During countless discussions regarding the best Android architecture we often forget about principles of an object-oriented programming and proper domain modeling.
This repository contains an example of a Domain Driven Design in the Android application. You can find more details and an in-depth explanation in the Medium article.
For a sake of simplicity the app is built in a single app module. It's struture can be scaled up and divided into multiple modules if needed.
Application follows an official guide to app architecture and is split into 4 major architectural layers:
ui- Screens, ViewModels, Themedomain- Use Cases and corresponding data structuresdata- The main Model of the applicaton with corresponding Repositoriescore- Setup for Coroutines, Data Store and Retrofit
- Jetpack Compose + View Model for the UI
- Coroutines + Flow for an asynchronous processing
- Hilt for a Dependency Injection
- Retrofit for an HTTP communication
- Data Store for a simple key-value persistance
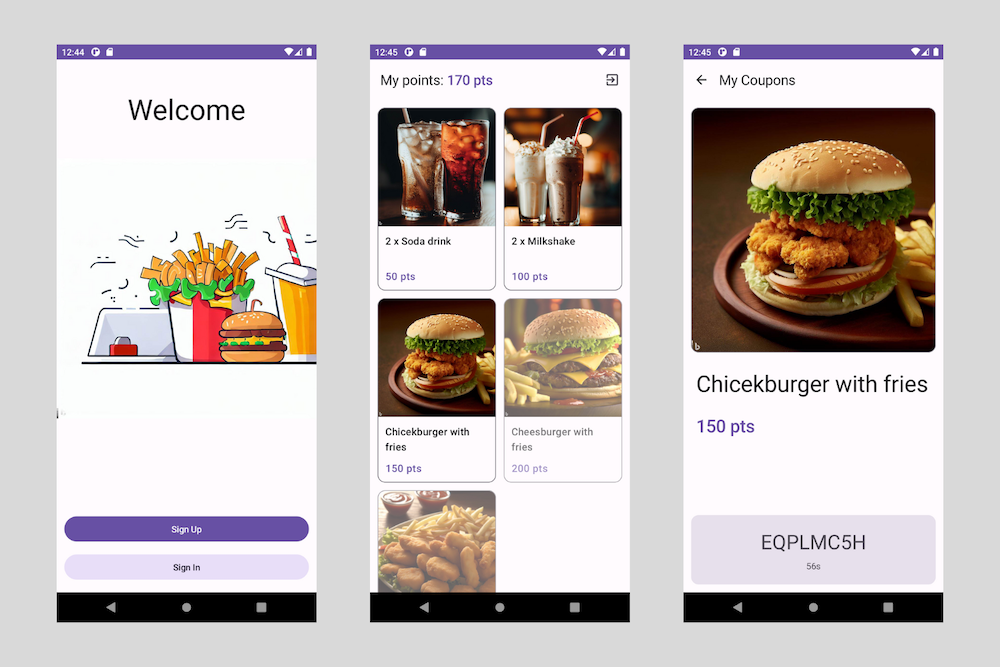
It is a loyalty application for the fast-food type of restaurant, inspired by the McDonalds app, where user can collect points and exchange them for the coupons.
User can browse the list of available coupons which are ordered from the cheapest to the most valueable one.
Each coupon can be clicked and then the full screen preview of it is displayed.
For buying the food user collects the points. Each coupon in the app has a value expreseed in points.
User can use collected points and exchange them for the coupons.
When user exchanges points for the coupon this coupon becomes active for 60 seconds.
During this time an activation code is displayed on the screen and user can use it in the restaurant to receive a free meal.
To collect the points user needs an account. Account can be created directly in the application.
User needs to enter an email address and accept Terms & Conditions notes.