This guide shows you how to run Emacs with the Windows Subsystem for Linux WSL (Version 1 and 2) on Windows 10 using Ubuntu 20.04 LTS as Linux distribution and VcXsrv as X server to run Emacs in a graphical display.
- Preparation
- Enable WSL 1 or WSL 2
- Install Ubuntu 20.04
- Install Emacs 28.1
- Run Emacs in Terminal
- Run Emacs in a Graphical Display
- Optional Additions
- FAQ
- Troubleshooting
Clone this repository with Git or download it to any place on your machine to be able use the batch scripts (recommended) later on.
Open PowerShell as Administrator and run:
dism.exe /online /enable-feature /featurename:Microsoft-Windows-Subsystem-Linux /all /norestart
For WSL 2 (see requirements) you have to enable another feature:
dism.exe /online /enable-feature /featurename:VirtualMachinePlatform /all /norestart
Restart the computer.
Download and install the Linux kernel update package.
If you want to use WSL 2 you should set it as default before intstalling
Ubuntu:
wsl --set-default-version 2
If you are not able to install WSL with this instructions go have a look at the official Microsoft docs (site) on how to install WSL.
To install Ubuntu 20.04 open PowerShell and run:
Use PowerShell Version 5 which is the preinstalled Version else the Appx module might not be available and you will get an error when running this command.
curl.exe -L -o ubuntu-2004.appx https://aka.ms/wslubuntu2004
Add-AppxPackage .\ubuntu-2004.appx
After installation open Start (WIN) and launch the
Ubuntu 20.04 LTS terminal. After a short while you will be prompted to enter a
username and a password. This user will be your default user for the
distribution and is considered the Linux administrator with the ability to run
sudo commands.
Make sure everything is up to date:
sudo apt update && sudo apt upgrade -yIf you already have been using another Linux distribution you might want to set Ubuntu 20.04 as default. Open PowerShell and run:
wsl --set-default Ubuntu-20.04
To install Emacs 28.1 in Ubuntu 20.04 follow those steps:
- Install all dependencies (taken from the snap):
sudo apt update sudo apt install -y autoconf automake bsd-mailx dbus-x11 debhelper dpkg-dev \ gcc-10 libacl1-dev libasound2-dev libdbus-1-dev libgccjit-10-dev libgif-dev \ libgnutls28-dev libgpm-dev libgtk-3-dev libjansson-dev libjpeg-dev \ liblcms2-dev liblockfile-dev libm17n-dev libncurses5-dev liboss4-salsa2 \ libotf-dev libpng-dev librsvg2-dev libselinux1-dev libsystemd-dev libtiff-dev \ libxi-dev libxml2-dev libxpm-dev libxt-dev procps quilt sharutils texinfo \ zlib1g-dev gvfs language-pack-en-base libasound2 libaspell15 libasyncns0 \ libatk-bridge2.0-0 libatk1.0-0 libatspi2.0-0 libbrotli1 libc6 libc6-dev \ libcairo-gobject2 libcairo2 libcanberra-gtk3-0 libcanberra-gtk3-module \ libcanberra0 libcroco3 libdatrie1 libdb5.3 libdrm2 libegl1 libenchant1c2a \ libepoxy0 libflac8 libfontconfig1 libfreetype6 libgbm1 libgccjit0 libgcc-s1 \ libgdk-pixbuf2.0-0 libgif7 libgl1 libglvnd0 libglx0 libgpm2 libgraphite2-3 \ libgstreamer-gl1.0-0 libgstreamer-plugins-base1.0-0 libgstreamer1.0-0 \ libgtk-3-0 libgudev-1.0-0 libharfbuzz-icu0 libharfbuzz0b libhyphen0 libice6 \ libicu66 libisl22 libjansson4 libjbig0 libjpeg-turbo8 liblcms2-2 liblockfile1 \ libltdl7 libm17n-0 libmpc3 libmpfr6 libnotify4 libnss-mdns libnss-myhostname \ libnss-systemd libogg0 liborc-0.4-0 libotf0 libpango-1.0-0 libpangocairo-1.0-0 \ libpangoft2-1.0-0 libpixman-1-0 libpng16-16 libpulse0 librsvg2-2 libsasl2-2 \ libsecret-1-0 libsm6 libsndfile1 libsoup2.4-1 libssl1.1 libstdc++6 libtdb1 \ libthai0 libtiff5 libvorbis0a libvorbisenc2 libvorbisfile3 libwayland-client0 \ libwayland-cursor0 libwayland-egl1 libwayland-server0 libwebp6 libwebpdemux2 \ libwoff1 libx11-6 libx11-xcb1 libxau6 libxcb-render0 libxcb-shm0 libxcb1 \ libxcomposite1 libxcursor1 libxdamage1 libxdmcp6 libxext6 libxfixes3 libxi6 \ libxinerama1 libxkbcommon0 libxml2 libxpm4 libxrandr2 libxrender1 libxslt1.1 \ libyajl2 libwebp-dev libwebkit2gtk-4.0-devThere might be a dialog about the mail server configuration, just select
no configurationto leave it as it is and confirm with OK (use TAB and RET to get through this). - Download and extract Emacs:
cd ~ wget https://ftp.gnu.org/pub/gnu/emacs/emacs-28.1.tar.gz tar -xzvf emacs-28.1.tar.gz
- Configure and install Emacs:
This Step will take a while and you might be prompted to enter your password once. If you don’t want to usenative compilationjust remove the compilation flag in the following instructions:cd ~/emacs-28.1 export CC="gcc-10" CXX="gcc-10" ./configure --with-json --with-native-compilation --with-xwidgets make sudo make install rm ~/emacs-28.1.tar.gz
Keep the directory where Emacs was cloned to be able to reinstall (if a step fails), to reconfigure or to uninstall it.
To try out if Emacs is working just run it directly in the terminal with emacs
-nw.
To update to a new Emacs version uninstall the current one by going to the
folder you used for the installation (for instance ~/emacs-28.1) and run sudo
make uninstall.
Then install the new version.
To use the latest snapshot you can clone the git repository. Just replace step 2 from above with:
cd ~
git clone git://git.sv.gnu.org/emacs.gitThen in step 3 make sure to cd ~/emacs instead. You can also add the
--with-pgtk (pure GTK) compilation flag.
Run Emacs with emacs -nw in Ubuntu terminal.
If you have Windows 11 you want to use WSLg to run Emacs in a graphical display instead of installing an X-Server and VcXsrv. This makes the rest of this section obsolete.
If you are on Windows 10 you need to install an X-Server and then run Emacs using it.
An X-server lets you access a Linux application or desktop environment’s graphic user interface (GUI). This guide is using VcXsrv (free, open source, GPLv3).
Download VcXsrv from https://sourceforge.net/projects/vcxsrv/ and install it. Check out the next section about the firewall configuration before launching it (app is called XLaunch) for a first time to add the firewall rules.
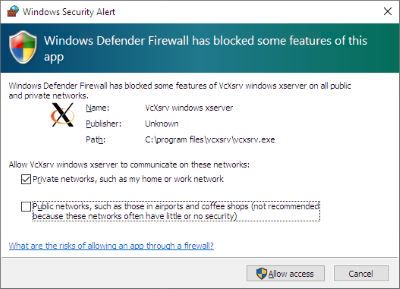
The first time you launch VcXsrv you are notified that Windows Defender Firewall has blocked some features.
You have to allow VcXsrv to communicate on:
WSL 1Private networksWSL 2Private and public networks.
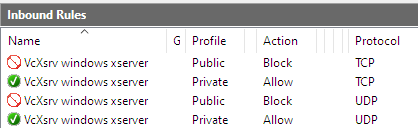
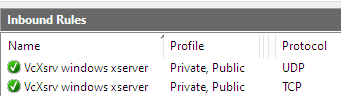
After allowing access the following inbound rules are added:
WSl 1
WSL 2
If you missed this step or are not sure what you’ve chosen or if you are switching from WSL 1 to WSL 2 you can retrigger this dialog by deleting the inbound rules (admin rights needed) and restart VcXsrv. The inbound rules shown above can be found at WIN Windows Defender Firewall > Advanced Settings (or WIN-r wf.msc RET).
To make VcXsrv work with WSL 2 you have to disable access control. Disabling the
user access control with the -ac flag has some security issues:
-ac disables host-based access control mechanisms. Enables access by any host, and permits any host to modify the access control list. Use with extreme caution. This option exists primarily for running test suites remotely.
Therefore we want to restrict the access as much as possible. Unfortunately you
can’t modify the firewall rules if you have no admin rights. In that case you
have to live with the security issue (not sure how severe it is).
If you have admin rights you can add an inbound firewall rule to restrict
access as much as possible. As the IP used by WSL 2 is dynamic a powershell
script is provided later on to create/update the rule.
If you want to use the additional firewall rule make sure that you disable the existing inbound rules:
- Go to the inbound rule settings with WIN Windows Defender Firewall > Advanced Settings (or WIN-r wf.msc RET).
- Search for VcXsrv entries (there should be two) and disable all found.
To run Emacs in a graphical display you have to:
WSL 2 only, optionalCreated/update the inbound firewall rule (admin rights needed)- Run VcXsrv
- Run Emacs
For convenience there are batch scripts (double-clickable) to (you can copy the run-emacs folder for WSL 1 or WSL 2 to wherever you want):
WSL 1- Run VcXsrv and Emacs ./run-emacs-wsl-1/wsl-1_0-run-all.bat
- Run VcXsrv ./run-emacs-wsl-1/wsl-1_1-vcxsrv.bat
- Run Emacs ./run-emacs-wsl-1/wsl-1_2-emacs.bat
WSL 2- Run all (Firewall rule, VcXsrv and Emacs) ./run-emacs-wsl-2/wsl-2_0-run-all.bat
- Run Firewall rule and VcXsrv ./run-emacs-wsl-2/wsl-2_1-firewall-rule-vcxsrv.bat
- Run Firewall rule (admin rights needed). ./run-emacs-wsl-2/wsl-2_2-firewall-rule.bat
- Run VcXsrv ./run-emacs-wsl-2/wsl-2_3-vcxsrv.bat
- Run Emacs ./run-emacs-wsl-2/wsl-2_4-emacs.bat
As described in WSL 2 Additional Firewall Configuration we want to restrict the access by adding a firewall rule. Make sure you have disabled the existing VcXsrv firewall rules.
To create or update the inbound firewall rule you can use the batch script ./run-emacs-wsl-2/wsl-2_2-firewall-rule.bat. If VcXsrv was running before the firewall rule was updated it has to be restarted.
To run VcXsrv use the batch script provided or run the following commands in cmd (if you haven’t used the default installation path you have to adapt the script/command):
WSL 1./run-emacs-wsl-1/wsl-1_1-vcxsrv.batstart "" "C:\Program Files\VcXsrv\vcxsrv.exe" :0 -multiwindow -clipboard -wgl
WSL 2./run-emacs-wsl-2/wsl-2_3-vcxsrv.batstart "" "C:\Program Files\VcXsrv\vcxsrv.exe" :0 -multiwindow -clipboard -wgl -ac
If you are using the additional firewall rule make sure to create/update the rule before launching VcXsrv.
If VcXsrv is already running it will show an error message. In that case stop VcXsrv if needed and run the script again.
To run Emacs you can launch Ubuntu terminal and run the following commands or use the batch script:
WSL 1./run-emacs-wsl-1/wsl-1_2-emacs.batexport DISPLAY=:0.0 export LIBGL_ALWAYS_INDIRECT=1 setsid emacs
WSL 2./run-emacs-wsl-2/wsl-2_4-emacs.batexport DISPLAY=$(ip route | awk '/^default/{print $3; exit}'):0.0 export LIBGL_ALWAYS_INDIRECT=1 setsid emacs
You can add the lines without setsid emacs to ~/.bashrc and then just use
setsid emacs to launch Emacs in the background. If you do so VcXsrv has to
be running before launching the terminal else this will give an error when
starting the terminal and in that case slow the startup down.
To not have to type this over and over add an alias in ~/.bashrc and then
run Emacs with ema (needs a restart):
WSL 1alias ema=" export DISPLAY=:0.0 export LIBGL_ALWAYS_INDIRECT=1 setsid emacs "
WSL 2alias ema=" export DISPLAY=$(ip route | awk '/^default/{print $3; exit}'):0.0 export LIBGL_ALWAYS_INDIRECT=1 setsid emacs "
The network connection between Windows and WSL2 breaks when your machine goes into standby or hibernate. Graphical Emacs & other GUI apps will terminate.
Should you want to preserve your GUI Emacs sessions between sleep, there are three options:
- Use X2Go - virtual X11 server with Windows client
This is the most preferred option
a) Fix SSH host keys
sudo apt-get remove --purge openssh-server sudo apt-get install openssh-server sudo service ssh --full-restartb) Install X2Go on your Linux distribution
apt install x2goserverc) Download and install the client for Windows.
d) Configure the
Host: localhost Login: <your user> Session type: Published Applications
e) After each WSL/Windows restart
Launch ssh in Linux (if not started yet): sudo service ssh start Launch “X2Go Client” on Windows ad connect to the server with user/password Now you can launch X11 apps via the tray icon (see X2Go Published Applications)
Source: Development Environment in WSL2
- Forward X11 unix socket from WSL2 via WSL1 to X410/Vcxsrv/etc. running on Windows
Using Emacs on Windows with WSL2 | Emacs Redux microsoft/WSL#4619 {WSL 2} WSL 2 cannot access windows service via localhost:…
- WSL Daemon - Stable X11 connection for WSL2
GitHub - nbdd0121/wsld: WSL Daemon - Stable X11 connection and time synchroni…
Install Windows Terminal from Microsoft from the Microsoft Store.
The Windows Terminal is a modern, fast, efficient, powerful, and productive terminal application for users of command-line tools and shells like Command Prompt, PowerShell, and WSL.
To make it open WSL by default:
- Open the Windows Terminal.
- Open the settings by clicking on the dropdown button in the tab bar and then select settings (bound to Ctrl-,).
- Copy the GUID for WSL (example: {12345678-1234-1234-1234-1234567890AB}).
- Set the default profile to the one copied from WSL:
{ ... "defaultProfile": "{12345678-1234-1234-1234-1234567890AB}", ...
To change the default path to ~:
- Go to the settings (Ctrl-,).
- Add a line in the WSL part at the end (make sure to also add the ~,~ on the
previous line):
{ ... "source": "Windows.Terminal.Wsl", "startingDirectory": "//wsl$/Ubuntu-20.04/home/<username>/" },
If you want to change the keyboard layout used make sure x11-xkb-utils is
installed (sudo apt install x11-xkb-utils) and add for instance
setxkbmap -layout usto ~/.bashrc or to the alias to use the US keyboard layout. Or add it to
the scripts used to run Emacs (... && setxkbmap -layout us && setsid
emacs).
Generate a new ED25519 SSH key pair:
ssh-keygen -t ed25519 -C "email@example.com"A dialog will ask you to:
- input a file path: use the suggested path by pressing
Enter - enter a password: enter your password
To copy the generated ssh key into the clipboard use:
clip.exe < ~/.ssh/id_ed25519.pubBash on Ubuntu on Windows starts on the language defined in your Country or Region settings (maybe this got changed, not 100 % sure). If you want to change the default language to en_US you may need to run the following commands:
sudo apt install -y language-pack-en language-pack-en-base manpages
sudo locale-gen en_US.UTF-8
sudo update-locale LANG=en_US.UTF8To do so the fstab file needs to be configured.
For instance to mount H: add this to “/etc/fstab” (the directory has to exist to
make this work, so in this case sudo mkdir /mnt/h is needed beforehand):
H: /mnt/h drvfs defaults 0 0
From now on that network drive is automatically mounted.
If you want to use zsh and oh-my-zsh:
sudo apt install zsh
chsh -s $(which zsh)
sh -c "$(curl -fsSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/robbyrussell/oh-my-zsh/master/tools/install.sh)"Restart WSL.
In some scripts you need to change bash to zsh to be able to use it when emulating a terminal in Emacs.
The root is accessible as \\wsl$ in file explorer followed by the
distribution. You can show the current distribution name by running wsl -l -q
in cmd.
Run explorer.exe . in WSL to open the Windows File Explorer at the current
location. The path will start with \\wsl$ unless it is a mounted drive. In the
File Explorer the files and folders can be copied, moved and edited as usual
(see this blog post).
To start WSL from Windows File Explorer just type wsl into the location input
box or hold down Shift while right-clicking and select Open Linux shell here
from the context menu. If it’s a network drive it has to be mounted else this
will not work.
See https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/wsl/wsl-config#ways-to-run-wsl.
Check out the Microsoft docs:
Check your firewall settings (see WSL 2 Additional Firewall Configuration).