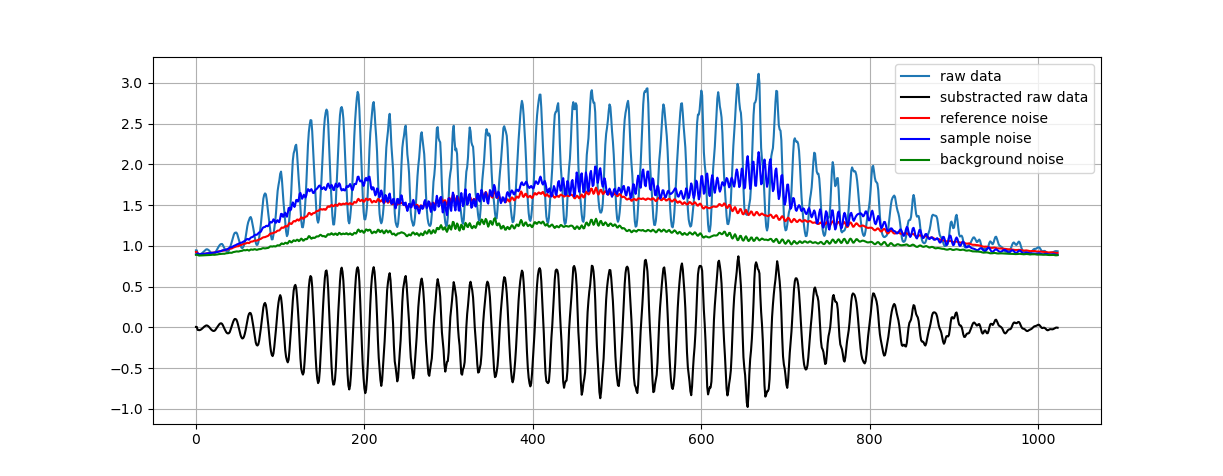
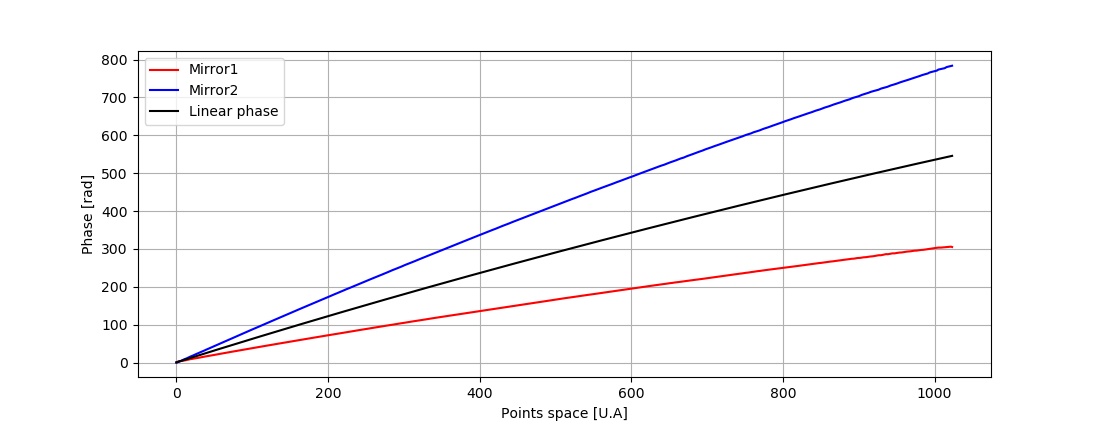
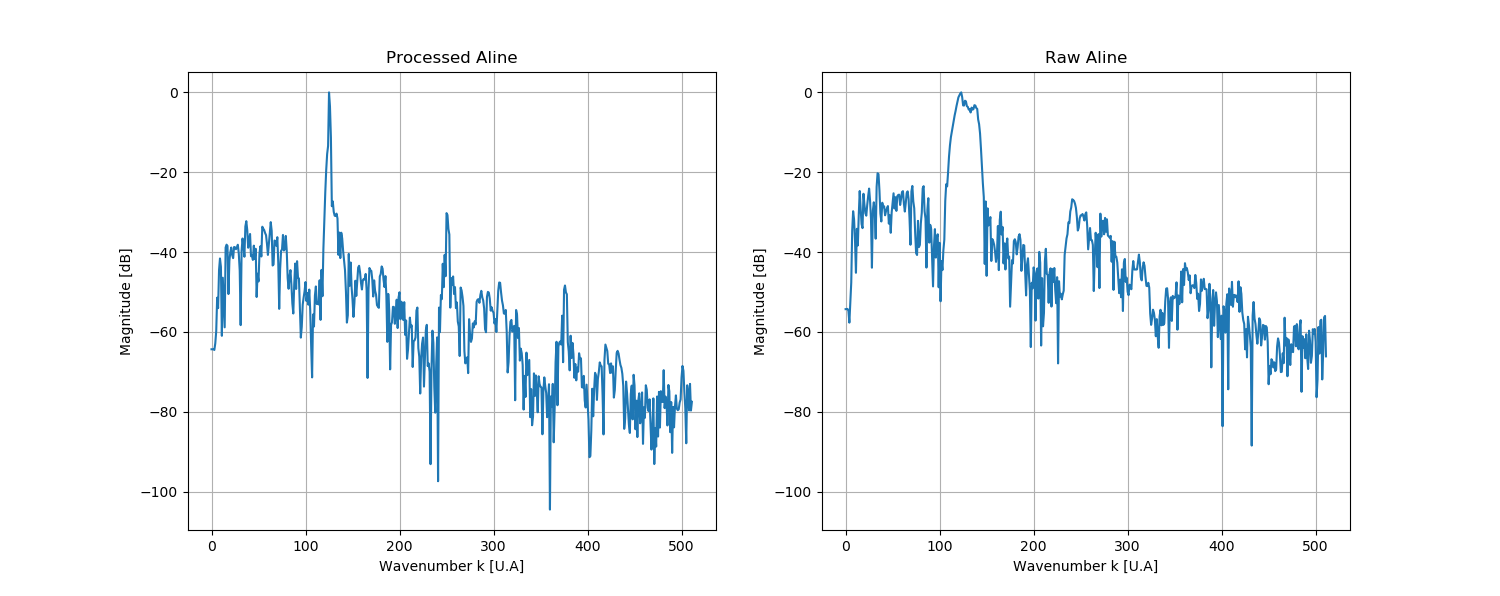
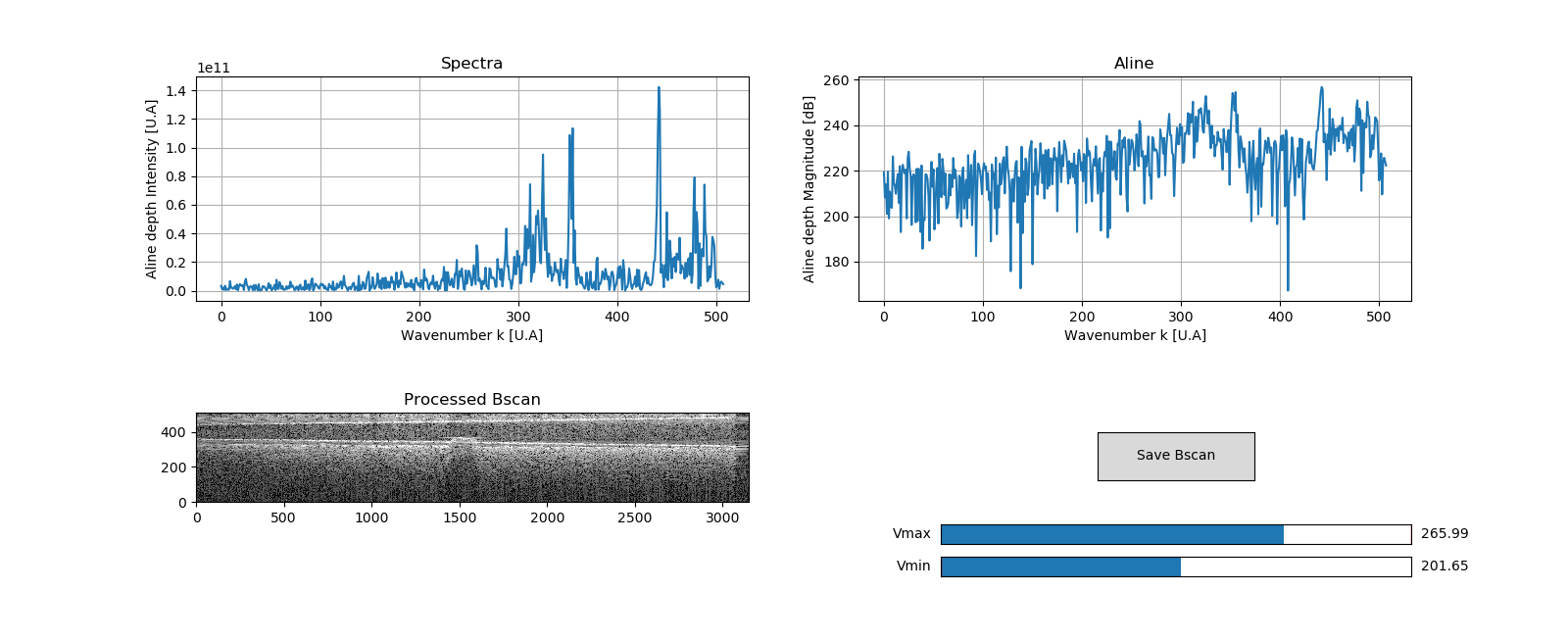
This project aims to produce an easy to use tool to calibrate any SD or SS-OCT. The processing is based on Attendu et al. "Simple and robust calibration procedure for k-linearization and dispersion compensation in optical coherence tomography." (doi: 10.1117/1.JBO.24.5.056001)
By calibrate I mean substracting background - k-linearize spectra - evaluate and compensate dispersion. In order to compute the calibration the algorithm need multiple measurements:
- mirror1.npy (OCT interferogram with mirror in one side of the zero delay as sample)
- dark_sample.npy (OCT interferogram with ref arm blocked)
- mirror2.npy (OCT interferogram with mirror in the other side of the zero delay as sample)
- dark_ref.npy (OCT interferogram with sample arm blocked)
- dark_not.npy (OCT interferogram with both arm blocked)
Those .npy file should be saved into a file in data/calibration/<your-name> directory.
In order to use the Py-OCT-Calibration Library, one must have installed the following packages:
- Numpy
- Scipy
- json
- matplotlib
- Cupy (fot Nvidia GPU acceleration)
- sphynx (for developer only)
- git (for developer only)
- Napari (for 3D-rendering)
- profile-viewer (for developer only)
To install CuPy librarie, one should refer to their website, link: CuPy installation
For the other dependencies and using pip3 one can use the following commands:
>>> pip3 install Numpy
>>> pip3 install Scipy
>>> pip3 install matplotlib
>>> pip3 install gitpython
>>> pip3 install Cupy
>>> pip3 install napari
>>> apt-get install python-sphinx (for Unix OS)
>>> sudo port install py27-sphinx (for Mac OS)The folder architecture is presented as :
- setup.py (setup installation tool for compilation)
- makefile (for tests and installation)
- data/ (contain all data)
- calibration/
- Aline/
- Bscan/
- Cscan/
- src/
- processing/
- calibration.py (compute calibration parameters)
- Aline.py (process one Aline)
- Bscan.py (process one Bscan)
- Cscan.py (process one Cscan)
- post_processing.py (3D rendering of Cscan volume)
- toolbox/ (contain tools to do all the processing)
- Doc/ (not yet fully developped)
- images/ (images for README.md)
- profiling/ (for optimization endings)
- documentation/ (auto-generated documentation)
- README.md (literally this)
Verify installation is correct by running some tests:
>>> make test_calibration
>>> make test_Cscan_cpu
>>> make test_Cscan_gpu (only with CUDA installed)
>>> make build_doc (generating html documentation)In order to run a calibration example one can tape the following command on command prompt:
>>> python3 src/processing/calibration.py --dispersion=1 --input-dir=./data/calibration/example/ --output-file=data/calibration/example/calib.json
Arguments for src/processing/calibration.py are:
- --dispersion : [1] for normal dispersion, [-1] for anormal
- --input-dir : directory of the input files for calibration
- --output-file : name of the output .json file containing all the calibration parameters which is saved in same directory as input-dir
In order to process one example of Aline, one can tape the following command on command prompt:
>>> python3 src/processing/Aline.py --dispersion=1 --input-file=data/Aline/example.txt --calibration-file=data/calibration/example/calib.json
Arguments for src/processing/Aline.py are:
- --dispersion : [1] for normal dispersion, [-1] for anormal
- --input-file : directory of the input Aline file
- --calibration : directory for the output .json file containing all the calibration parameters
- --output-file : directory for the processed Aline file
In order to process one example of Bscan, one can tape the following command on command prompt:
>>> python3 src/processing/Bscan.py --dispersion=1 --input-file=data/Bscan/example.npy --calibration-file=data/calibration/example/calib.json
Arguments for src/processing/Bscan.py are:
- --dispersion : [1] for normal dispersion, [-1] for anormal
- --input-file : directory of the input Bscan file
- --calibration : directory for the output .json file containing all the calibration parameters
- --output-file : directory for the processed Bscan file
In order to process one example of Cscan, one can tape the following command on command prompt:
>>> python3 src/processing/Cscan.py --dispersion=1 --input-dir=Cscan/example/ --calibration-file=data/calibration/example/calib.json --dimension 100 100 1024
Arguments for src/processing/Cscan.py are:
- --dispersion : [1] for normal dispersion, [-1] for anormal
- --input-file : directory of the input Aline file
- --calibration : directory for the output .json file containing all the calibration parameters
- --output-file : directory for the processed Cscan file
Documentation on project is available in a html file "docs/documentation/build/index.html"
In order to keep a clean and consistent code, one can follow the convention as presented in the following link:
https://www.python.org/dev/peps/pep-0008/#documentation-strings