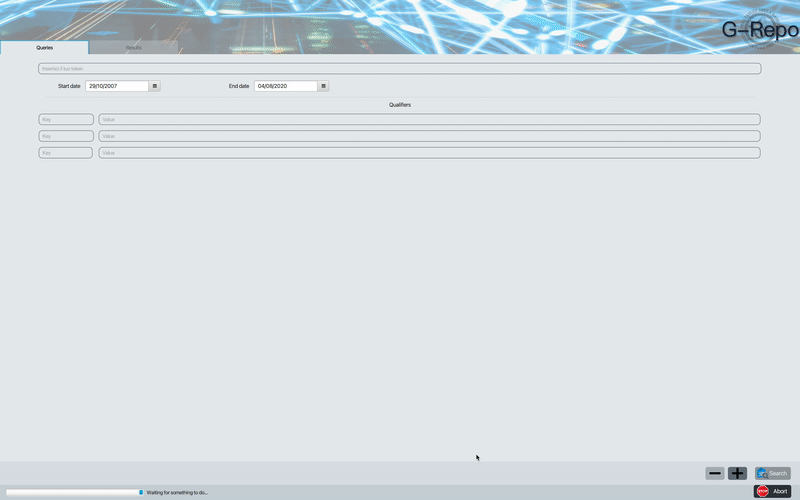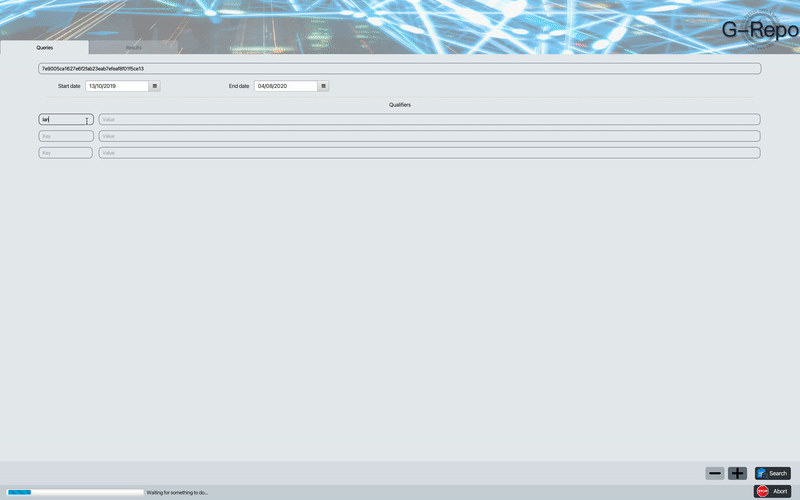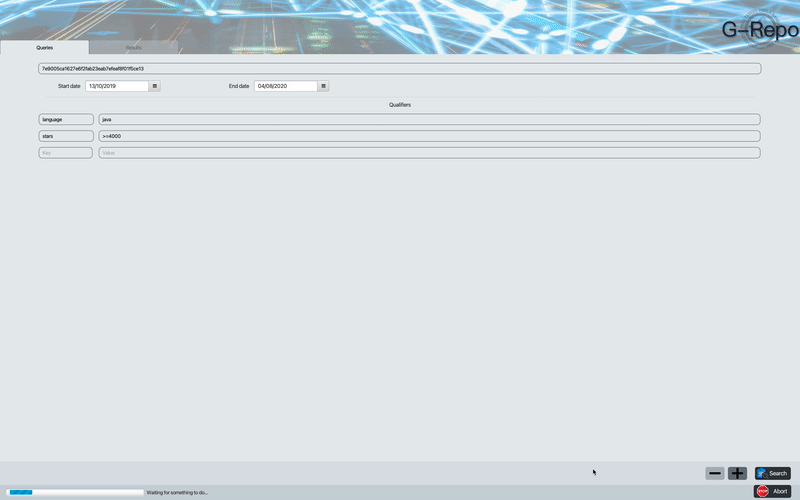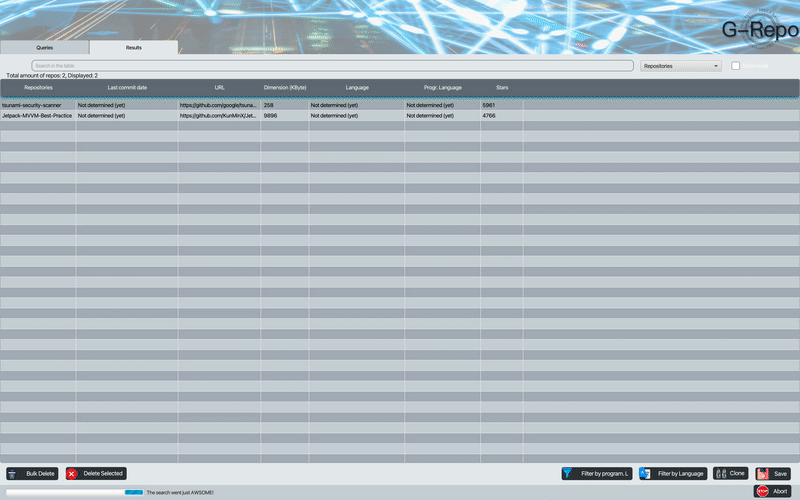
G-Repo is a tool developed in Java and Python and it is useful to Mine Software Repository (i.e., to collect empirical evidence using the data available in software repositories). For example:
“When and Why Your Code Starts to Smell Bad (and Whether the SmellsGo Away)”
“Do Developers Feel Emotions? An Exploratory Analysis of Emotions in Software Artifacts”
Many MSR studies use GitHub as a data source because:
- It contains millions of open source repositories.
- Provides a REST API to extract this data.
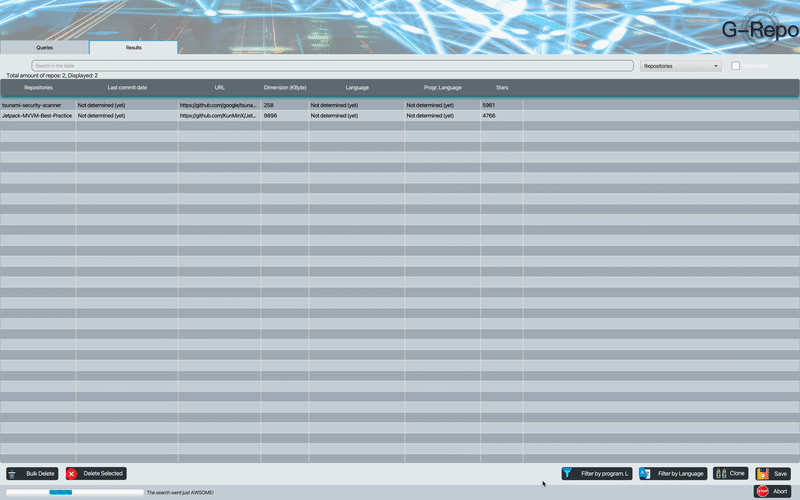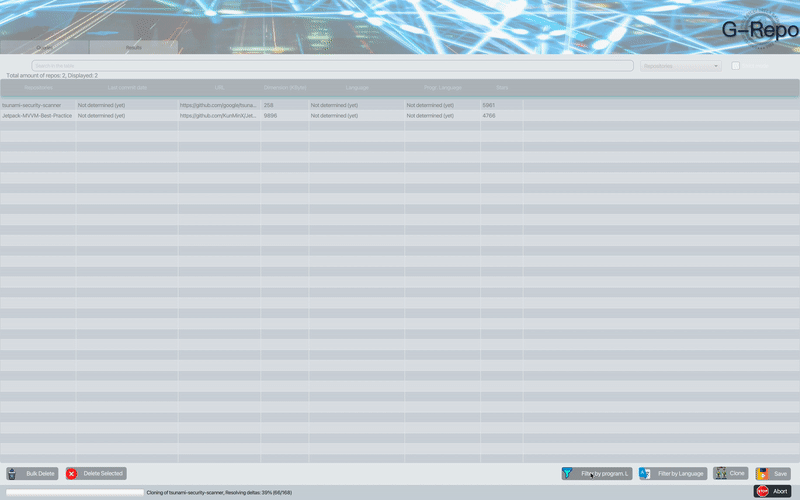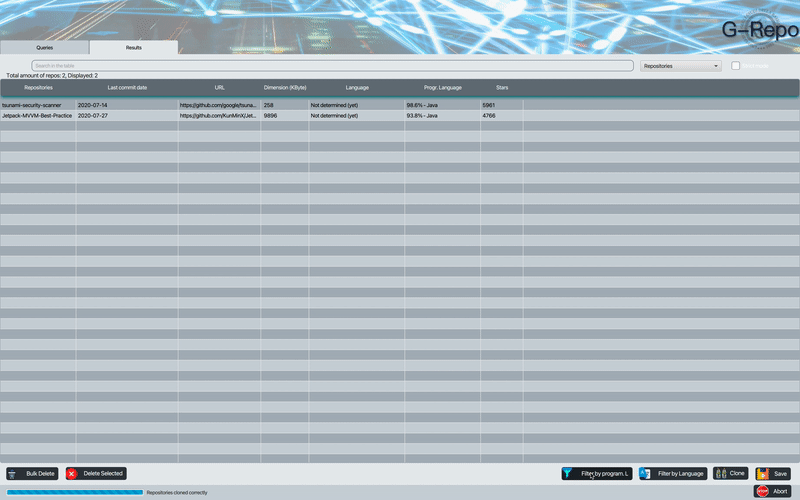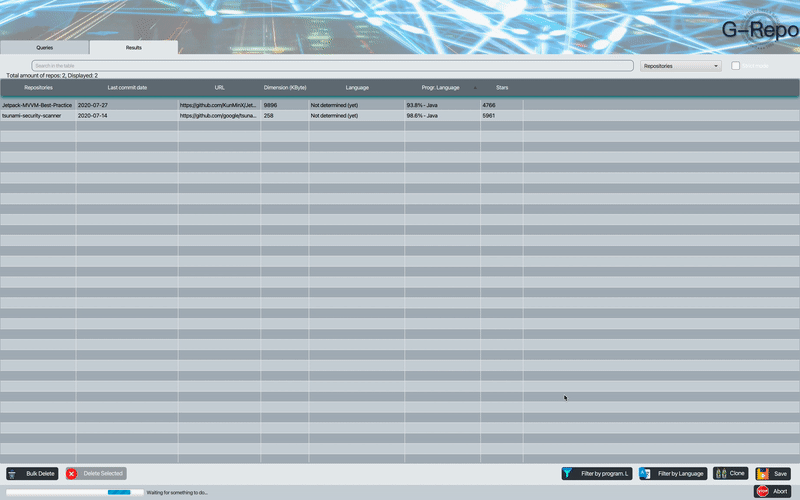
But which repositories must be chosen to conduct an MSR study?
- A trend is to select a number of top starred repositories, which are the most voted repositories by GitHub users.
-
#1: Limitations of the Github API; The GitHub Search API, which also allows to download information about the repositories, returns a maximum of 1000 results. So if a query returns more than 1000 results, they are truncated for best-matching.
-
#2: Repository not containing the files in the required programming language; The search often returns repositories that are not actually written in the requested programming language.
-
#3: Non-English language repositories; Not all repositories are written in English, so as a result of a search it is very likely that the user gets repositories with a readme written in different language(s) and these should be discarded.
$ pip3 install six
$ pip3 install langdetect
To launch G-Repo.jar move in G-Repo-jar folder and run the command:
java -jar --module-path "absolut/path/to/javaFX-sdk/lib" --add-modules=javafx.controls,javafx.fxml G-Repo.jar
G-Repo provides functionality to search for repositories by native GitHub qualifiers listed below:
| Type of Search | Qualifier to specify |
|---|---|
| By Repos Name | repo:owner/name |
| Within User’s or Organization’s Repos | user:USERNAME, org:ORGNAME |
| By Size in KB | size:n, size:(>;<=;>=;<)n, size:n1..n2 |
| By Number of Followers | followers:n, followers:(>;<=;>=;<)n, followers:n1..n2 |
| If Forked or not | fork:true(false) |
| By Number of Stars | stars:n, stars:(>;<=;>=;<)n, stars:n1..n2 |
| By Language | language:LANGUAGE |
| By Topic | topic:TOPIC |
| By Number of Topics | topics:n, topics:(>;<=;>=;<)n, topics:n1..n2 |
| By License | license:LICENSE |
| If Public or Private | is:public(private) |
| If a Mirror or ot | mirror:true(false) |
| If Archived or not | archived:true(false) |
| By Number of Issues good-first | good-first-issues:>n |
| By Number of Issues help-wanted | help-wanted-issues:>n |
In order for the search to be successful, you must have a valid token!
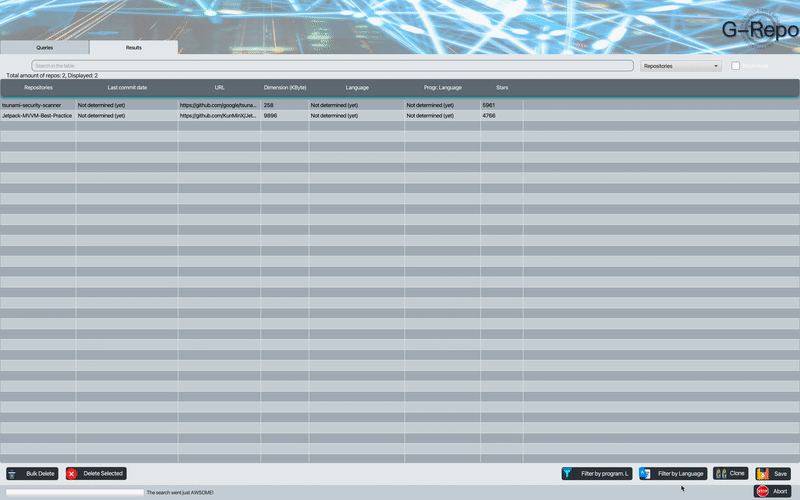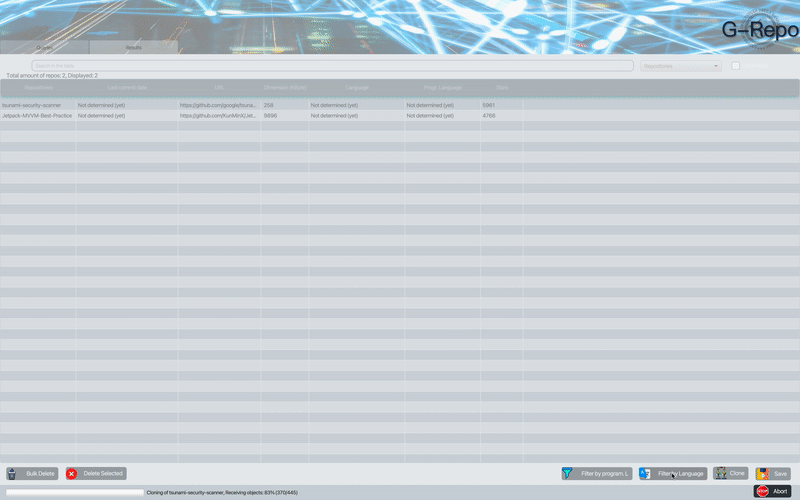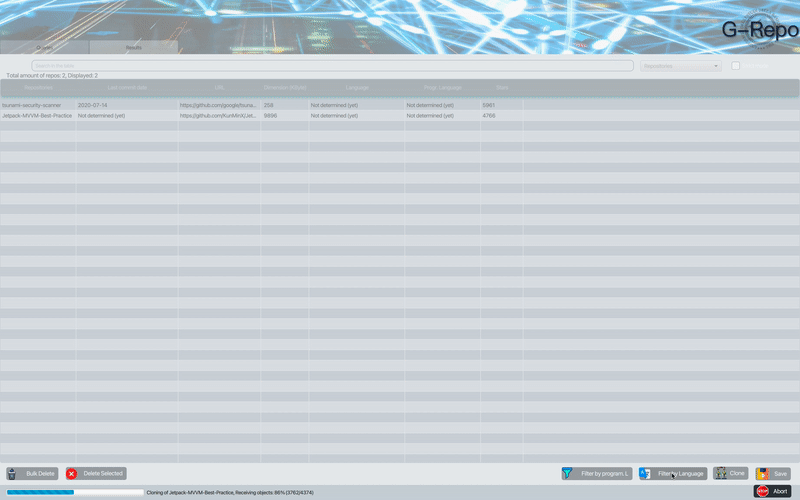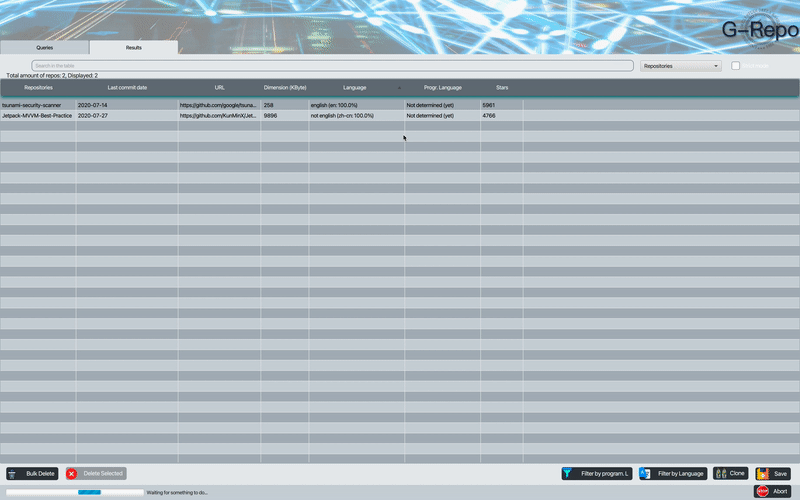
The programming language detection feature allows to detect the programming language - markup most used within the repositories; if the repositories found are empty the result will be not classifiable.
G-Repo is also able to detect the language used for a given repository by analyzing its README.md file. The language detector script that G-Repo uses is capable of classifying the repositories according to the language used within the README.md.
By default the script used by G-Repo uses a nondeterministic classification algorithm. This functionality is part of a design from the original Google project. If you want to force it to use a deterministic approach put translation_type = 0.
If the repository lacks a README file, it is empty, does not have enough text, or it only contains special characters then the repository will be classified as unknown, and the same applies in case some repository throws an exception during the parserization process, otherwise if everything goes fine it will be classified as english, not-english or mixed.
- The language-map repository was used to generate the file used for the detection of the programming language-markup.
- For the language recognition see Language Detection 🚀