Prediction of Credit Card Churners
INTRODUCTION
Customer relations are essential for businesses to keep up proactive relations and maintain a high standard of communication. In banks, credit card customers churn, and Banks lose business. The dataset of bank credit card customers' churn provides many customer profile characteristics. They list various cardholders' profiles and capture their tiers of credit limits, account age, and other activity and demographic features. We analyzed the factors that affected the customers' attrition and developed models to predict and identify customers at high risk for attrition so that the bank management can understand the potential reasons for churning customers and proactively act upon them. The study is intended to provide a direction of building up the strategies that can increase user engagement and allow customer relations to interact with those high-risk customers and maintain them proactively.
ANALYSIS APPROACH
- Task 1: Pre-processing
- Load the data and check the data property
- Cast the variables into the appropriate types
- Create dummy columns for categorial features
- Task 2: Exploratory phase
- Analyze features correlations
- Apply Cluster analysis
- Task 3: Models building
- Stochastic Gradient Descent
- Decision Trees
- Random Forests
- Task 4: Reporting
- Consolidate findings and finalize report
PROCESS
We applied the following process to achieve our results:
- Data Selection
- Preprocessing 00_cleaning
- Transformation 00_cleaning
- Analysis 02_analysis
- Prediction 03_models
DATA SOURCE
The data is from the Kaggle website. It has 10K observations and 20 features. The dataset does not have any missing values. Minimal data cleaning was required.
https://www.kaggle.com/sakshigoyal7/credit-card-customers
EXPLORATORY DATA ANALYSIS
EDA is applied in two steps. The first step is to generate an overview of the whole data to understand the data distributions per feature. Also, to find apparent relations and patterns using correlations. This part is auto-generated using SweetViz after performing the data cleaning step to generate a consolidated overview report. The report can be found in 01_eda_sweetviz.html. The second step is to apply targeted and specific analysis on the most interesting features identified during the first step.
CORRELATED FEATURES
We investigated the correlations between the features trying to identify any linear correlation among the features. The correlation heatmap below shows the top features having absolute correlations above 0.6. We can observe that there are highly collinear features such (avg_open_to_buy and credit_limit), (is_male and is_female) and (is_single and is_married). The gender and marital status are expected to have an inverse correlation as these are the dummy variables created from the categorical features, so they usually can never co-exist.
MODELING APPROACH
After cleaning and analyzing the data, the cleaned dataset is split into training and testing datasets. The training dataset is used for tuning and validation, while the testing dataset is held out for final evaluations.
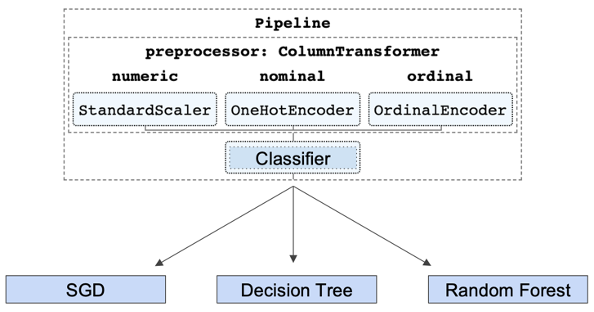
The process used for modeling is performed by setting up a pipeline that executes two steps. The first step is preprocessing (scaling and encoding), then the second step is applying the estimator (classifier). The pipeline is passed into a grid search for tuning the hyperparameters of the classifier. The models are also tuned using the class_weight parameter to counter the imbalance of the target variable. Different class weight multipliers are evaluated to achieve the best outcomes. This process is repeated for each estimator, and the results are collected, compared, and presented for analysis.
The ROC AUC score is not the best-scoring method when the data is imbalanced, so the F1/recall/precision scores will be used for the best model selection.
The grid search is executed using the training dataset and applies 5-fold cross-validations to find the best hyperparameter combination to achieve the best bias/variance trade-off point. The classification scores [f1, recall, precision, balanced_accuracy, accuracy, roc auc] are collected for each classifier with its best hyperparameters, but the f1 score is the main balanced score influences the decision making and the best model selection.
During the hyperparameters tuning, the tuning begins by using a wide range for each parameter, and then after each run, the range is reduced and converged toward the best scale. This process is repeated until a constant parameter is decided or a reasonable range is identified to help present the hyper parameters' effect on the bias/variance trade-off points.
After each grid search, the results are presented for the best estimator hyperparameter configuration with the cross-validation training and validation scores. A plot presents the bias/variance at each hyperparameter combination tested, and the best configuration is highlighted at the index matching the best configuration. Each configuration's details are then presented in a tabular format indexed to match the plot x-axis numbers, including all the details of the parameters and the scores achieved with this configuration.
For each tuned estimator, the best model is tested against the testing dataset to get the final scores that will be compared for the final models' evaluation.
Finally, the best configuration and scores are presented in a tabular format to compare the estimators.
Features Importance:
By analyzing the importance of the features to predict attrited customers that the Random Forest model provided, we can observe that all of the demographical features such as marital status, income, and educational levels were diminished. In contrast, the most influential features were more related to having a high or low activity profile, such as total transactions count and total transactions amount.
CONCLUSIONS
- Random Forests are very versatile and powerful but tend to overfit, leading to high variance
- Using hyperparameter tuning, we can restrict the model complexity, decreasing the variance and achieving high prediction accuracy and the required F1 score balance
- The attired customers can be predicted with the high accuracy of 0.95 and F1 0.86 scores
- Customers leaving accounts can be predicted by monitoring their activity levels and not by any demographic profiling