checkpoint]
history = model.fit(
augmented_X_train, augmented_y_train,
batch_size=batch_size,
epochs=epochs,
validation_data=(X_val, y_val),
callbacks=callbacks,
verbose=1
)
# Retrieve best epoch and corresponding metrics from EarlyStopping based on Mean IoU
best_epoch = history.history['val_mean_iou'].index(max(history.history['val_mean_iou'])) # Index of the best validation mIoU
best_val_miou = max(history.history['val_mean_iou']) # Best validation mIoU
best_val_loss = history.history['val_loss'][best_epoch] # Best validation loss at that epoch
# Print the best metrics
print(f"Training completed after {best_epoch + 1} epochs (Early Stopping).")
print(f"Best Validation Mean IoU: {best_val_miou:.4f}")
print(f"Corresponding Validation Loss: {best_val_loss:.4f}")
# Save the final model after training
model.save(model_filename)
print(f"Model saved to {model_filename}")# Load the most recent model
model = tfk.models.load_model(model_filename, compile = False)
print(f"Model loaded from {model_filename}")
model.compile(
optimizer=optimizer,
loss=loss_fn,
metrics=[metric_main, MeanIntersectionOverUnion(num_classes=5, labels_to_exclude=[0])]
)
# Predictions
preds = model.predict(X_test)
preds = np.argmax(preds, axis=-1)
print(f"Predictions shape: {preds.shape}")
# Convert predictions to DataFrame
def y_to_df(y):
n_samples = len(y)
y_flat = y.reshape(n_samples, -1)
df = pd.DataFrame(y_flat)
df["id"] = np.arange(n_samples)
cols = ["id"] + [col for col in df.columns if col != "id"]
return df[cols]
# Save predictions to CSV
submission_filename = f"sub_{model_name}_{timestamp}.csv"
submission_df = y_to_df(preds)
submission_df.to_csv(submission_filename, index=False)
# Download submission
if COLAB:
from google.colab import files
files.download(submission_filename)
print(f"Submission saved to {submission_filename}")# Function to visualize predictions for a list of indices with a legend
def visualize_predictions(idx_list):
# Ensure idx_list is a list even if a single integer is provided
if isinstance(idx_list, int):
idx_list = [idx_list]
# Create legend patches
patches = [mpatches.Patch(color=colors[i], label=label_mapping[i]) for i in label_mapping]
for idx in idx_list:
img = X_val[idx]
true_mask = y_val[idx]
pred_mask = model.predict(img[np.newaxis, ...])[0]
pred_mask = np.argmax(pred_mask, axis=-1)
plt.figure(figsize=(18, 6))
# Input Image
plt.subplot(1, 3, 1)
plt.title(f'Input Image (Index: {idx})')
if img.shape[-1] == 1:
plt.imshow(img.squeeze(), cmap='gray')
else:
plt.imshow(img)
plt.axis('off')
# True Mask
plt.subplot(1, 3, 2)
plt.title('True Mask')
plt.imshow(true_mask.squeeze(), cmap=cmap, vmin=0, vmax=len(label_mapping)-1)
plt.axis('off')
# Predicted Mask
plt.subplot(1, 3, 3)
plt.title('Predicted Mask')
plt.imshow(pred_mask.squeeze(), cmap=cmap, vmin=0, vmax=len(label_mapping)-1)
plt.axis('off')
# Add Legend
plt.legend(handles=patches, bbox_to_anchor=(1.05, 1), loc='upper left', borderaxespad=0.)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
# Example usage with a list of indices
visualize_predictions([i for i in range(27, 37)]) # Adjust the range as needed