This hackathon is an open invitation to all KubeCon NA 2019 attendees to try out Ballerina with Kubernetes, complete a series of coding challenges, and win some amazing prizes.
- Overview
- Challenges
- Prizes
- Getting Started
- Submission Guidelines
- Judging Criteria
- Rules
- FAQ
- Hackathon policies
These coding challenges are all about having fun, learning a new programming language, mashing up microservices, and deploying them on Kubernetes. Here are some essential details about this hackathon.
-
Start: Nov 19, 2019 at 10:00 a.m.
-
Submission deadline: Nov 21, 2019 12:00 p.m.
-
Winners will be announced at 3:00 p.m. on Nov 21 at the Ballerina booth
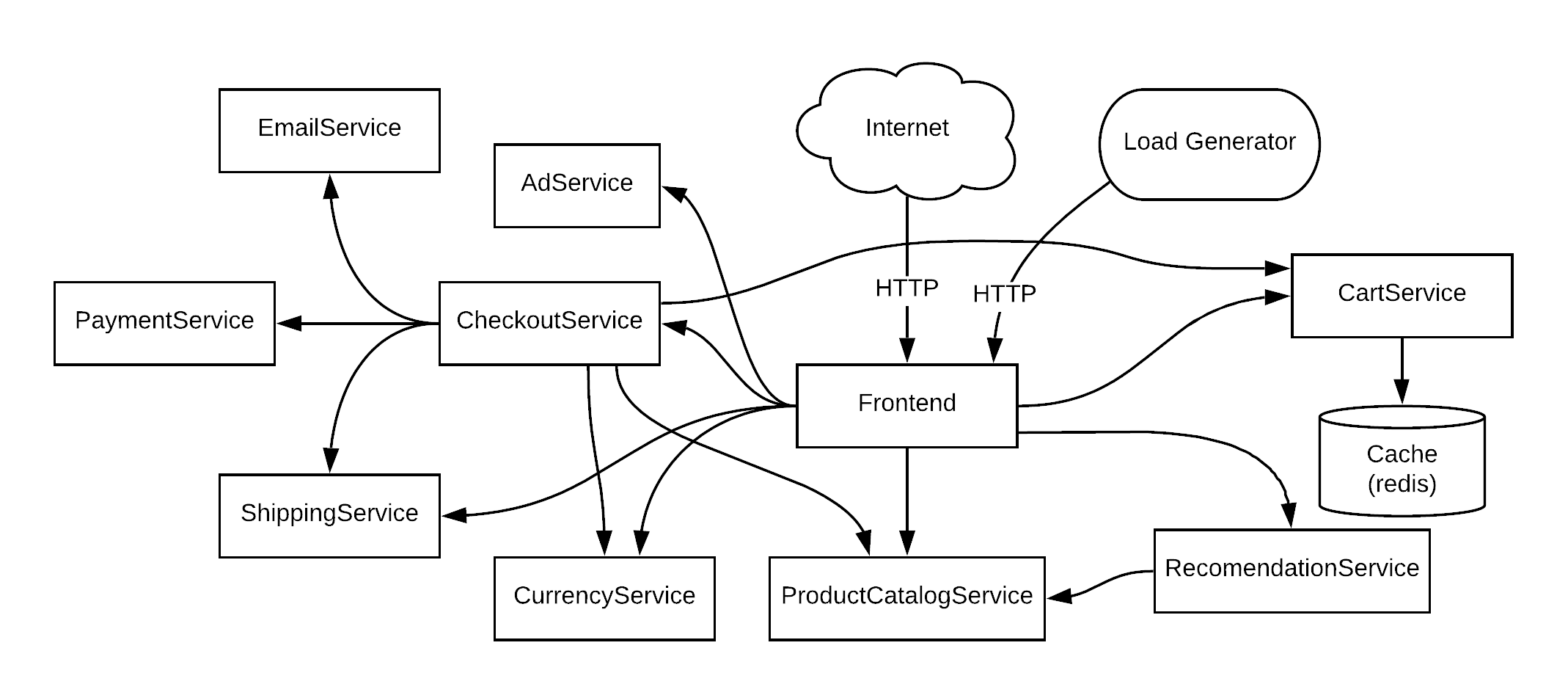
The challenges are based on the “Hipster Shop: Cloud-Native Microservices Demo Application” developed by Google Cloud. It is a web-based e-commerce application with 10 microservices written in different programming languages that talk to each other over gRPC. You can refer to the original README.md file to learn more about this application. Here is a brief overview of the service architecture.
All you have to do is implement the following microservices in Ballerina. Order of services indicate how much Ballerina knowledge you will need to implement it as the first service require very little knowledge of Ballerina as well as the lines of code. We recommend you to complete the challenges in the order they appear in the below table to make the learning process easy.
| Microservice | Original Language | Description |
|---|---|---|
| adservice | Java | Provides text ads based on given context words |
| currencyservice | NodeJS | Converts a certain amount in one currency to another currency. |
| checkoutservice | Go | Retrieves the user cart, prepares the order and orchestrates the payment, shipping and the email notification. |
Take a look at the steps for each service below to understand how you need to implement the logic. Check out the original source code for more information.
| Microservice | Instructions |
|---|---|
| adservice |
|
| currencyservice |
|
| checkoutservice |
|
The Getting Started section has more details on how to complete these challenges
Here are the cool prizes you can win by completing the 3 challenges.
-
First Prize - Bose Quiet Comfort 35 wireless headphones II Star Wars: The Rise of Skywalker Edition
-
Second Prize - Echo Studio
-
The next best 10 submissions will receive $50 worth Amazon vouchers.
Read the Judging Criteria to see how you can win!
[TODO] Document eligibility criteria
- Visit https://ballerina.io/downloads/ to install the latest ballerina version 1.0.4 as well as the VSCode or IntelliJ IDEA plugins.
- Download the latest VSCode plugin here: https://ballerina.io/learn/tools-ides/vscode-plugin/
- Download the latest IntelliJ IDEA plugin here: https://ballerina.io/learn/tools-ides/intellij-plugin/
- Use Docker for Mac to install on Mac.
- Use Docker for Windows to install on Windows.
- Install Docker CE and Minikube on Linux.
Note: Execute eval $(minikube docker-env) after installing Minikube so
that the Docker client points to Minikube’s docker registry.
-
Create a private GitHub repository in your account. Do not fork this repository if you want to keep your code private during the hackathon. An example repository name would be
ballerina-hackathon-kubecon-na-19. -
Run the following commands to merge the microservices-demo content to your newly created repository.
$ git clone https://github.com/<gitbubusername>/ballerina-hackathon-kubecon-na-19 $ cd ballerina-hackathon-kubecon-na-19 $ git remote add upstream https://github.com/ballerina-guides/microservices-demo.git $ git pull upstream master $ git push origin master
-
Clone this repository, and go to the repository directory.
-
Run
kubectl apply -f ./release/kubernetes-manifests.yamlto deploy the app. -
Run
kubectl get podsto see whether pods are in a Ready state. -
If all the pods are running,
kubectl get service/frontend-external -
Find the IP address of your application, then visit the application on your browser to confirm installation. (http://localhost:80)
kubectl get service/frontend-external
Note: If you are on Minikube, get the hostname by executing
minikube ip. e.g., <MINIKUBE_IP>:<FRONTEND_EXTERNAL_PORT>Congrats, you have successfully installed the default application by now.
-
Run
kubectl delete -f ./release/kubernetes-manifests.yamlto delete what's deployed.
To help you get started, we’ve already implemented the recommendation service in Ballerina, and the source code is available in the src/recommendatationservice_ballerina directory.
-
Go to the repository directory and run the start script:
sh scripts/start.sh
-
Check pods with
kubectl get pods -
Access the web UI (http://localhost:80 or
http://<MINIKUBE_IP>:<FRONTEND_EXTERNAL_PORT>) -
Run the
scripts/stop.shscript to delete what's deployed.
Now that you’ve successfully installed and deployed the Hipster Shop application with one microservice written in Ballerina, it’s time to start working on the challenges.
The microservices in this application talk to each other over gRPC. I.e, the microservices that you are implementing will receive requests over gRPC and they will also integrate with other microservices over gRPC. You can find the protocol buffers description here.
The first step would be to generate Ballerina gRPC service skeletons and client stubs. You can follow the following guides to learn more about gRPC support in Ballerina.
- https://ballerina.io/learn/how-to-generate-code-for-protocol-buffers/
- https://github.com/ballerina-guides/grpc-service
- https://ballerina.io/learn/by-example/grpc-unary-blocking.html
Go to your repository directory and run the following command to generate Services from proto file.
ballerina grpc --input pb/demo.proto --output stubs --mode serviceNow the “stubs” directory will have the generated Ballerina services and client artifacts as below.
Services skeletons
- AdService_sample_service.bal
- CheckoutService_sample_service.bal
- PaymentService_sample_service.bal
- RecommendationService_sample_service.bal
- ProductCatalogService_sample_service.bal
- CurrencyService_sample_service.bal
- CartService_sample_service.bal
- EmailService_sample_service.bal
- ShippingService_sample_service.bal
Client stubs
- demo_pb.bal
Note: You can copy the relevant service skeleton file and the demo_pb.bal file to your project.
Let’s start by writing the recommendationservice in Ballerina. We’ve already implemented this service for your reference. Here are the steps that we followed. You can repeat the same for all 3 challenges.
In Ballerina, the code is structured using projects and modules. A module is a directory which provides collaboration, sharing, and reuse of Ballerina code. Projects can have multiple related modules. Please find more information here.
In this demo, our recommendation is to create a Ballerina project for each microservice. Let’s append “_ballerina” to the name of the microservices that you are working on.
-
Go to the src directory and run the following command to create a new project.
$ cd src $ ballerina new recommendationservice_ballerina -
Change the directory to the project directory you just created.
$ cd recommendationservice_ballerina -
Add a new Ballerina module. This is where we maintain the code that belongs to the recommendationservice.
$ ballerina add recommendationservice
Note: You can delete the unnecessary generated files such as the main.bal file and the tests and resources directories inside the module directory.
-
Copy the corresponding service template source file and the demo_pb.bal file to the module directory.
$ cp ../../stubs/demo_pb.bal src/recommendationservice/ $ cp ../../stubs/RecommendationService_sample_service.bal src/recommendationservice/
Note: The demo_pb.bal file needs to copied to each project which contains clients and common constructs.
-
Now that you have some Ballerina code try compiling the code with the
ballerina build -acommand. This command builds all the modules in your project. If the build is successful, you can find an executable JAR file in the project'starget/bindirectory. -
Refer the original instructions of each service defined in the Challenges section, and rewrite the logic in ballerina. Refer to the original source code to get an understanding of the business logic.
-
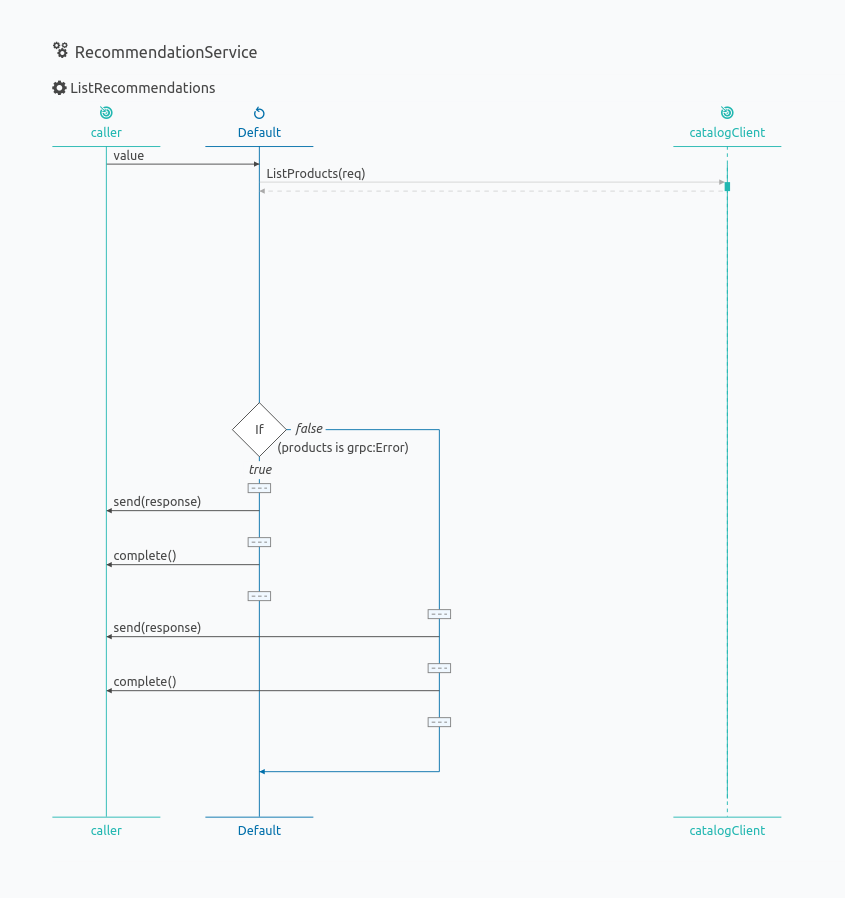
Checkout the diagram view for the service you implement.
You can follow the plugin specific instructions to view the diagram.
For example, the current implementation for the recommendation service would generate the following diagram.
-
Introduce
@kubernetes:Serviceand@kubernetes:Deploymentannotations to integrate generating the k8s artifacts during the build (Refer the recommendation service for examples). Make sure to use correct service name.You can refer the following resources for detailed explanations on using the annotations:
- Kubernetes Deployment Ballerina by Example
- The Kubernetes-Based Deployment section of How to Run and Deploy Ballerina Programs
e.g.,
@kubernetes:Service { serviceType: "ClusterIP", name: "recommendationservice" }
Note: A k8s deployment will be created by default, but if you need to change the k8s deployment, you can introduce the
@kubernetes:Deploymentannotation with the relevant configuration.Additionally, if you are using Minikube you would have to introduce the following deployment config.
@kubernetes:Deployment { dockerHost: "tcp://<docker_ip>:<docker_port>", dockerCertPath: ".minikube/certs" }
You can still skip the above when using Minikube by executing
eval $(minikube docker-env). -
Build and generate the k8s artifacts, to ensure there are no errors.
$ ballerina build recommendationservice_ballerina
-
Once you’ve completed a service, update the start.sh file to use the Ballerina implementation of that service. You can replace the current command for the particular service with the Ballerina commands for them instead.
e.g.,
kubectl apply -f $DEMO_HOME/kubernetes-manifests/recommendationservice.yaml # ballerina build --sourceroot $DEMO_HOME/src/recommendationservice_ballerina/src/recommendationservice --all # kubectl apply -f $DEMO_HOME/src/recommendationservice_ballerina/target/kubernetes/recommendationservice
Here, comment out the first line and uncomment the second and third lines to use the Ballerina build and generated artifacts for the service.
-
Repeat step 10 for the stop.sh file.
-
Run the modified setup script and check the status of the pods.
$ kubectl get pods
-
Tail the logs of your services.
$ kubectl logs -f <pod-name>
-
Access the web UI (http://localhost:80 or http://<MINIKUBE_IP>:<FRONTEND_EXTERNAL_PORT>)
-
Use the stop script to clean the deployments.
-
Then move on to the next challenge and repeat steps 1 - 15.
Once you complete all 5 challenges, you can submit the source code and other details via the following mechanism.
- Document everything that we need to be aware of your solution in the root README.md file of your repository.
- Download a zip file of your GitHub repository using the GitHub web interface.
- Then follow the instructions given in this Google form. [TODO]
A panel of judges will review each successful submission based on the following criteria.
[TODO]
- You have to be a KubeCon North America 2019 attendee to participate in this hackathon.
- [TODO]
-
How do I get help with queries related to the hackathon?
If you have general questions on Ballerina, ask them on our Slack channel, Google group, or on Stackoverflow with the tag [ballerina]. If you have specific questions related to the hackathon, please visit the Ballerina booth(P13).
-
Is this an individual challenge, or can I form a team for this?
[TODO]
-
Who can participate in the hackathon?
You have to be a KubeCon North America 2019 attendee to participate in this hackathon.
-
[TODO]
[TODO]