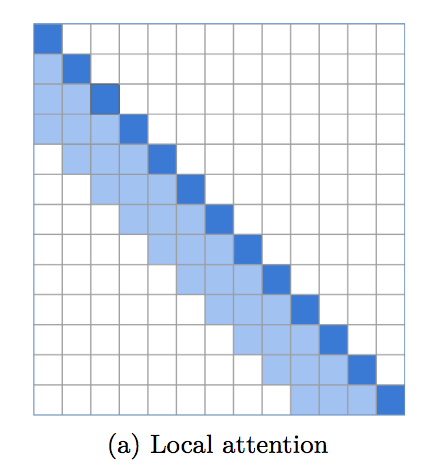
An implementation of local windowed attention, which sets an incredibly strong baseline for language modeling. It is becoming apparent that a transformer needs local attention in the bottom layers, with the top layers reserved for global attention to integrate the findings of previous layers. This repository makes it easy to immediately employ local window attention.
This code has been battletested in multiple repositories already, alongside different implementations of sparse long-range attention.
$ pip install local-attentionimport torch
from local_attention import LocalAttention
q = torch.randn(8, 2048, 64)
k = torch.randn(8, 2048, 64)
v = torch.randn(8, 2048, 64)
attn = LocalAttention(
dim = 64, # dimension of each head (you need to pass this in for relative positional encoding)
window_size = 512, # window size. 512 is optimal, but 256 or 128 yields good enough results
causal = True, # auto-regressive or not
look_backward = 1, # each window looks at the window before
look_forward = 0, # for non-auto-regressive case, will default to 1, so each window looks at the window before and after it
dropout = 0.1, # post-attention dropout
exact_windowsize = False # if this is set to true, in the causal setting, each query will see at maximum the number of keys equal to the window size
)
mask = torch.ones(1, 2048).bool()
out = attn(q, k, v, input_mask = mask) # (1, 8, 2048, 64)This library also allows for local attention in the setting of shared query/key space. The normalization of the keys, as well as the masking of tokens to itself, will be taken care of.
import torch
from local_attention import LocalAttention
qk = torch.randn(8, 2048, 64)
v = torch.randn(8, 2048, 64)
attn = LocalAttention(
dim = 64,
window_size = 512,
shared_qk = True,
causal = True
)
mask = torch.ones(1, 2048).bool()
out = attn(qk, qk, v, input_mask = mask) # (1, 8, 2048, 64)If you wish for the module to automagically pad your query / key / values as well as the mask, simply set the autopad keyword to True
import torch
from local_attention import LocalAttention
q = torch.randn(8, 2057, 64)
k = torch.randn(8, 2057, 64)
v = torch.randn(8, 2057, 64)
attn = LocalAttention(
window_size = 512,
causal = True,
autopad = True # auto pads both inputs and mask, then truncates output appropriately
)
mask = torch.ones(1, 2057).bool()
out = attn(q, k, v, input_mask = mask) # (1, 8, 2057, 64)@inproceedings{rae-razavi-2020-transformers,
title = "Do Transformers Need Deep Long-Range Memory?",
author = "Rae, Jack and Razavi, Ali",
booktitle = "Proceedings of the 58th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics",
month = jul,
year = "2020",
address = "Online",
publisher = "Association for Computational Linguistics",
url = "https://www.aclweb.org/anthology/2020.acl-main.672"
}@misc{roy*2020efficient,
title = {Efficient Content-Based Sparse Attention with Routing Transformers},
author = {Aurko Roy* and Mohammad Taghi Saffar* and David Grangier and Ashish Vaswani},
year = {2020},
url = {https://arxiv.org/pdf/2003.05997.pdf}
}@misc{beltagy2020longformer,
title = {Longformer: The Long-Document Transformer},
author = {Iz Beltagy and Matthew E. Peters and Arman Cohan},
year = {2020},
eprint = {2004.05150},
archivePrefix = {arXiv},
primaryClass = {cs.CL}
}